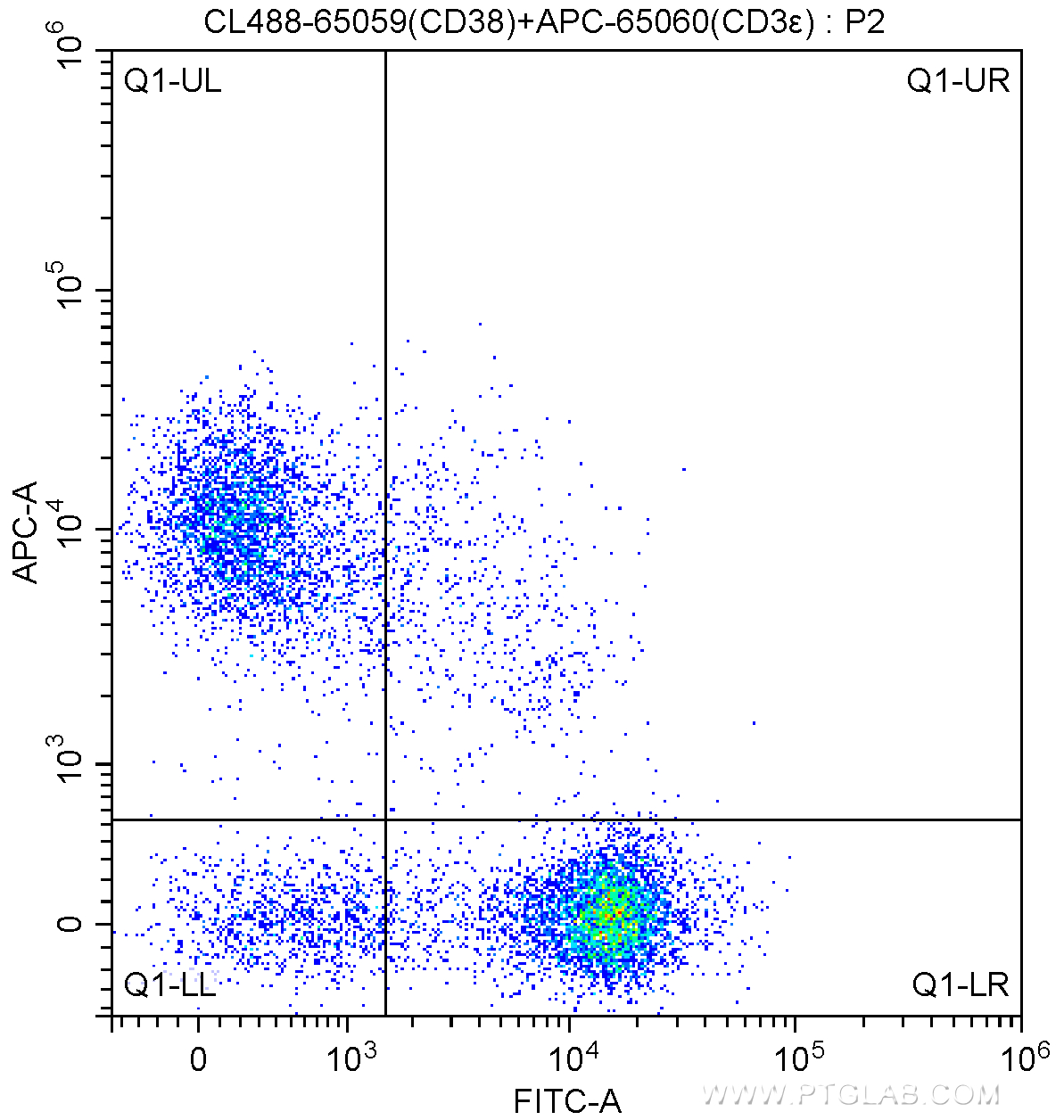
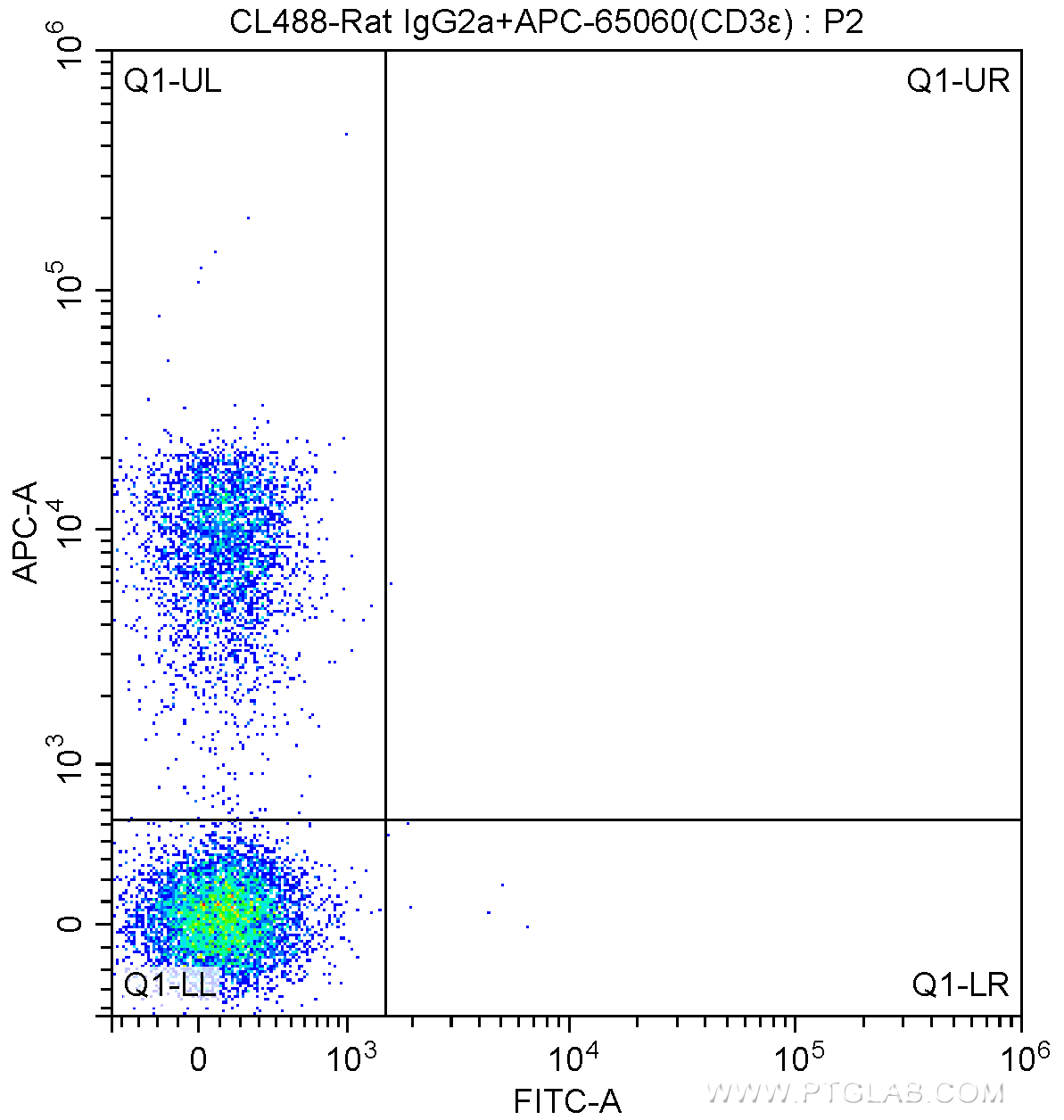
验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
| Positive FC detected in | mouse splenocytes |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| This reagent has been tested for flow cytometric analysis. It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
产品信息
CL488-65059 targets CD38 in FC applications and shows reactivity with Mouse samples.
| 经测试应用 | FC Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | Mouse |
| 免疫原 | Mouse bone marrow pre-B cells 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rat / IgG2a, kappa |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | CD38 antigen |
| 别名 | Cd38, CD38 antigen, Cd38 rs1 |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC046312 |
| 基因名称 | Cd38 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 12494 |
| RRID | AB_2883155 |
| 偶联类型 | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| 最大激发/发射波长 | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P56528 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. |
背景介绍
CD38, also known as ADP-ribosyl cyclase 1, is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein with a short N-terminal cytoplasmic tail, a single membrane-spanning domain, and a C-terminal extracellular region with four N-glycosylation sites (PMID: 2319135). The extracellular domain of CD38 has bifunctional enzyme activities that catalyze synthesis of cyclic ADP ribose from nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP ribose to adenosine diphosphoribose (PMID: 10636863). CD38 is expressed on a variety of hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells and is involved in diverse processes such as generation of calcium-mobilizing metabolites, cell activation, and chemotaxis (PMID: 25938500).
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for CL Plus 488 CD38 antibody CL488-65059 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |