Recombinant Rat MMP9 protein (His Tag)
ED50
/
Species
Rat
Purity
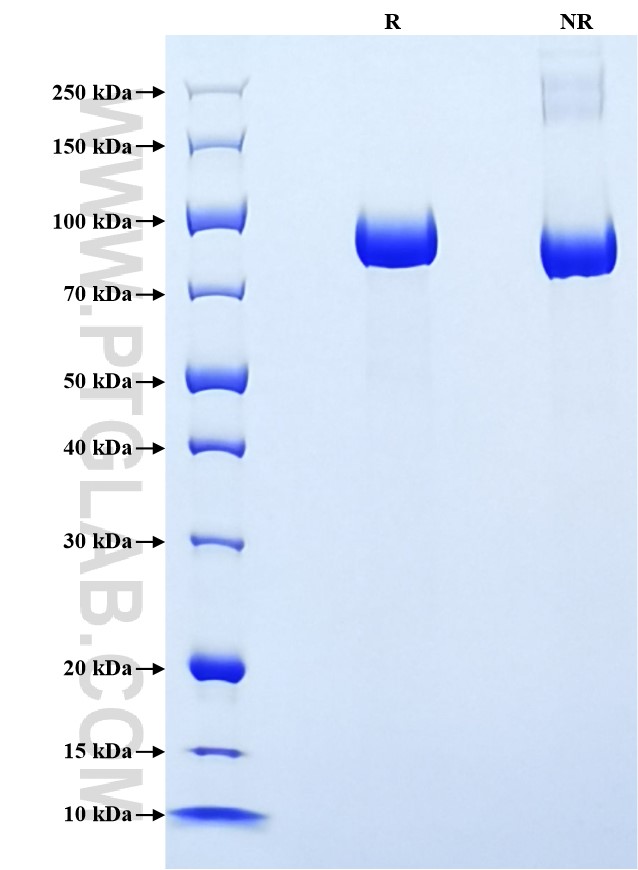
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
GeneID
81687
Accession
EDL96479.1
验证数据展示
Technical Specifications
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin Level | <1.0 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Biological Activity |
Not tested |
| Source | HEK293-derived Rat MMP9 protein Ala20-Pro708 (Accession# EDL96479.1) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 80.2 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 75-100 kDa, reducing (R) condition |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
MMP9 (matrix metallopeptidase 9), also named as Gelatinase B, is a member of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family. The MMP family of enzymes is comprised of critically important extracellular matrix remodeling proteases whose activity has been implicated in normal embryogenesis, tissue remodelling and many diseases such as arthritis, cancer, periodontitis, glomerulonephritis, encephalomyelitis, atherosclerosis and tissue ulceration. MMP9 is produced by a variety of normal and transformed cells including neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, astrocytes, fbroblasts, osteoclasts and so on. Transgenic mouse models report that MMP9 contributes to skin carcinogenesis, suppresses development of experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms, and triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis.
References:
1. Roy, Roopali et al. (2009) J Clin Oncol. 27(31):5287-5297. 2. Tanindi, Asli et al. (2011) Open Cardiovasc Med J. 5:110-116. 3. Coussens, L M et al. (2000) Cell. 103(3):481-490. 4. Pyo, R et al. (2000) J Clin Invest. 105(11):1641-1649. 5.Bergers, G et al. (2000) Nat Cell Biol. 2(10):737-744.