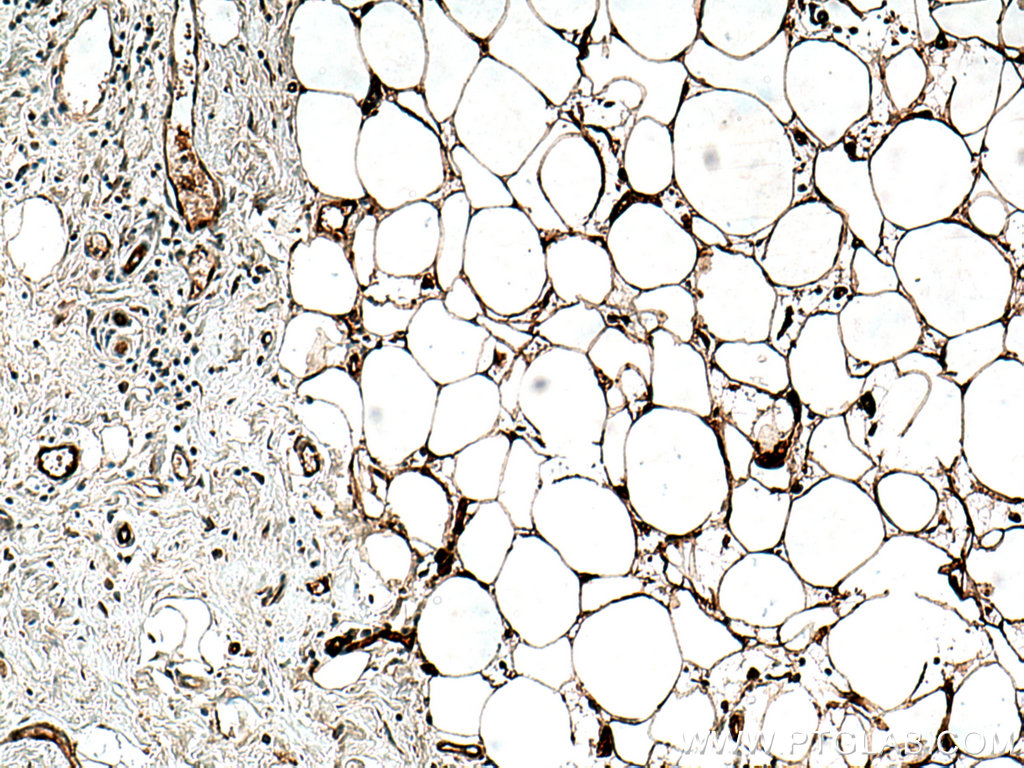
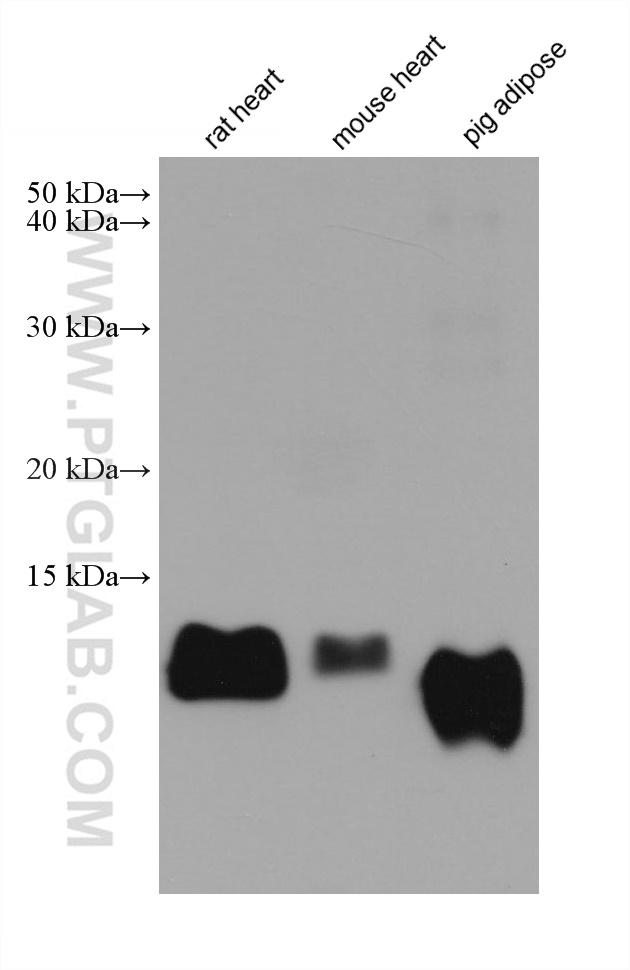
验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
| Positive WB detected in | rat heart tissue, mouse heart tissue, pig adipose tissue |
| Positive IHC detected in | human breast cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:800-1:4000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
发表文章中的应用
| WB | See 7 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
产品信息
67167-1-Ig targets FABP4 in WB, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human, mouse, rat, pig samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, ELISA Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | WB, IHC |
| 经测试反应性 | Human, mouse, rat, pig |
| 文献引用反应性 | human, mouse |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag8565 Product name: Recombinant human FABP4 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 6-132 aa of BC003672 Sequence: VGTWKLVSSENFDDYMKEVGVGFATRKVAGMAKPNMIISVNGDVITIKSESTFKNTEISFILGQEFDEVTADDRKVKSTITLDGGVLVHVQKWDGKSTTIKRKREDDKLVVECVMKGVTSTRVYERA 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG2b |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | fatty acid binding protein 4, adipocyte |
| 别名 | A FABP, AFABP, ALBP, aP2, FABP4, Fatty acid binding protein 4 |
| 计算分子量 | 132 aa, 15 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 14 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC003672 |
| 基因名称 | FABP4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2167 |
| RRID | AB_2882463 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P15090 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
Fatty acid binding protein (FABP) 4 is a member of the FABP family which abundantly expressed, fatty acid carrier proteins. FABPs are capable of binding a variety of hydrophobic molecules such as long-chain fatty acids and are important for their uptake and intracellular trafficking. It was first identified as an adipocyte-specific protein, important for the maintenance of lipid and glucose metabolism. It is also detected in macrophages, where it participates in regulating inflammation and cholesterol trafficking via NFκB and PPAR. In more recent studies, FABP4 has been found in a variety of endothelial cells, where it has been identified as a target of VEGF and a regulator of cell proliferation and possibly angiogenesis. Pathologically, FABP4 has been associated with the development of metabolic syndrome, diabetes and cancer and vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques. FABP4 has been identified as a novel prognostic factor for both adverse cardiovascular events and breast cancer.
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for FABP4 antibody 67167-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for FABP4 antibody 67167-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Genes Dis Naked cuticle homolog 2 controls the differentiation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts and ameliorates bone loss in ovariectomized mice | ||
Stem Cell Res Ther Oncostatin M receptor regulates osteoblast differentiation via extracellular signal-regulated kinase/autophagy signaling. | ||
Int J Biol Sci LAMC1-mediated preadipocytes differentiation promoted peritoneum pre-metastatic niche formation and gastric cancer metastasis. | ||
Biol Pharm Bull Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) Extract-Induced Adipogenesis Is Independent of PPARγ Ser273 Phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. | ||
J Orthop Translat Accumulation of advanced oxidation protein products aggravates bone-fat imbalance during skeletal aging |