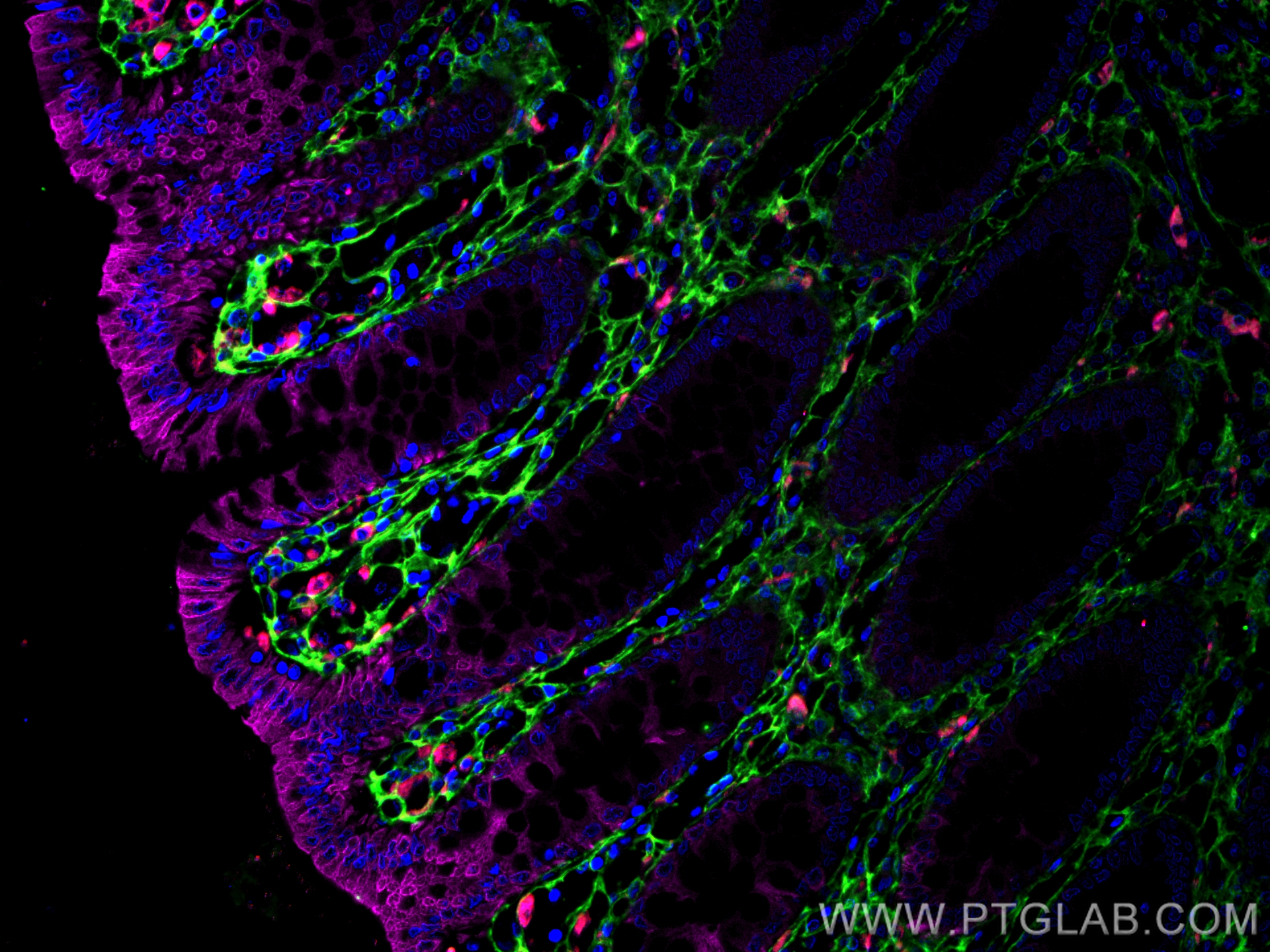
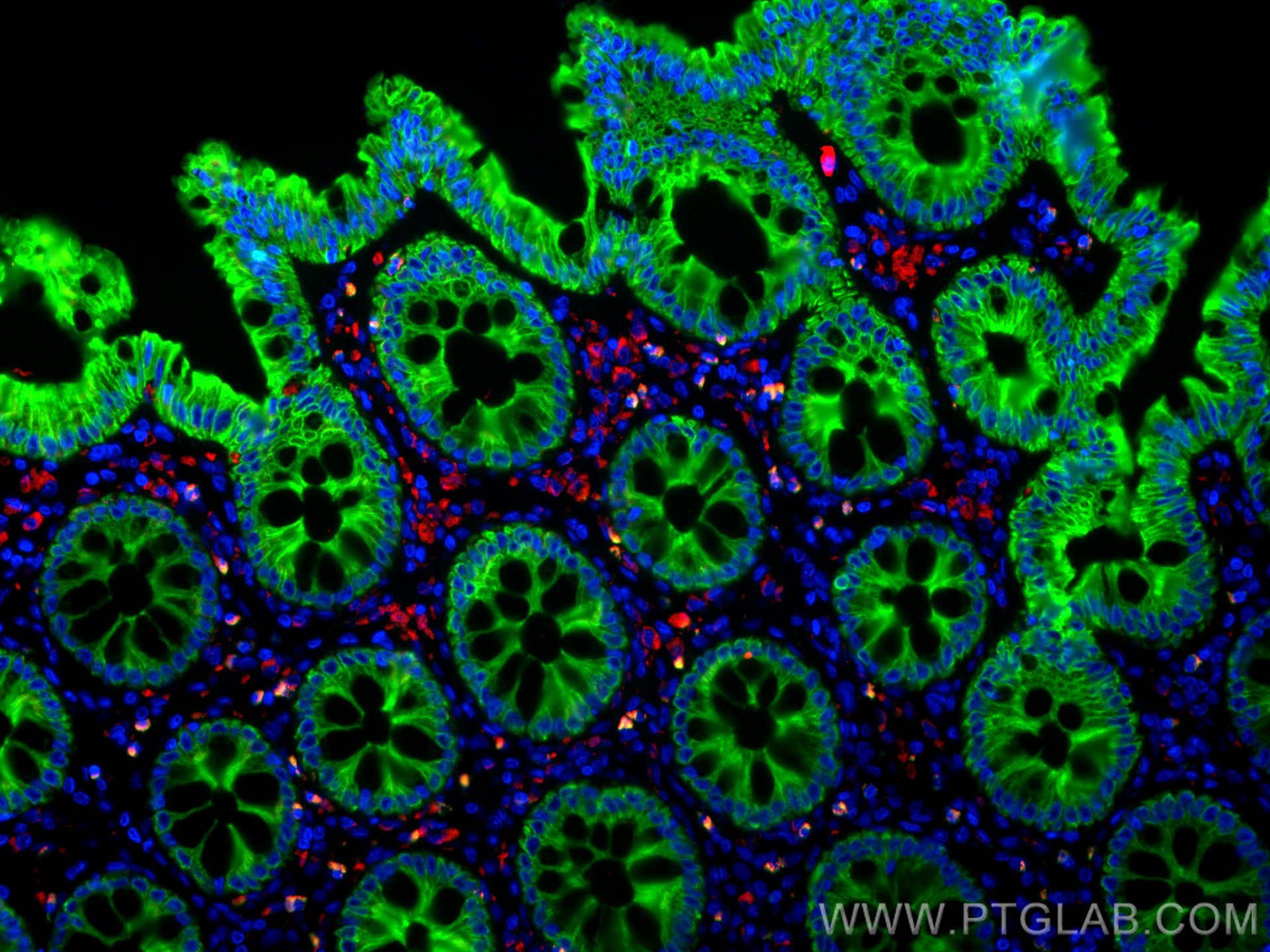
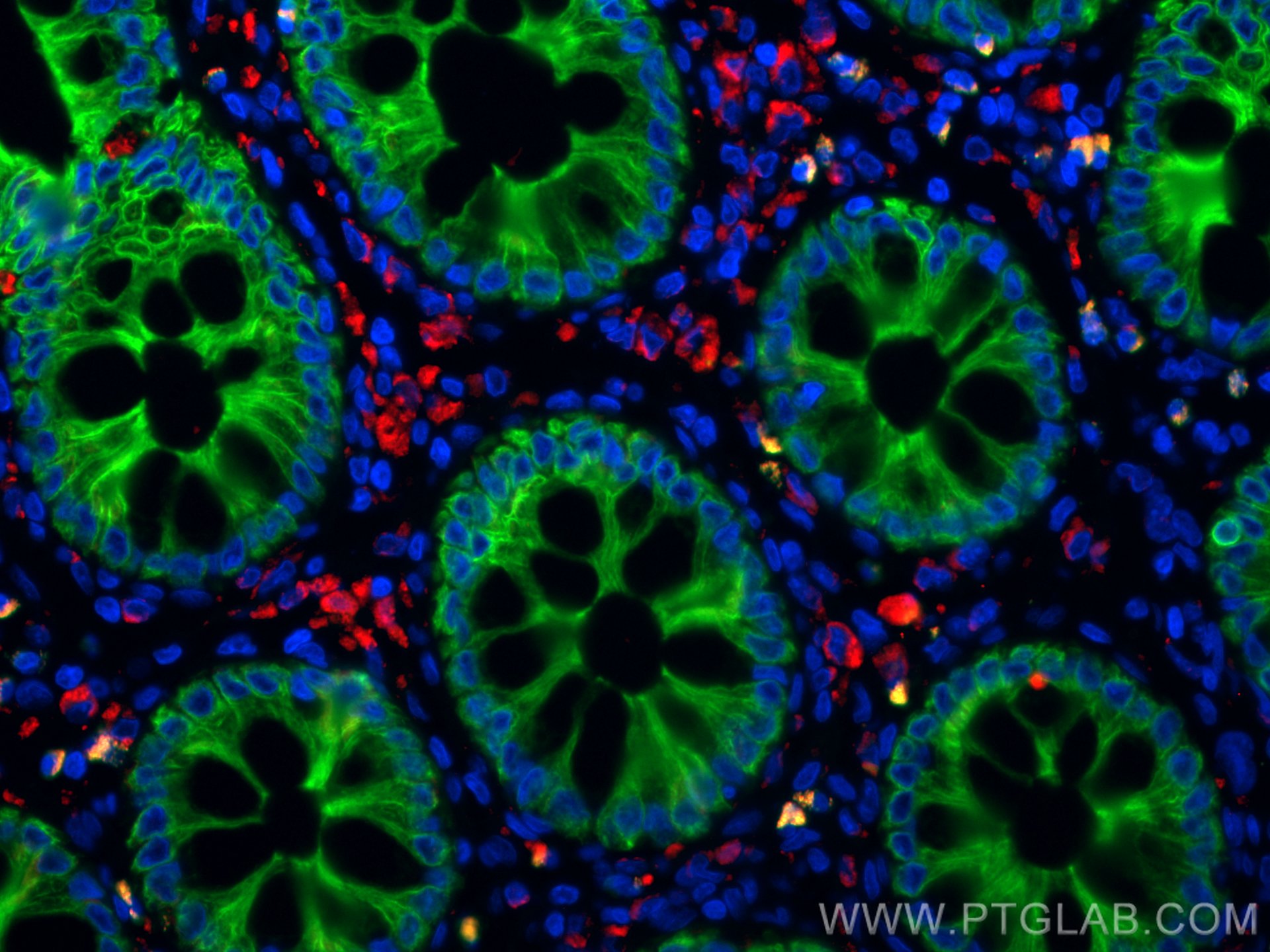
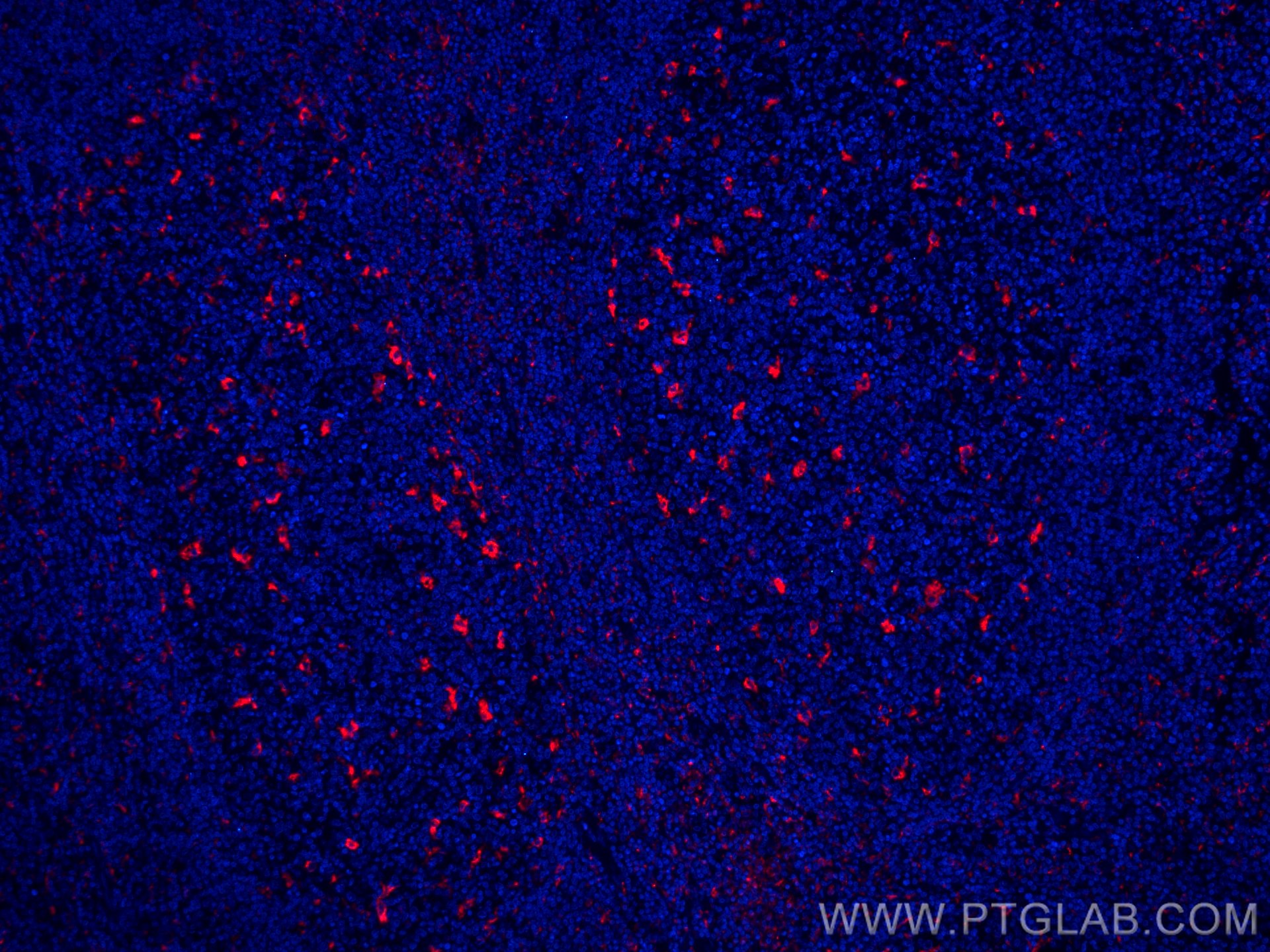
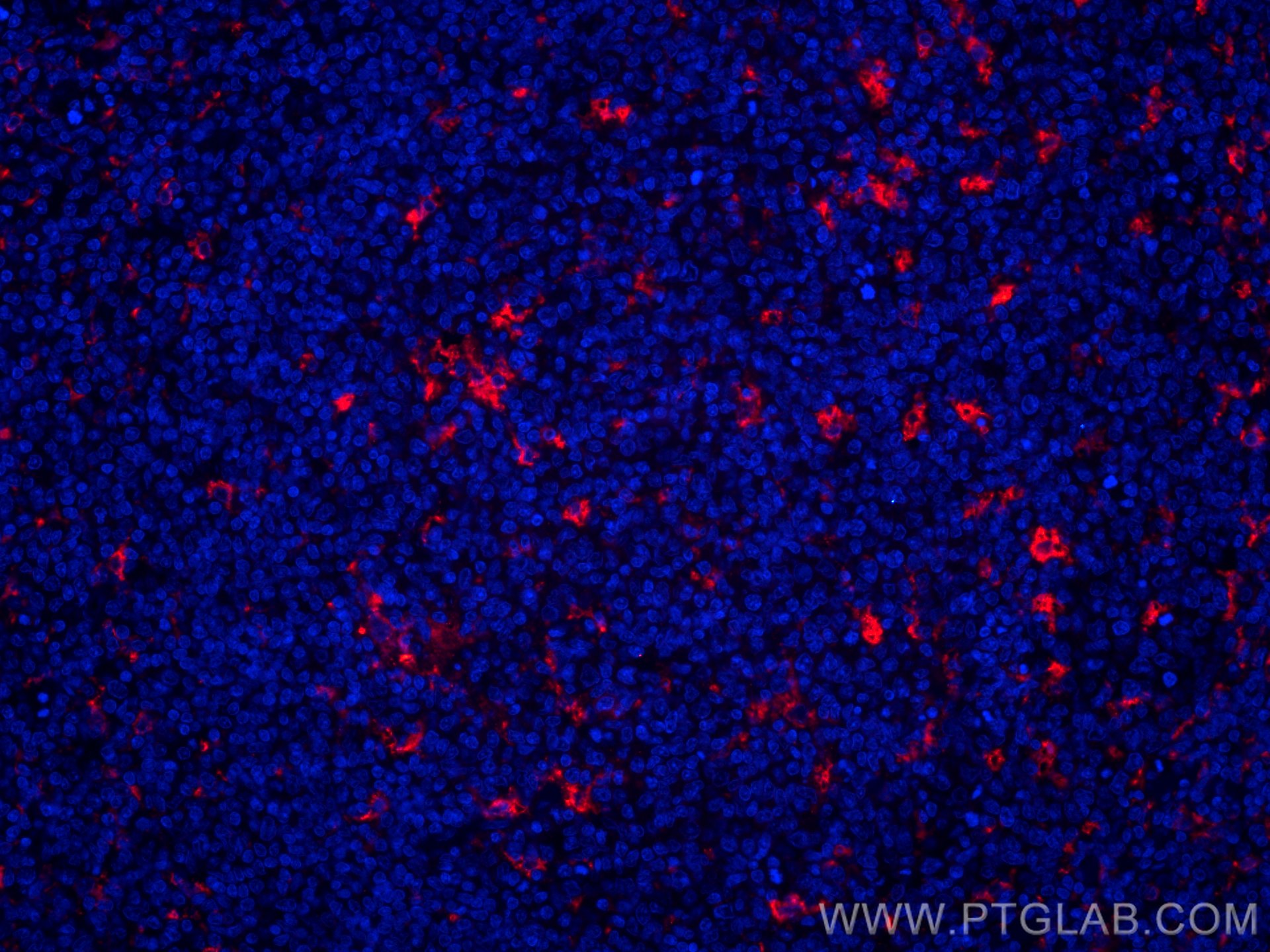
验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
| Positive IF-P detected in | human colon tissue, human tonsillitis tissue |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
发表文章中的应用
| IF | See 3 publications below |
产品信息
CL594-25747 targets CD68 in IF-P applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| 经测试应用 | IF-P Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | IF |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse |
