AbFlex HDAC2 antibody (rAb)
Host / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2a
Reactivity
Human
Applications
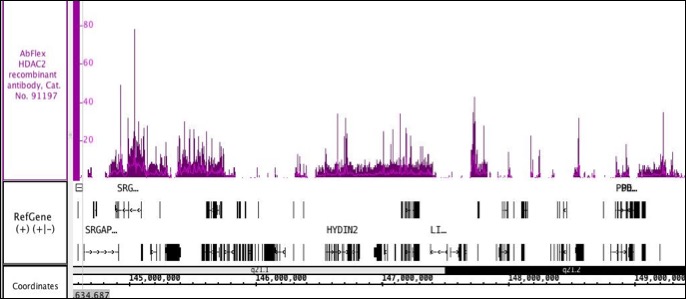
ChIP-Seq, WB
Cat No : 91197,91198 91197
Synonyms
验证数据展示
产品信息
| Tested Applications |
ChIP-Seq, WB
Applications Validated by Active Motif: ChIP-Seq: 4 - 10 ug per ChIP WB*: 0.2-2 ug/ml For optimal results, primary antibody incubations should be performed at room temperature. The addition of 0.1% Tween 20 to all blocking solutions may also reduce background. Individual optimization may be required. *Note: many chromatin-bound proteins are not soluble in a low salt nuclear extract and fractionate to the pellet. Therefore, we recommend a High Salt / Sonication Protocol when preparing nuclear extracts for Western Blot. |
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | This antibody was raised against peptide corresponding to amino acids 473-488 of human HDAC2. |
| Full Name | AbFlex HDAC2 antibody (rAb) |
| Synonyms | |
| Molecular weight | 55 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NP_001518 | RRID | AB_2793799 | Purification Method | Protein A Chromatography |
| Buffer | Purified IgG in 140 mM Hepes, pH 7.5, 70 mM NaCl, 35 mM NaOAc, 0.07% sodium azide, 30% glycerol. Sodium azide is highly toxic. |
| Storage | Some products may be shipped at room temperature. This will not affect their stability or performance. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles by aliquoting items into single-use fractions for storage at -20°C for up to 2 years. Keep all reagents on ice when not in storage. |
背景介绍
AbFlex antibodies are recombinant antibodies (rAbs) that have been generated using defined DNA sequences to produce highly specific, reproducible antibodies. Each AbFlex antibody contains a 6xHis Tag, a Biotinylation Tag for enzymatic biotin conjugation using the biotin ligase, BirA, and a sortase recognition motif (LPXTG) to attach a variety of labels directly to the antibody including fluorophores, enzymatic substrates (HRP, AP), peptides, drugs as well as solid supports. HDAC2 (Histone Deacetylase 2, also designated mammalian RPD3) is a member of the class I mammalian histone deacetylases (HDACs) involved in regulating chromatin structure during transcription. These enzymes catalyze the removal of acetyl groups from lysine residues of histones and other cellular proteins. Lysine N-e-acetylation is a dynamic, reversible and tightly regulated protein and histone modification that plays a major role in regulation of gene expression in various cellular functions. It consists of the transfer of an acetyl moiety from an acetyl coenzyme A to the e-amino group of a lysine residue. In vivo, acetylation is controlled by the antagonistic activities of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs). The HDACs are grouped into four classes, on the basis of similarity to yeast counterparts: HDAC class I (HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3 and HDAC8), class II (HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC6, HDAC7, HDAC9 and HDAC10), class III (SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT3, SIRT4, SIRT5, SIRT6 and SIRT-7) and class IV (HDAC11). HDAC2 is associated with many different proteins as YY1 (a mammalian zinc-finger transcription factor). HDAC2 also forms transcriptional repressor complexes containing, among others, HDAC1 or RBBP4. HDAC1, HDAC2 and HDAC3 are also ubiquitously expressed and can deacetylate both Histone H3 and Histone H4 in free histones or nucleosome substrate.