Recombinant Mouse CTLA-4 protein (His Tag)
ED50
0.1-0.4 μg/mL
Species
Mouse
Purity
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
GeneID
12477
Accession
NP_033973
验证数据展示
Technical Specifications
| Purity | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin Level | <1.0 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Biological Activity |
Measured by its ability to inhibit IL-2 secretion by stimulated Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cells. The ED50 for this effect is 0.1-0.4 µg/mL when stimulated with 1 µg/mL Recombinant Human CD80 in the presence of PHA. |
| Source | HEK293-derived Mouse CTLA-4 protein Glu36-Phe162 (Accession# NP_033973) with His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 14.8 kDa |
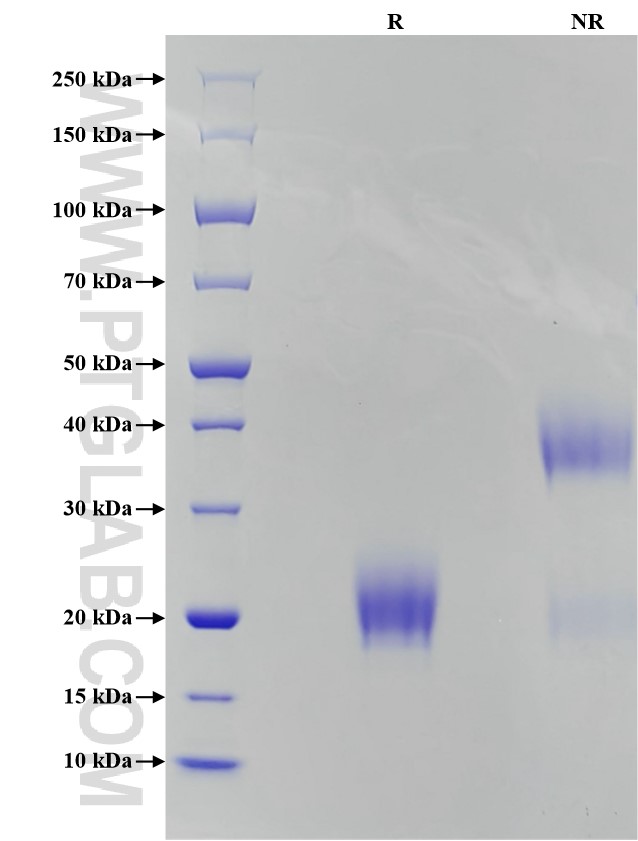
| SDS-PAGE | 18-23 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
CTLA-4, also known as CD152, belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, is primarily found on activated T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs). CTLA-4 is closely related to the T-cell costimulatory CD28, and both molecules bind to B7-1 and B7-2 on antigen-presenting cells. CTLA-4 acts as a negative regulatory molecule of T-cell responses. Besides the full-length transmembrane form, CTLA-4 also exists in a truncated soluble form (sCTLA-4).
References:
1. Brunet JF, et al. (1987) Nature. 328(6127):267-70. 2. Harper K, et al. (1991) J Immunol. 147(3):1037-44. 3. McCoy KD, et al. (1999) Immunol Cell Biol. 77(1):1-10. 4. Oaks MK, et al. (2000) Cell Immunol. 201(2):144-53.