验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
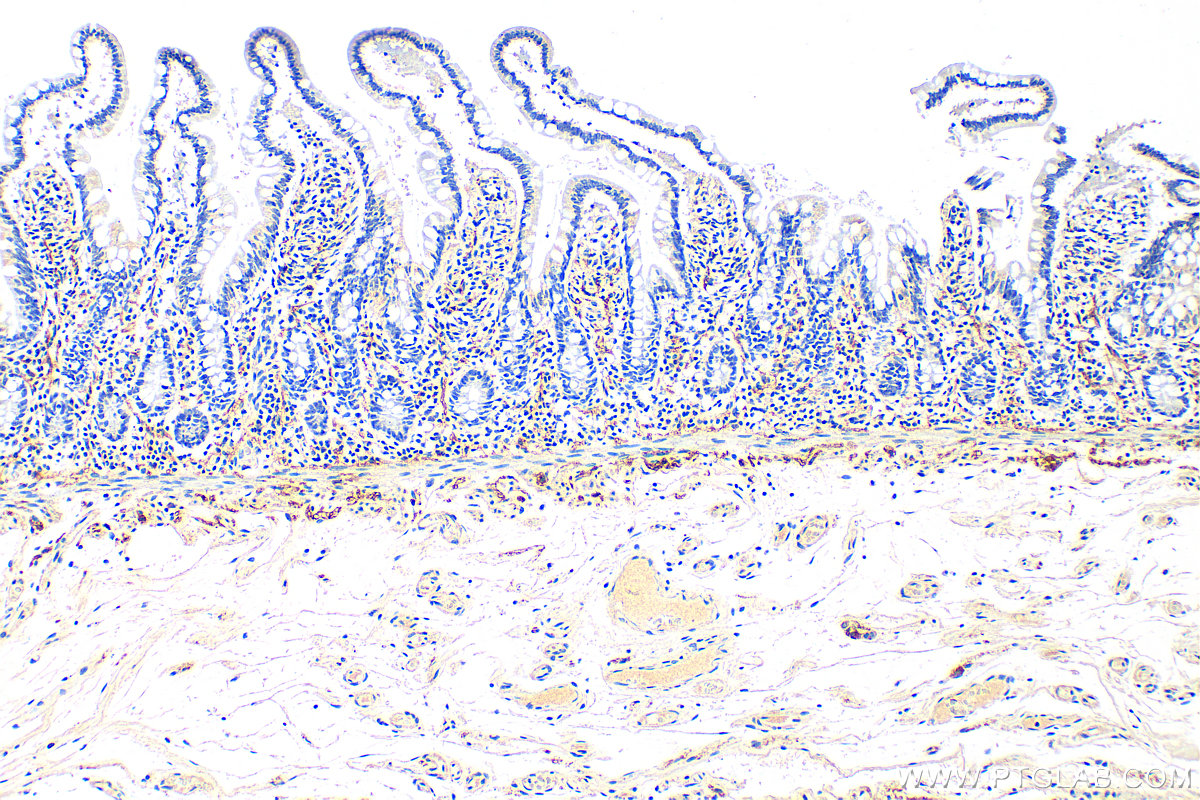
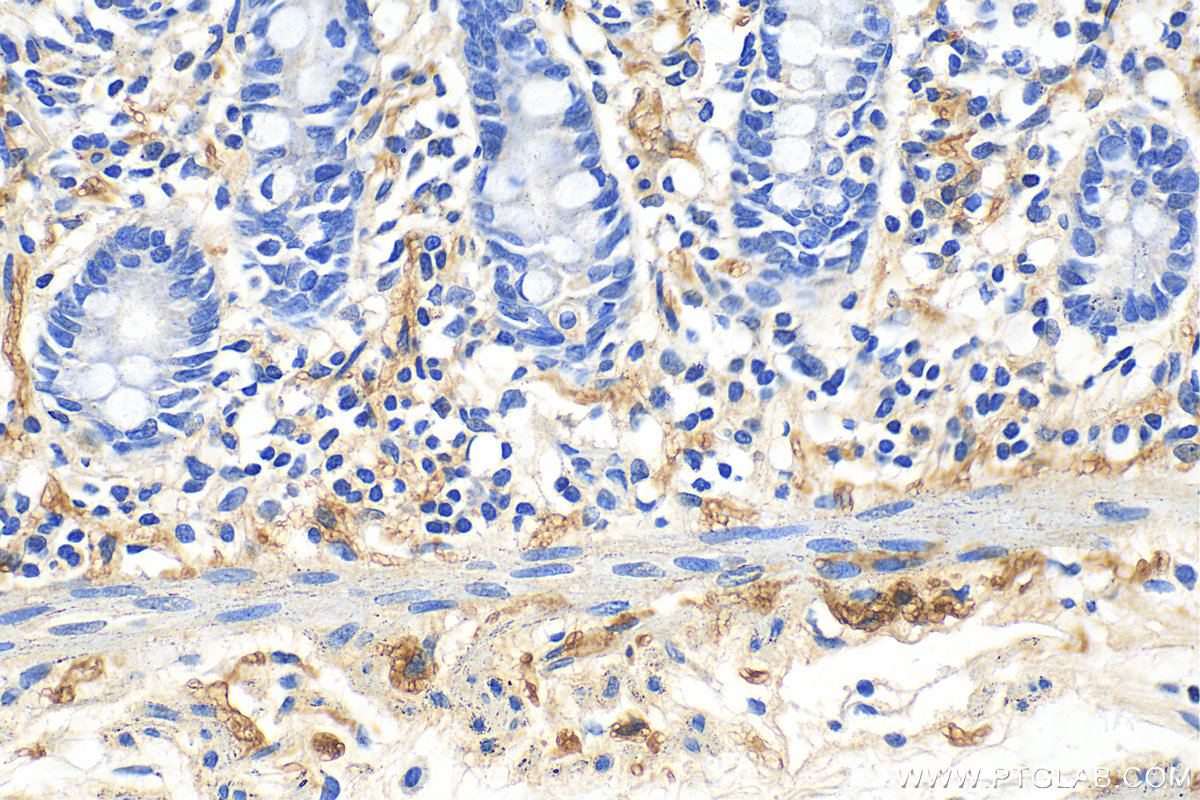
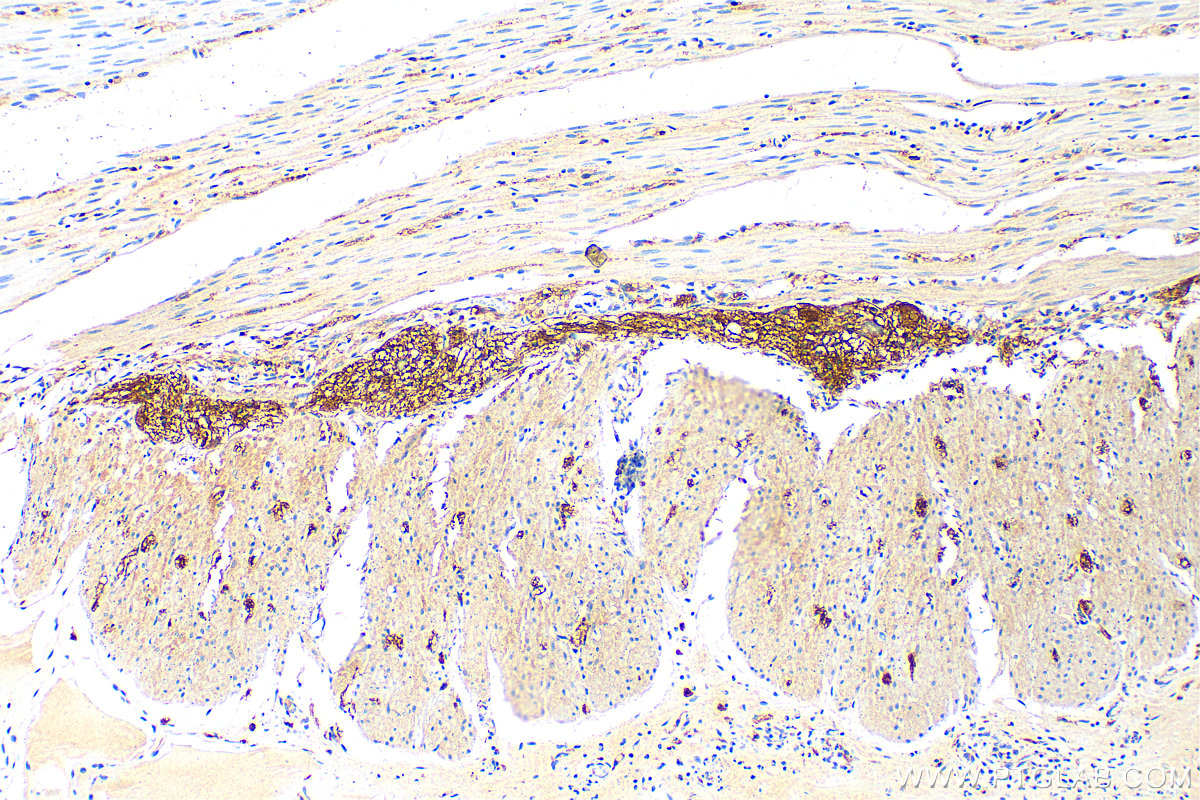
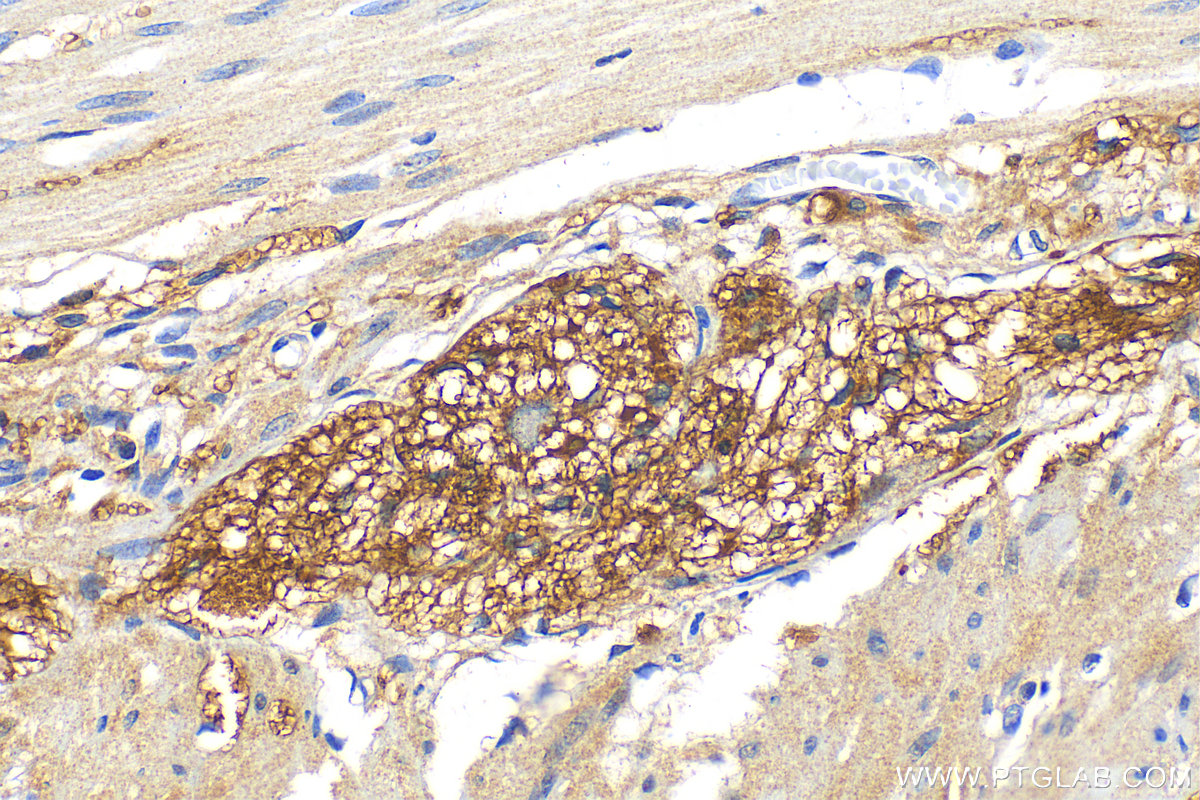
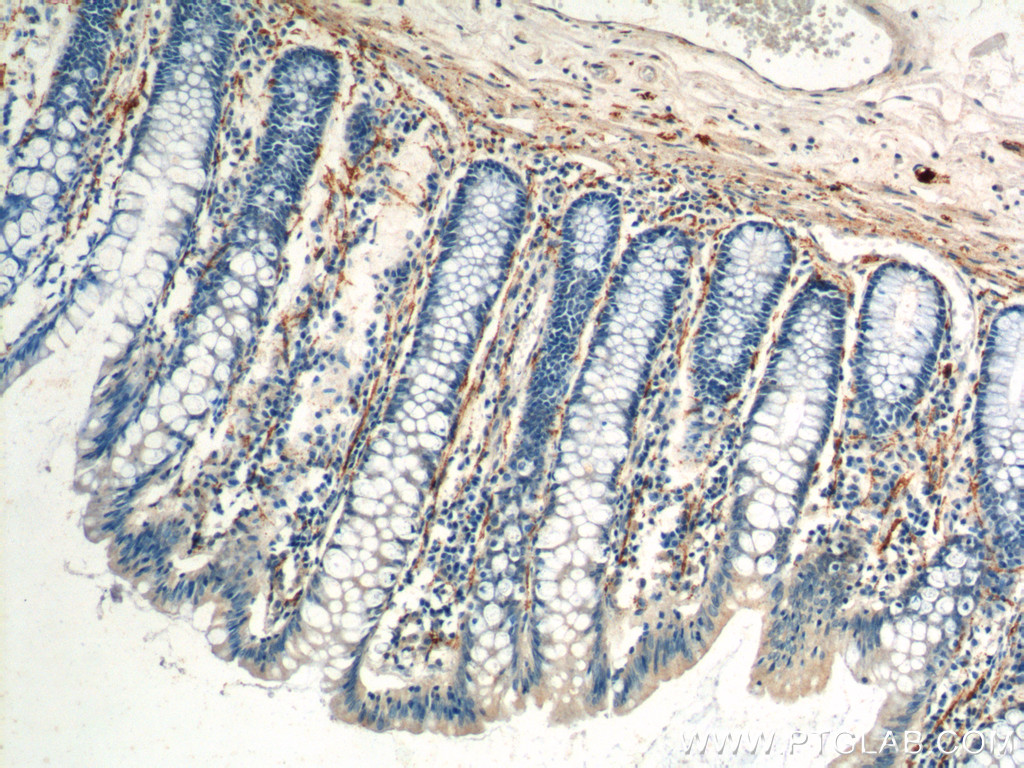
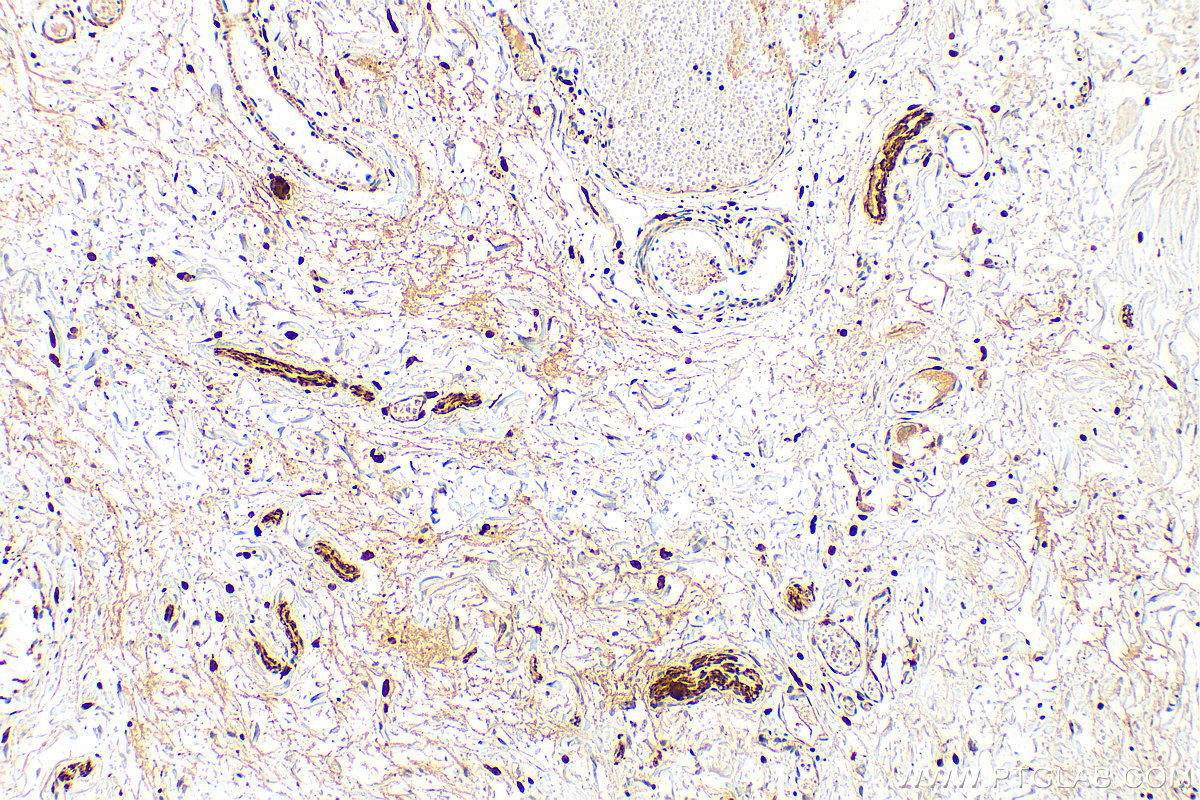
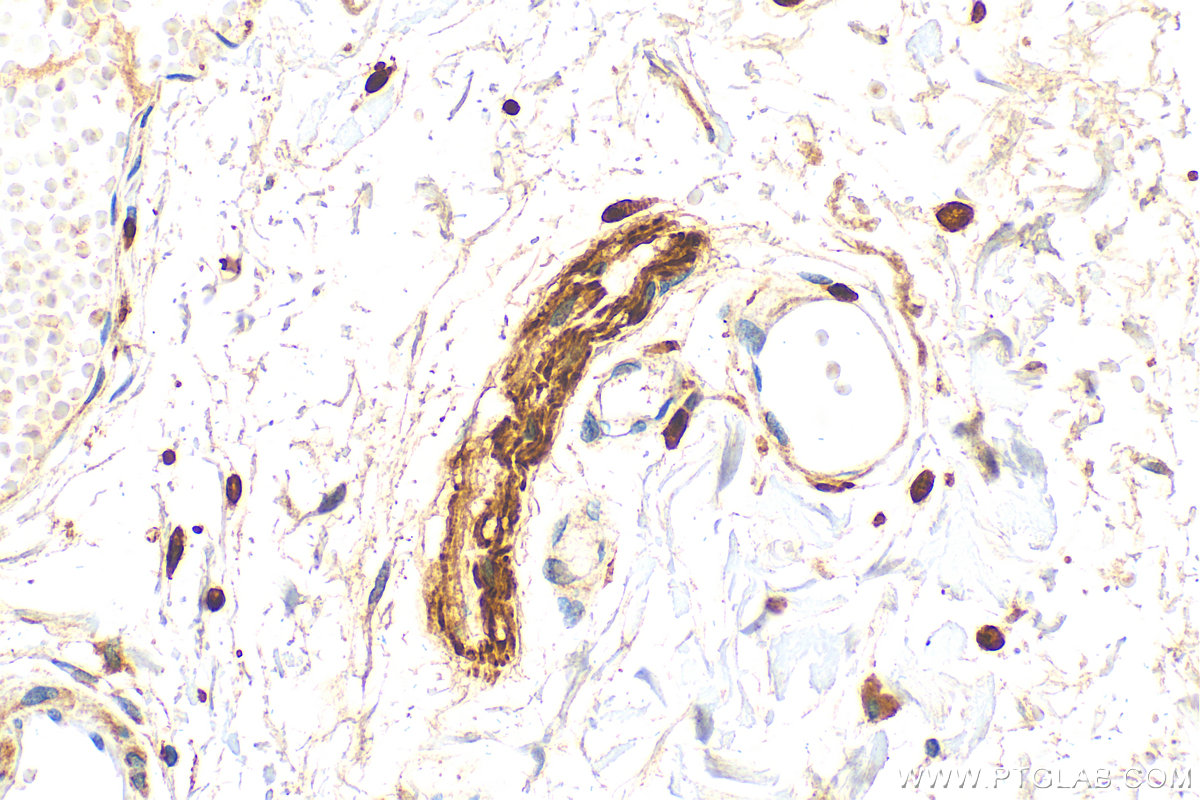
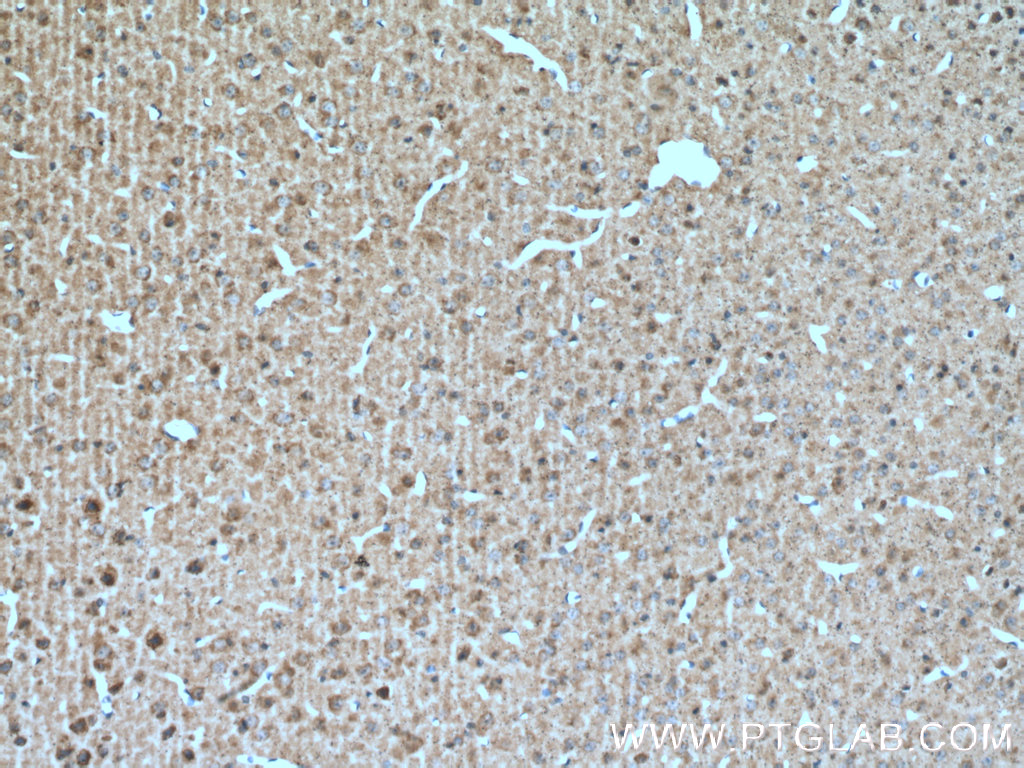
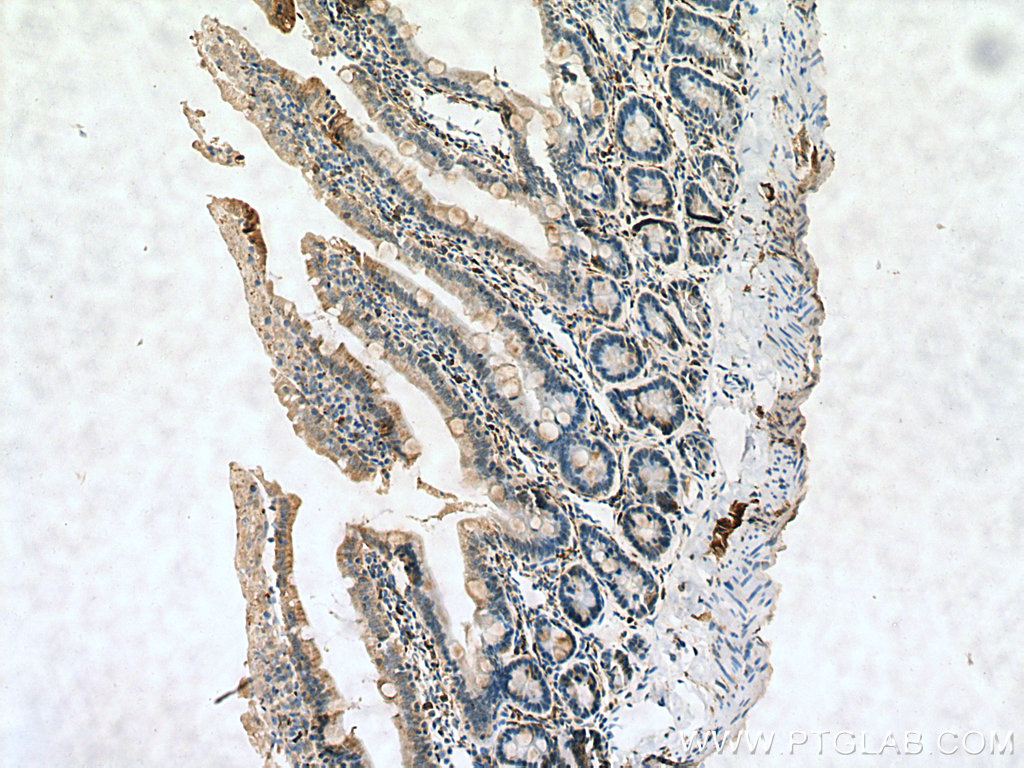
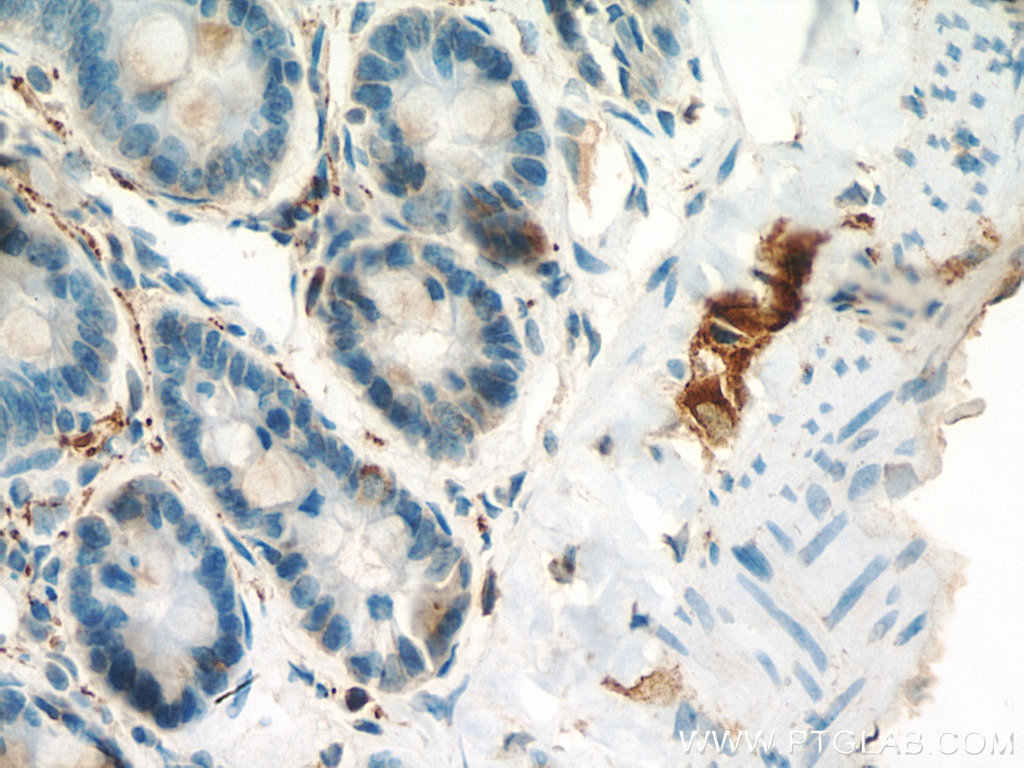
