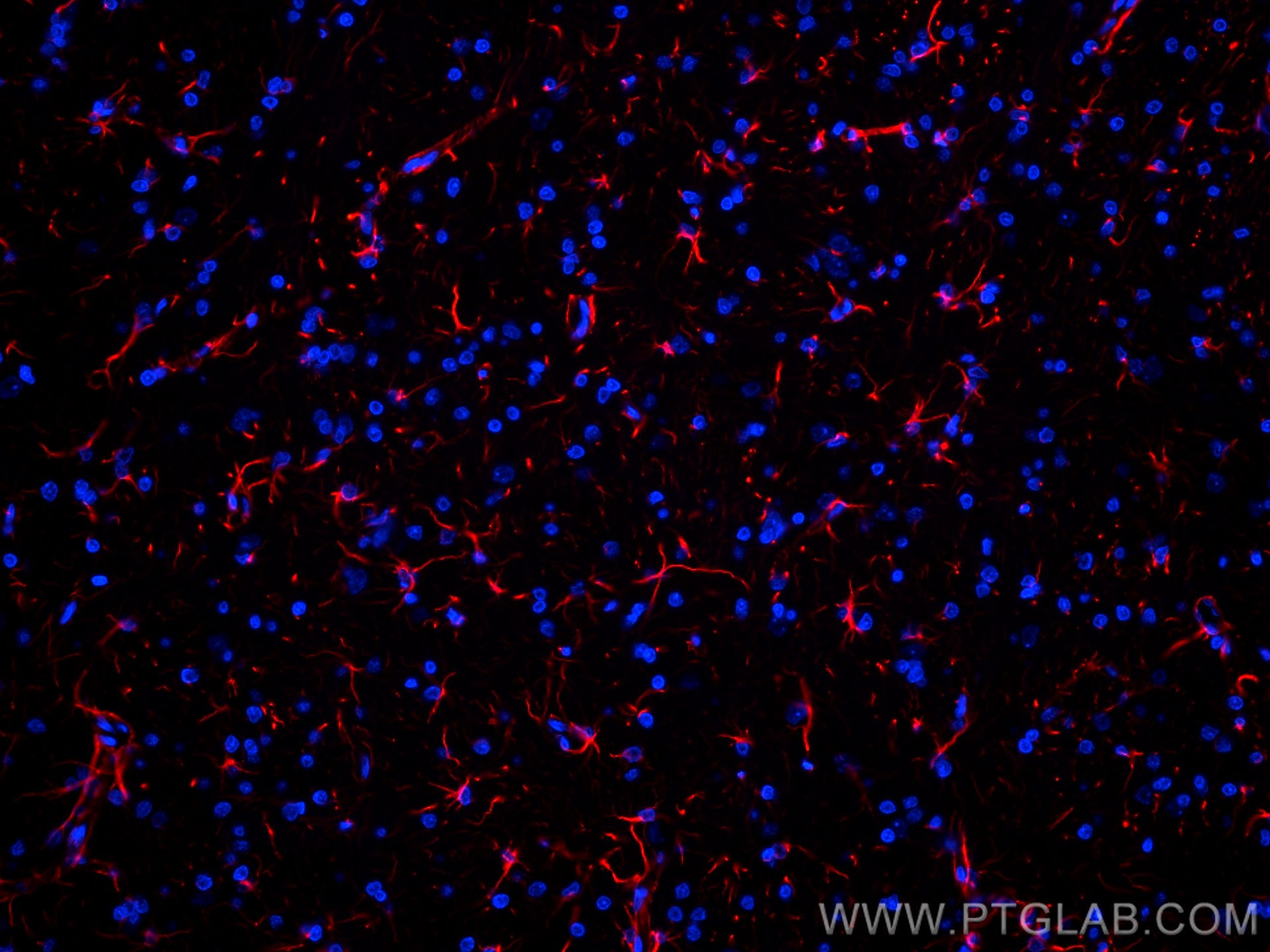
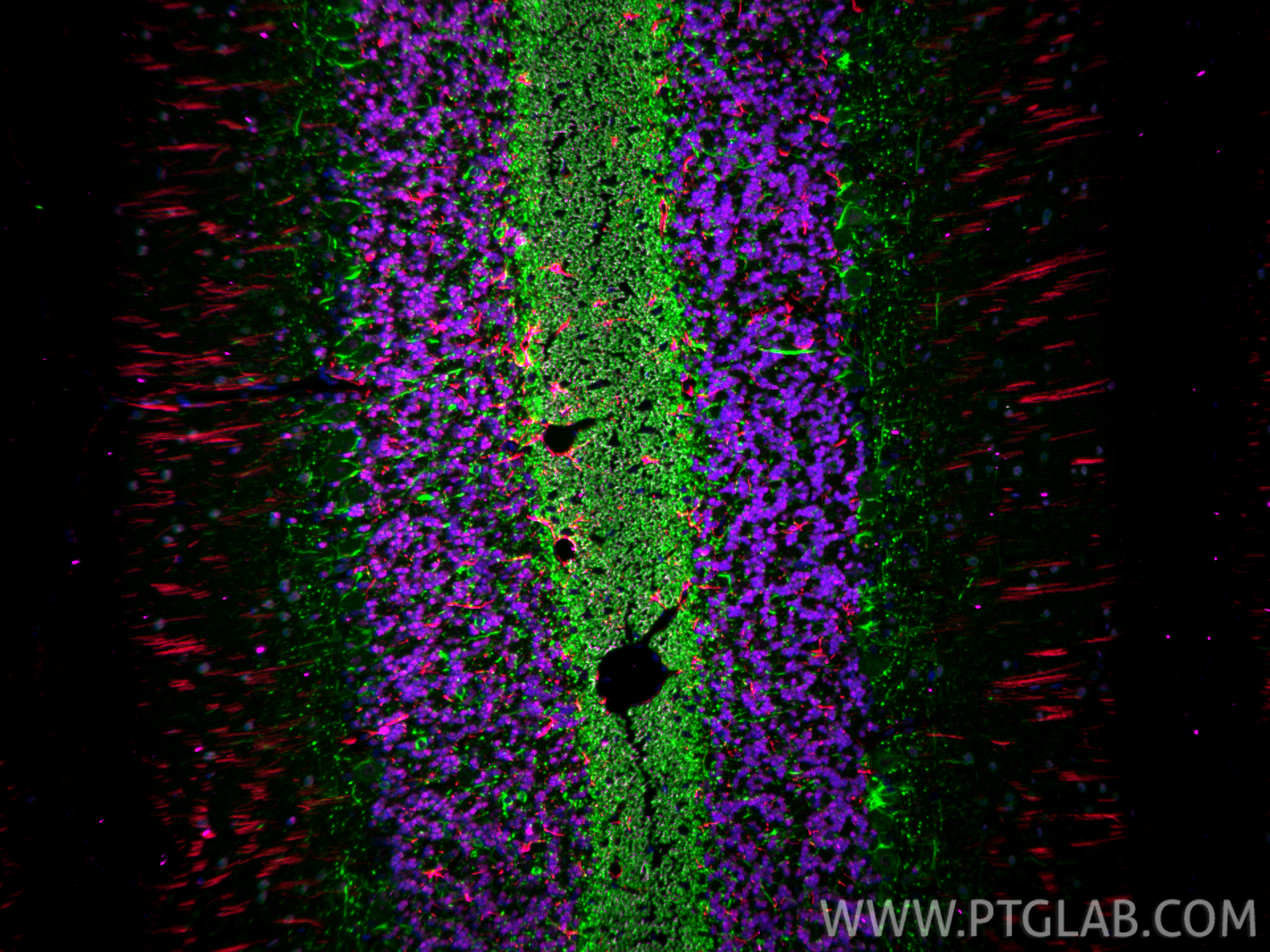
验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
| Positive IF-P detected in | rat brain tissue, rat cerebellum tissue |
This antibody is not recommended for immunocytofluorescent assays. It is not suitable for frozen sections.
