- HEK293 expressed
- Endotoxin-free
- Animal-component free
HumanKine® recombinant human IL-34 protein
Activity
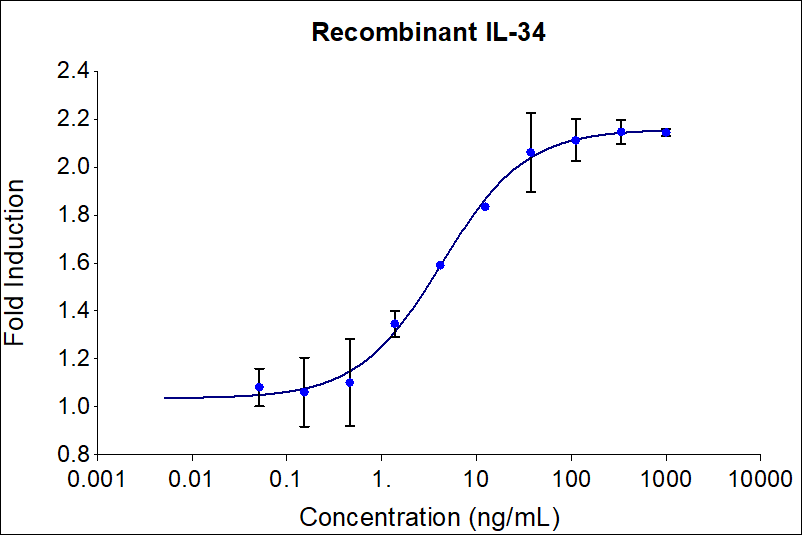
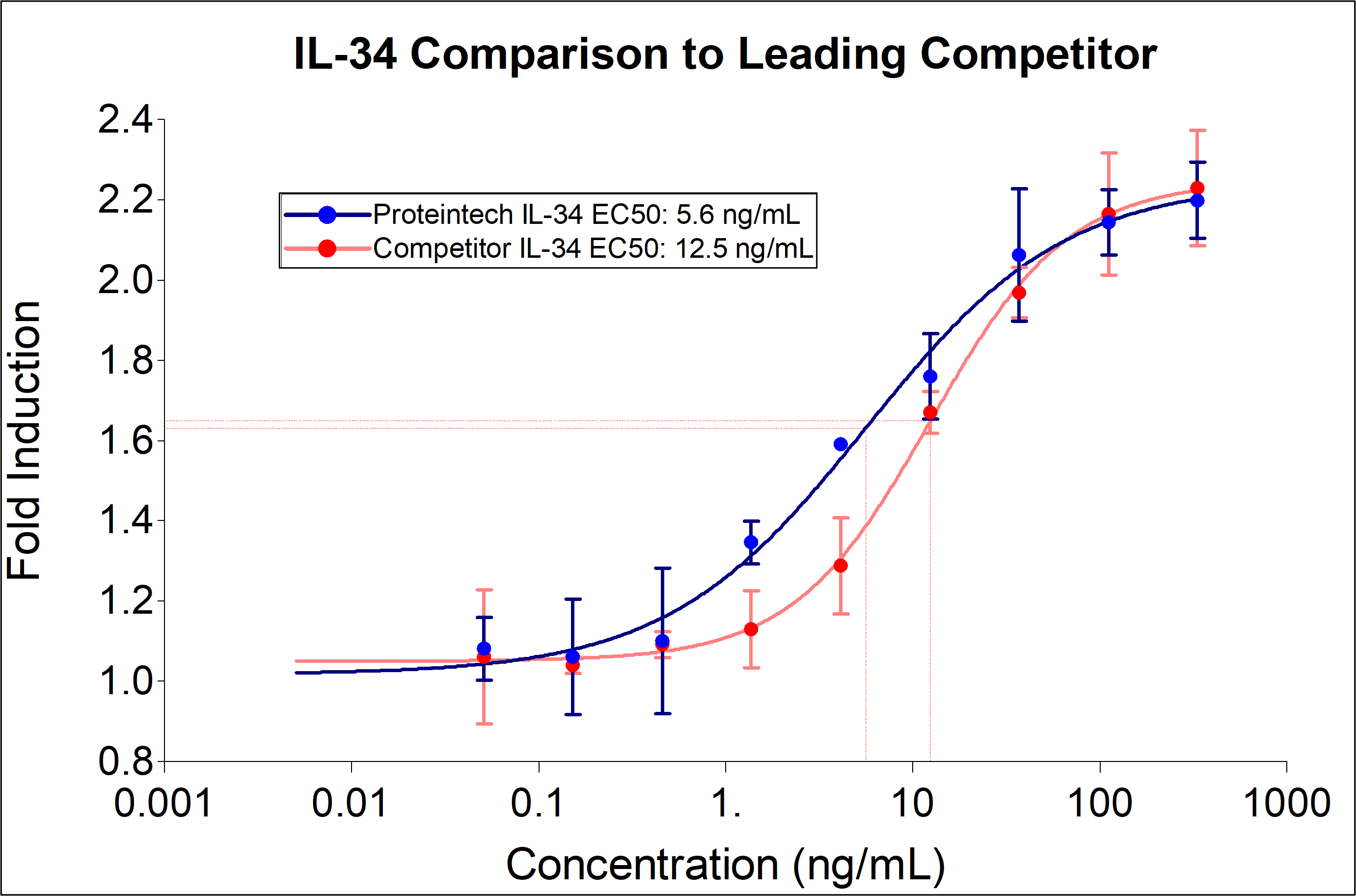
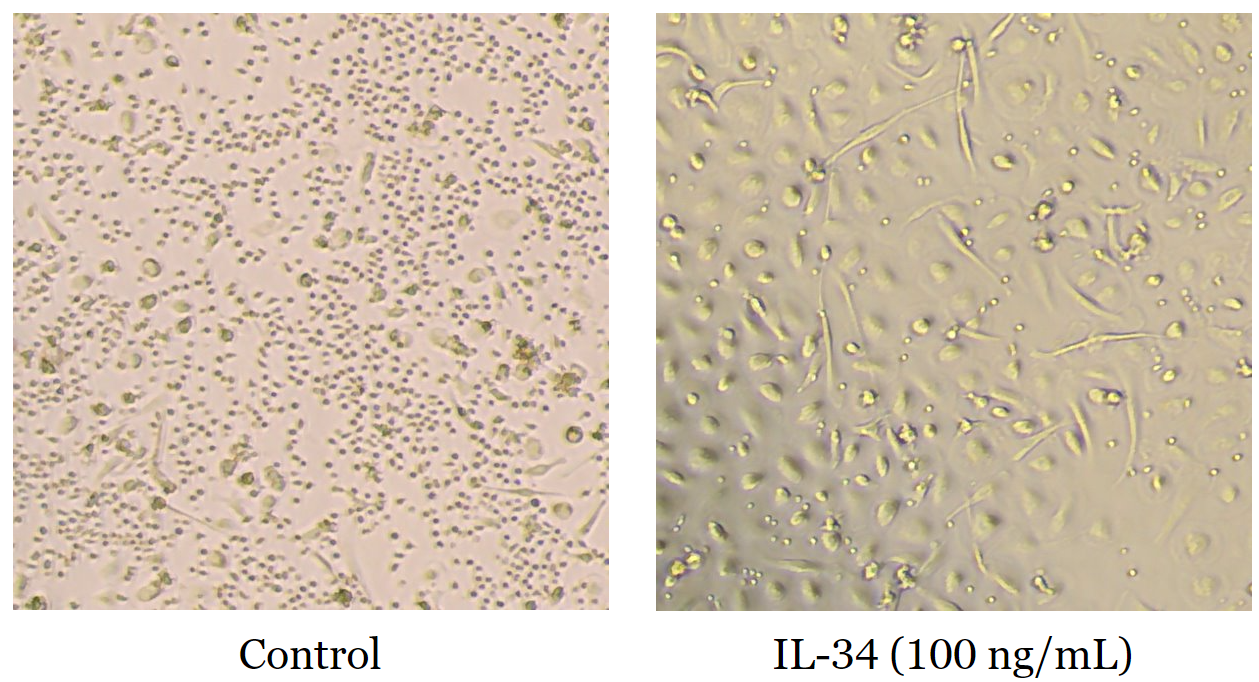
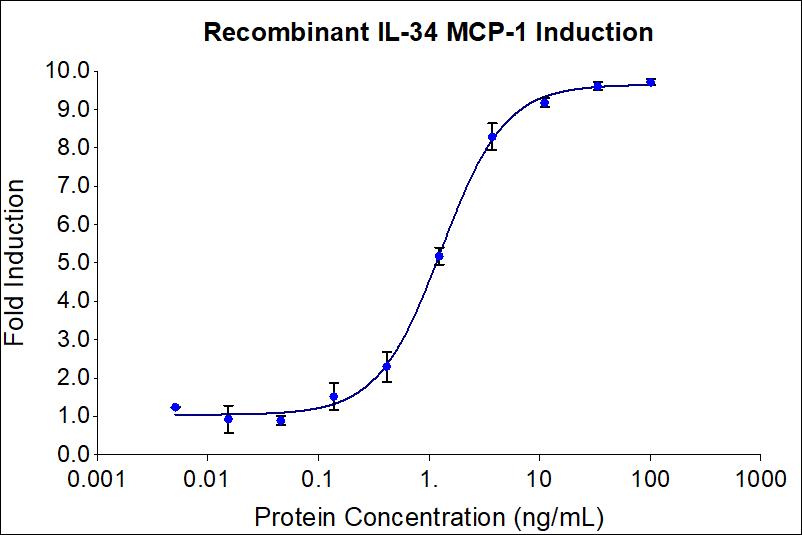
0.45-4.5 ng/mL in MCP-1 ELISA, 2-12 ng/mL in PBMCs Proliferation
Species Reactivity
human
Purity
>95%
Validation Data Gallery
Technical Specifications
| GeneID | 146433 |
| Species | Human |
| Expression | HEK293 |
| Activity | 0.45-4.5 ng/mL in MCP-1 ELISA, 2-12 ng/mL in PBMCs Proliferation |
| Purity | >95% |
| Endotoxin | <1 EU/µg |