| Positive IHC detected in | human colon tissue, rat small intestine tissue, mouse brain tissue, human small intestine tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
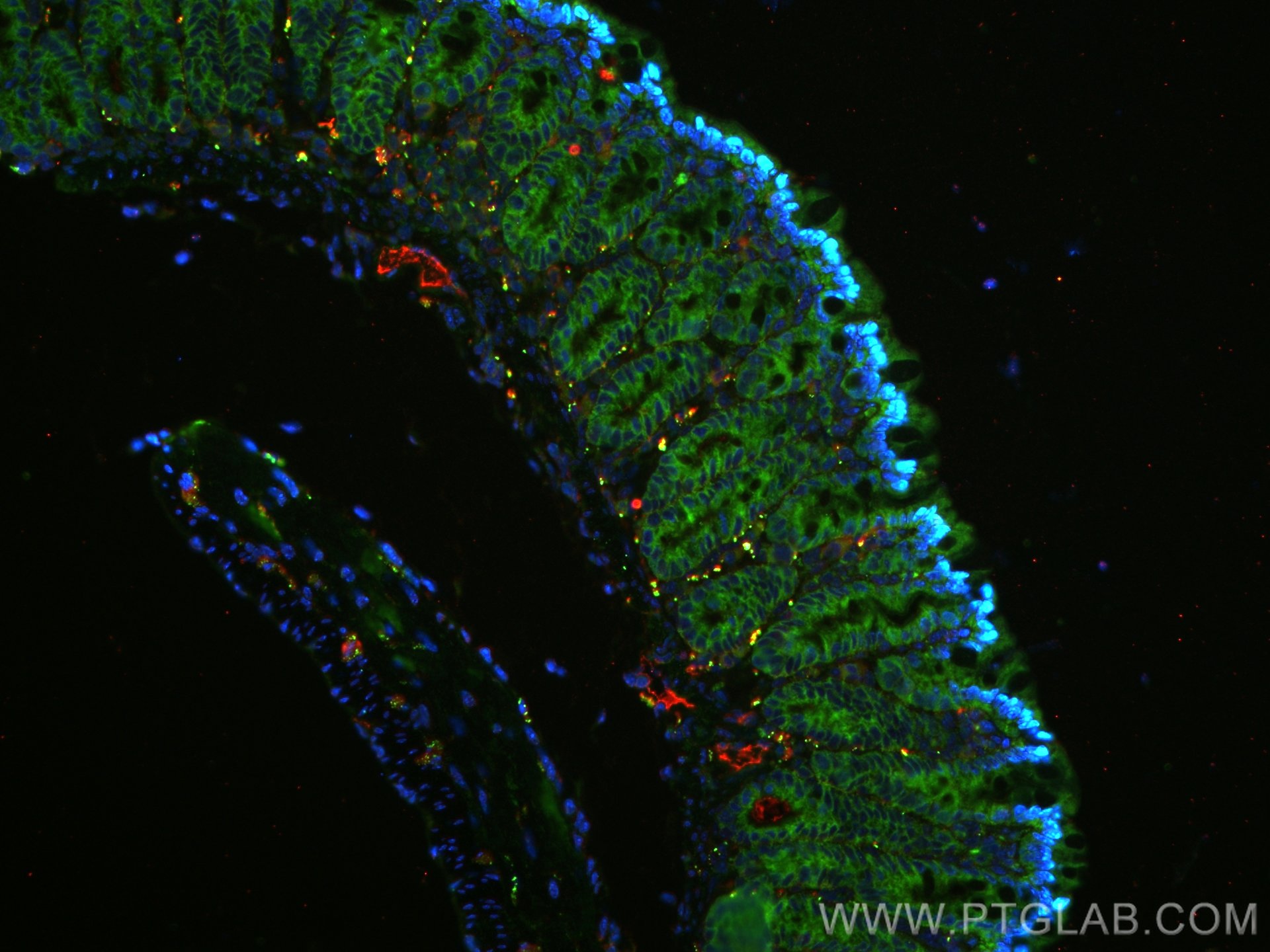
| Positive IF-P detected in | mouse colon tissue |
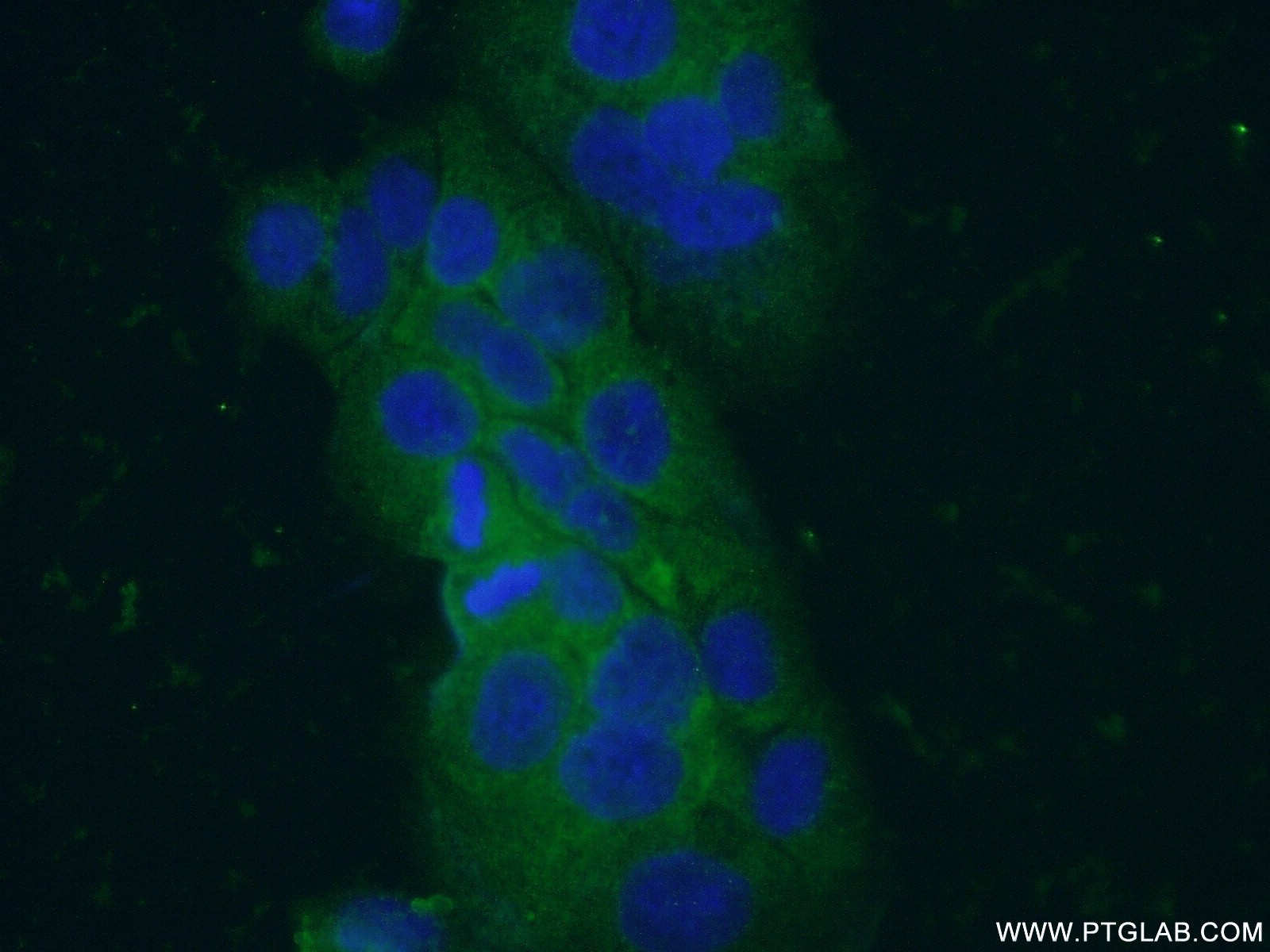
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | COLO 320 cells |
推荐稀释比
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:400-1:1600 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