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
发表文章中的应用
| IF | See 4 publications below |
产品信息
CL594-60190 targets GFAP in IF-P applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, pig samples.
| 经测试应用 | IF-P Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | IF |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat, pig |
| 文献引用反应性 | mouse |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag10452 Product name: Recombinant human GFAP protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 83-432 aa of BC013596 Sequence: YIEKVRFLEQQNKALAAELNQLRAKEPTKLADVYQAELRELRLRLDQLTANSARLEVERDNLAQDLATVRQKLQDETNLRLEAENNLAAYRQEADEATLARLDLERKIESLEEEIRFLRKIHEEEVRELQEQLARQQVHVELDVAKPDLTAALKEIRTQYEAMASSNMHEAEEWYRSKFADLTDAAARNAELLRQAKHEANDYRRQLQSLTCDLESLRGTNESLERQMREQEERHVREAASYQEALARLEEEGQSLKDEMARHLQEYQDLLNVKLALDIEIATYRKLLEGEENRITIPVQTFSNLQIRETSLDTKSVSEGHLKRNIVVKTVEMRDGEVIKESKQEHKDVM 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG2a |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| 别名 | 4B2E10, glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| 计算分子量 | 432 aa, 50 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC013596 |
| 基因名称 | GFAP |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2670 |
| RRID | AB_2883437 |
| 偶联类型 | CoraLite®594 Fluorescent Dye |
| 最大激发/发射波长 | 588 nm / 604 nm |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P14136 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
GFAP Function GFAP (Glial fibrillary acidic protein) is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein specific to the central nervous system (CNS). GFAP is one of the main components of the intermediate filament network in astrocytes and has been proposed as playing a role in cell migration, cell motility, maintaining mechanical strength, and in mitosis. Tissue specificity GFAP is expressed in central nervous system cells, predominantly in astrocytes. GFAP is commonly used as an astrocyte marker. However, GFAP is also present in peripheral glia and in non-CNS cells, including fibroblasts, chondrocytes, lymphocytes, and liver stellate cells (PMID: 21219963). Involvement in disease Mutations in GFAP lead to Alexander disease (OMIM: 203450), an autosomal dominant CNS disorder. The mutations present in affected individuals are thought to be gain-of-function. Upregulation of GFAP is a hallmark of reactive astrocytes, in which GFAP is present in hypertrophic cellular processes. Reactive astrogliosis is present in many neurological disorders, such as stroke, various neurodegenerative diseases (including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease), and neurotrauma. Isoforms Astrocytes express 10 different isoforms of GFAP that differ in the rod and tail domains (PMID: 25726916), which means that they differ in molecular size. Isoform expression varies during the development and across different subtypes of astrocytes. Not all isoforms are upregulated in reactive astrocytes. Post-translational modifications Intermediate filament proteins are regulated by phosphorylation. Six phosphorylation sites have been identified in GFAP protein, at least some of which are reported to control filament assembly (PMID: 21219963). Cellular localization GFAP localizes to intermediate filaments and stains well in astrocyte cellular processes. The antibody is conjugated with CL594, Ex/Em 593 nm/614 nm.
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL594 GFAP antibody CL594-60190 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Glia Mechanosensitive channel Piezo1 is an essential regulator in cell cycle progression of optic nerve head astrocytes | ||
Cell Death Differ Metabolic reprogramming in astrocytes prevents neuronal death through a UCHL1/PFKFB3/H4K8la positive feedback loop | ||
Neoplasia ZC3H15 suppression ameliorates bone cancer pain through inhibiting neuronal oxidative stress and microglial inflammation | ||
Neuron Metabolic reprogramming through histone lactylation in microglia and macrophages recruits CD8+ T lymphocytes and aggravates spinal cord injury |