| Accession Number | Q6ZMJ4 |
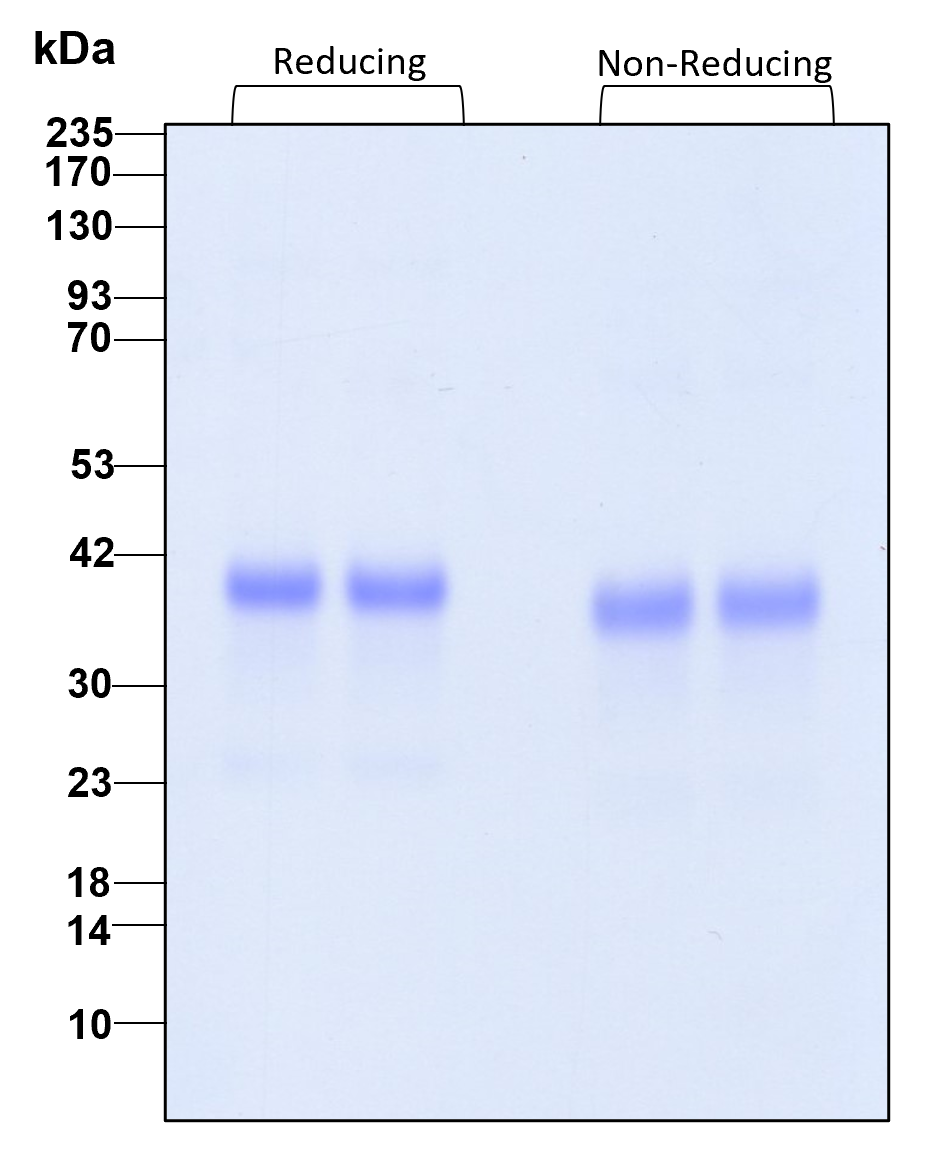
| Molecular Mass | 38 kDa reduced, 36 and 68 kDa non-reduced, homodimer, glycosylated |
| Formulation | 1 x PBS, See Certificate of Analysis for details |
| Species Reactivity | human |
Stability and Reconstitution
| Stability and Storage | Product Form | Temperature Conditions | Storage Time (From Date of Receipt) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lyophilized | -20°C to -80°C | Until Expiry Date | |
| Lyophilized | Room Temperature | 2 weeks | |
| Reconstituted as per CofA | -20°C to -80°C | 6 months | |