产品信息
16233-1-AP targets VIP in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Applications | IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA Application Description |
| Cited Applications | WB, IHC, IF |
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | mouse, rat |
| Immunogen | VIP fusion protein Ag8933 种属同源性预测 |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Full Name | vasoactive intestinal peptide |
| Synonyms | VIP peptides, Intestinal peptide PHV-42, Intestinal peptide PHM-27 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 169 aa, 19 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC009794 |
| Gene Symbol | VIP |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7432 |
| RRID | AB_2878233 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P01282 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), a short peptide containing 28 amino acids belonging to the secretin-glucagon family, is initially isolated from the gastrointestinal tract as a potent vasodilator peptide. VIP was initially identified in normal nervous tissue and neurons and was subsequently recognized as a neurotransmitter widely distributed in various tissues. The wide distribution of VIP determines its involvement in a range of biological activities, such as gut motility, hormonal regulation, circadian rhythms, immune responses, and carcinogenesis. The general physiologic effects of VIP include vasodilation, anti-inflammatory actions, cell proliferation, hormonal secretion, regulation of gastric motility, and smooth muscle relaxation; therefore, VIP has emerged as a promising drug candidate for the treatment of several diseases.
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for VIP antibody 16233-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for VIP antibody 16233-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Immun Inflamm Dis Vasoactive intestinal peptide exerts therapeutic action by regulating PTEN in a model of Sjögren's disease | ||
Pharm Biol Modified BuShenYiQi formula alleviates experimental allergic asthma in mice by negative regulation of type 2 innate lymphoid cells and CD4 + type 9 helper T cells and the VIP-VPAC2 signalling pathway | ||
Biomolecules Postweaning Development Influences Endogenous VPAC1 Modulation of LTP Induced by Theta-Burst Stimulation: A Link to Maturation of the Hippocampal GABAergic System | ||
J Neurosci Res Mismatch novelty exploration training shifts VPAC1 receptor-mediated modulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity by endogenous VIP in male rats | ||
Nat Commun Sensory neurons regulate stimulus-dependent humoral immunity in mouse models of bacterial infection and asthma |