Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
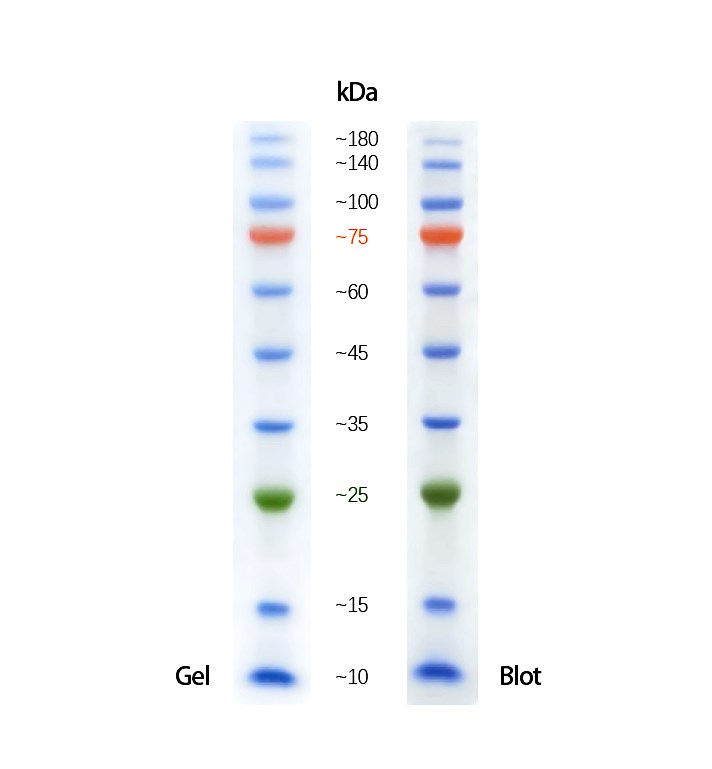
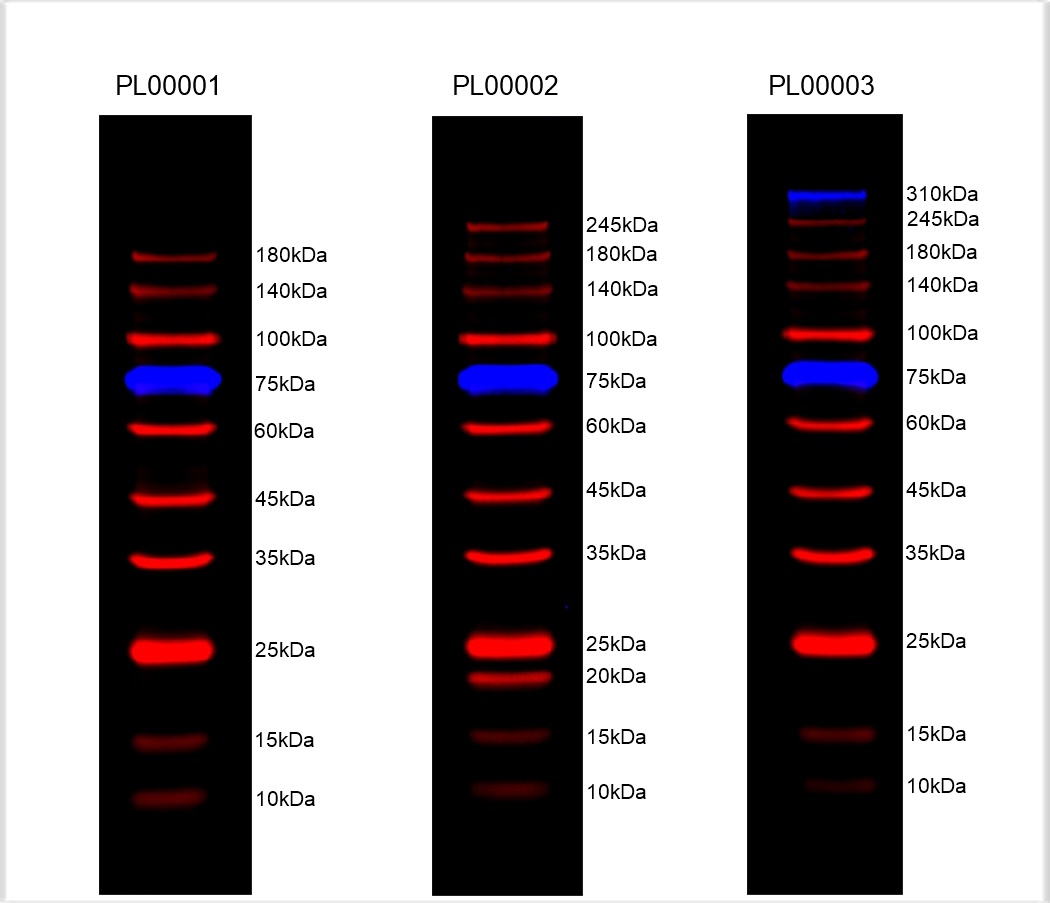
蛋白质常规分子量标记(Prestained Protein marker, PL00001)为即用型产品,内含10条预先染色的蛋白质条带,蛋白组分涵盖10 kDa至180 kDa(在Bis-Tris(MOPS)缓冲液中为9 kDa至170 kDa;在Bis-Tris(MES)缓冲液中为10 kDa至170 kDa)。本产品经电泳(Tris-Glycine缓冲液)分离后,10条参考条带分别于蓝色、绿色或红色发光基团共价键连接。为方便目测辨别分子量大小,绿色蛋白条带代表分子量25 kDa;红色蛋白条带代表分子量75 kDa。蛋白质常规分子量标记应用于辨别蛋白质电泳凝胶(SDS-PAGE)上的蛋白质大小及估算Western blot的转膜效率。
| 分子量 | ~ 10, 15, 25, 35, 45, 60, 75, 100, 140, 180 kDa |
| 分子量种类 | 10 |
| 范围 | 10-180 kDa |
| 染料颜色 | colors:Blue,Red,Green |
* 本产品可立即使用,请勿于上样前加热、稀释或加入还原剂处理。
产品介绍
组分:蛋白 Marker/管
* 每毫升缓冲液中各蛋白浓度约0.1~0.4毫克,缓冲液主要成分为 20 mM Tris-phosphate, pH 7.5,25℃,2 % 十二烷基硫酸鈉,0.2 mM Dithiothreitol,3.6 M 尿素,15 % (v/v) 甘油。