| Reconstituted as per CofA | 4°C | 1 week | |
| Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. | |||
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the vial before opening. It is recommended to reconstitute the protein to 0.2 mg/mL in sterile 1x PBS pH 7.4 + 0.1% HSA. Gently swirl or tap vial to mix. |
Background
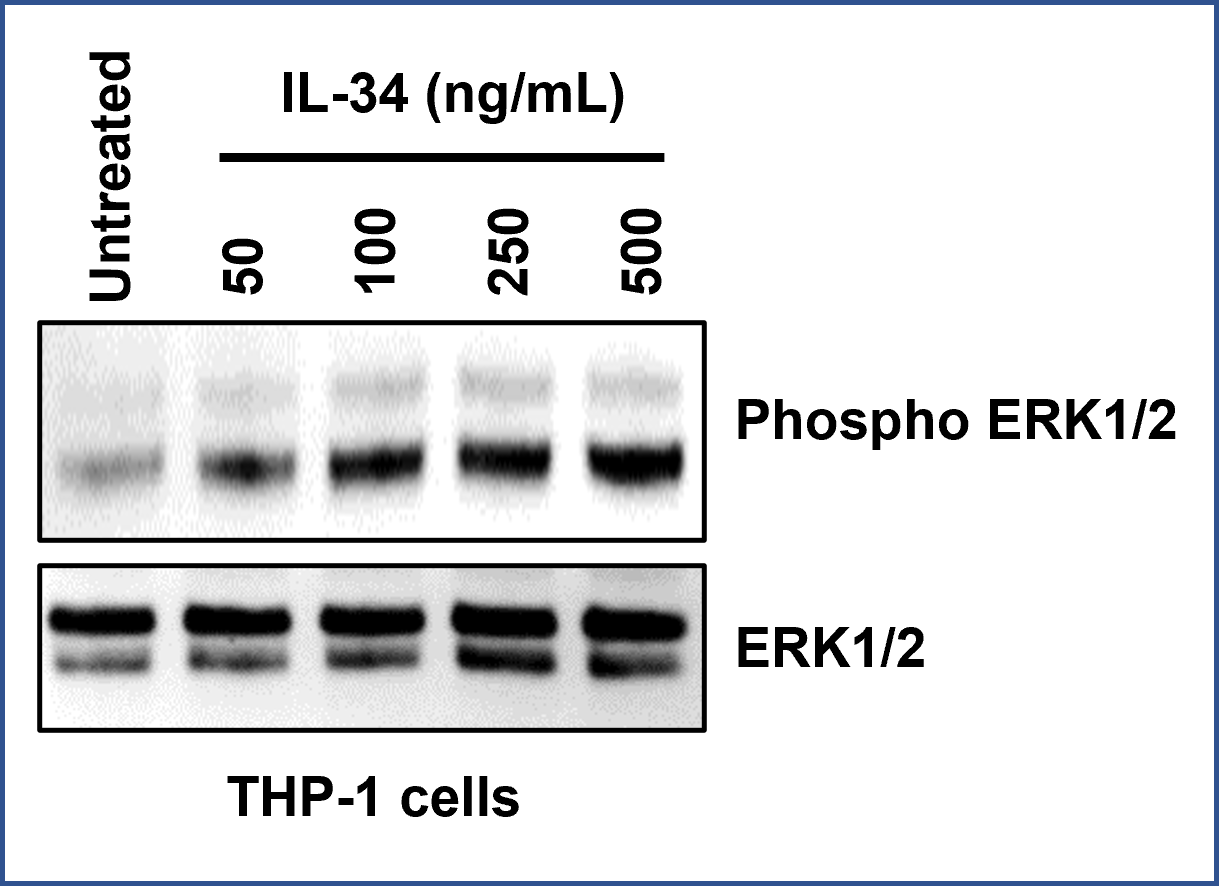
IL-34 is a 6-α-helix, proinflammatory cytokine that serves as a ligand for colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF1R). It is expressed most abundantly by spleen cells. It primarily stimulates human peripheral blood monocyte proliferation and macrophage colony formation. It is also required for Langerhans cell and microglia development. IL-34 has been shown to play a protective role in cancer and Alzheimer’s disease, but it can promote the progression of several autoimmune, inflammatory, and metabolic diseases. As such IL-34 could be used as a biomarker to mark the progression of these diseases (PMID: 22579672, 27577879, 31940023).
Synonyms
IL34, Interleukin-34, C16orf77, MGC34647
Publications
| Species | Title |
|---|---|
Cell Metab Microglial lipid droplet accumulation in tauopathy brain is regulated by neuronal AMPK | |