Recombinant Mouse APOE protein (His Tag)
种属
Mouse
纯度
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
标签
His Tag
生物活性
未测试
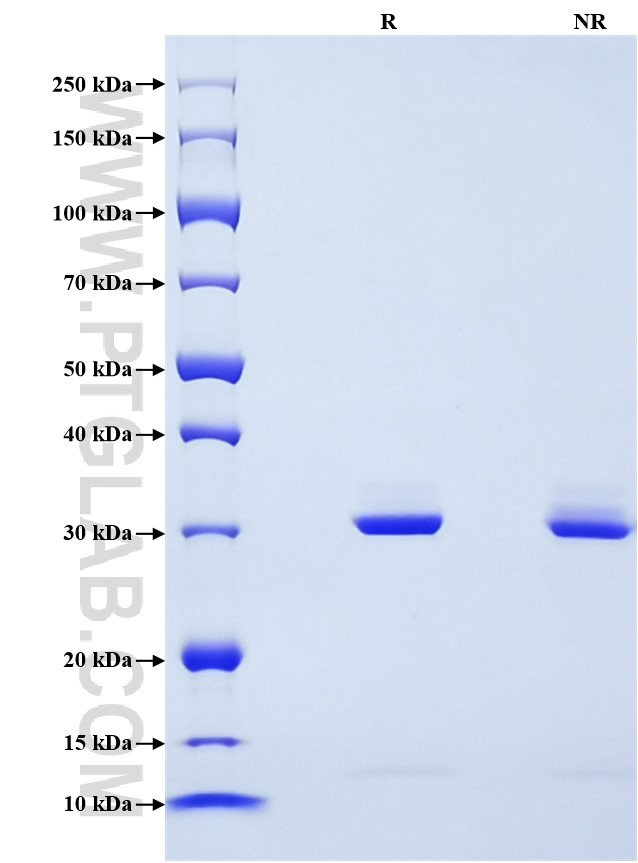
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 | Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Mouse APOE protein Glu19-Gln311 (Accession# P08226) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 11816 |
| 蛋白编号 | P08226 |
| 预测分子量 | 34.8 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 30-32 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
Apolipoprotein E (APOE) was first identified in the 1970s as one of the protein components of plasma very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and found to play a critical role in plasma cholesterol metabolism. APOE is a 299-amino acid polypeptide that mediates the binding, internalization, and catabolism of lipoprotein particles, and also serves as a ligand for the LDL (apo B/E) receptor and for the specific apo-E receptor (chylomicron remnant) of hepatic tissues. The very strong association of the APOE ɛ4 allele with AD risk and its role in the accumulation of amyloid β in brains of people and animal models solidify the biological relevance of APOE isoforms but do not provide mechanistic insight.
参考文献:
1. Montine K S, et al. (1998). J Lipid Res. 39,12: 2443-51. 2. Chen Y, et al. (2021). Neuron. 109(2):205-221. 3. Koutsodendris N, et al. (2022). Annu Rev Pathol. 17:73-99.