保存条件
4℃≤3个月,-20℃≤24个月。
使用方法
每孔槽注入5 uL,以确保电泳过程中清晰展示电泳时蛋白分子量的变化。
若使用较厚或较大的蛋白质电泳凝胶 (>1.5 mm),建议依情况增量使用。
注意
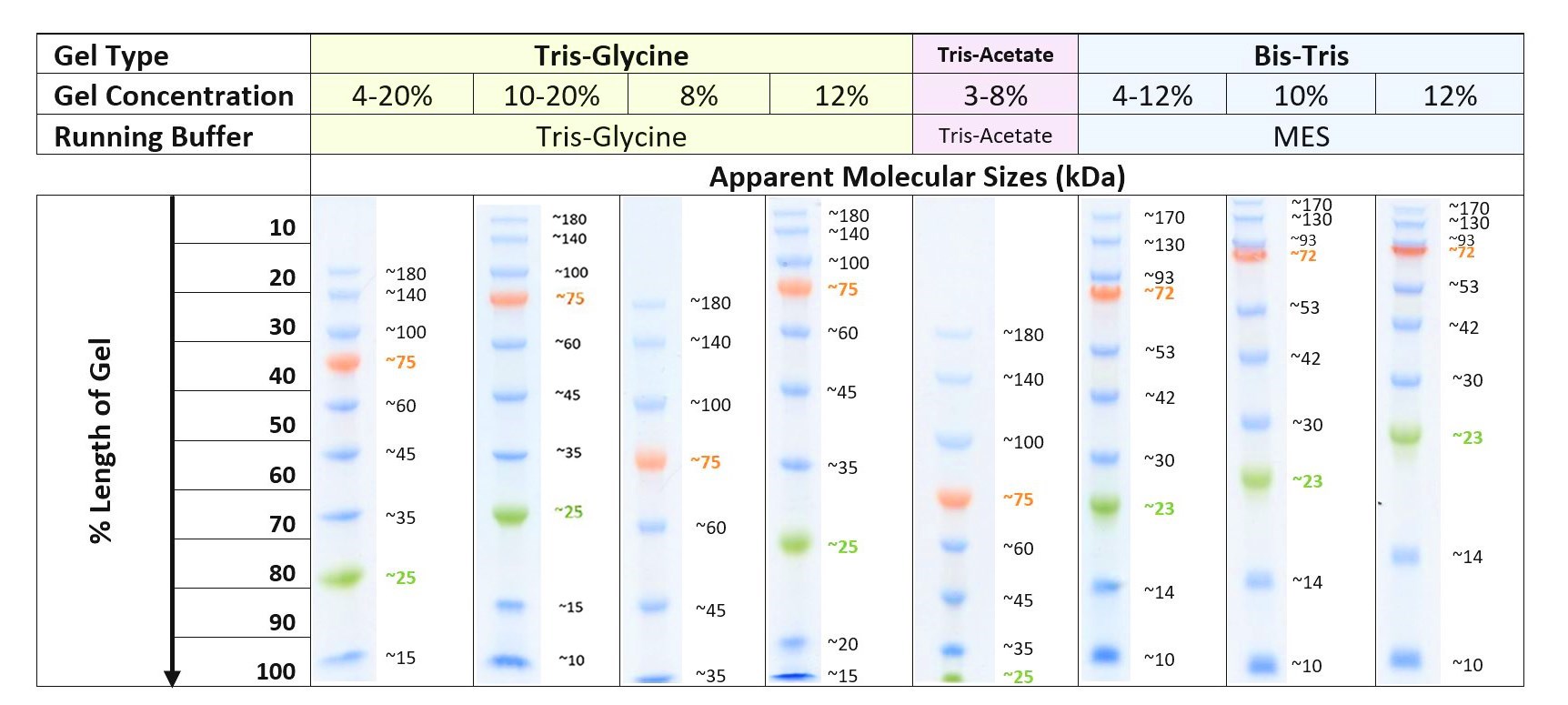
本产品的每条蛋白质分子量大小(kDa)已与未预染的蛋白质标记于相同电泳条件下校准比对完成;若使用不同的电泳条件,请参考蛋白质分子量估算表,以校正分子量。
分子量
~ 10, 15, 25, 35, 45, 60, 75, 100, 140, 180 kDa
范围
10 to 180 kDa
染料颜色
3 colors (Blue, Red, Green)
Publications
| Application | Title |
|---|---|
Cell Rep A p53/LINC00324 positive feedback loop suppresses tumor growth by counteracting SET-mediated transcriptional repression | |
Food Chem Fabrication of grape seed proanthocyanidin-loaded W/O/W emulsion gels stabilized by polyglycerol polyricinoleate and whey protein isolate with konjac glucomannan: Structure, stability, and in vitro digestion | |
J Ethnopharmacol Pharmacodynamics and pharmacological mechanism of Moluodan concentrated pill in the treatment of atrophic gastritis: A network pharmacological study and in vivo experiments | |
Front Immunol Roles of RAGE/ROCK1 Pathway in HMGB1-Induced Early Changes in Barrier Permeability of Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cell. | |
Molecules Chemical Analysis and Antioxidant Activities of Resin Fractions from Pistacia lentiscus L. var. Chia in Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells | |
Sci Rep Atypical chemokine receptor 2 expression is directly regulated by hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha in cancer cells under hypoxia |