| 文献引用反应性 | human, mouse |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag22815 Product name: Recombinant human CD68 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 29-319 aa of BC015557 Sequence: SATLLPSFTVTPTVTESTGTTSHRTTKSHKTTTHRTTTTGTTSHGPTTATHNPTTTSHGNVTVHPTSNSTATSQGPSTATHSPATTSHGNATVHPTSNSTATSPGFTSSAHPEPPPPSPSPSPTSKETIGDYTWTNGSQPCVHLQAQIQIRVMYTTQGGGEAWGISVLNPNKTKVQGSCEGAHPHLLLSFPYGHLSFGFMQDLQQKVVYLSYMAVEYNVSFPHAAQWTFSAQNASLRDLQAPLGQSFSCSNSSIILSPAVHLDLLSLRLQAAQLPHTGVFGQSFSCPSDRS 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | CD68 molecule |
| 别名 | CD68 molecule, GP110, Macrosialin, SCARD1 |
| 计算分子量 | 37 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 60 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC015557 |
| 基因名称 | CD68 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 968 |
| RRID | AB_2919875 |
| 偶联类型 | CoraLite®594 Fluorescent Dye |
| 最大激发/发射波长 | 588 nm / 604 nm |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P34810 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
CD68 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is highly expressed by human monocytes and tissue macrophages. It belongs to the lysosomal/endosomal-associated membrane glycoprotein (LAMP) family and primarily localizes to lysosomes and endosomes with a smaller fraction circulating to the cell surface. CD68 is also a member of the scavenger receptor family. It may play a role in phagocytic activities of tissue macrophages. The apparent molecular weight of CD68 is larger than calculated molecular weight due to post-translation modification.
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for CL594 CD68 antibody CL594-25747 | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for CL594 CD68 antibody CL594-25747 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Front Mol Biosci Blockage of ERCC6 Alleviates Spinal Cord Injury Through Weakening Apoptosis, Inflammation, Senescence, and Oxidative Stress. | ||
Phytomedicine Acacetin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by targeting HSP90 ATPase domain to promote COX-2 degradation | ||
Nat Immunol Chemotherapy-induced CA-repeat DNA fragments in breast cancer trigger antitumor immune responses |