AbFlex Lamin A/C antibody (rAb)
Host / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2a
Reactivity
Human
Applications
IF, WB
Cat No : 91189,91190 91189
Synonyms
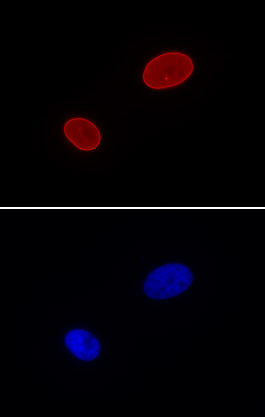
验证数据展示
产品信息
| Tested Applications |
IF, WB
Applications Validated by Active Motif: WB: 0.5 – 2 ug/ml IF: 2 ug/ml AbFlex recombinant antibodies are genetically derived from DNA sequences of parental hybridoma clones. For details on the parental clone, see Catalog No. 39287. |
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | This Lamin A/C antibody was raised against a recombinant protein corresponding to amino acids 430-545 of human Lamin A. |
| Full Name | AbFlex Lamin A/C antibody (rAb) |
| Synonyms | Lamin A/C, Clone 3A6-4C11, CDCD1, LMN1, EMD2, CMT2B1, FPLD, antibody, antibodies, monoclonal, stem cell, stem cells, AbFlex, recombinant antibody |
| Molecular weight | 80 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NP_733821 | RRID | AB_2793795 | Purification Method | Protein A Chromatography |
| Buffer | Purified IgG in 140 mM Hepes, pH 7.5, 70 mM NaCl, 32 mM NaOAc, 0.035% sodium azide, 30% glycerol. Sodium azide is highly toxic. |
| Storage | Some products may be shipped at room temperature. This will not affect their stability or performance. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles by aliquoting items into single-use fractions for storage at -20°C for up to 2 years. Keep all reagents on ice when not in storage. |
背景介绍
AbFlex antibodies are recombinant antibodies (rAbs) that have been generated using defined DNA sequences to produce highly specific, reproducible antibodies. Each AbFlex antibody contains a 6xHis Tag, a Biotinylation Tag for enzymatic biotin conjugation using the biotin ligase, BirA, and a sortase recognition motif (LPXTG) to attach a variety of labels directly to the antibody including fluorophores, enzymatic substrates (HRP, AP), peptides, drugs as well as solid supports. AbFlex Lamin A/C antibody was expressed as full-length IgG with mouse immunoglobulin heavy and light chains (IgG2a isotype) in mammalian 293 cells. Nuclear lamins are intermediate filament proteins that are the major structural component of the nuclear lamina on the inner surface of the nuclear envelope. Lamins A and Lamins C are splice variants of the Lamin A gene. Lamin A/C (CDCD1, LMN1, EMD2) expression is a hallmark of embryonic stem cell differentiation. In addition to adding structural integrity to the nucleus, lamins contribute to the makeup of the nuclear matrix. Lamins also help organize interphase chromatin through interactions with several chromatin proteins, including histones and Lap2, such that alteration in lamin organization results in disruption of DNA replication, transcription and RNA processing.