Recombinant Human RBP4 protein (Myc Tag, His Tag)
种属
Human
纯度
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
标签
Myc Tag, His Tag
生物活性
未测试
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 | Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Human RBP4 protein Glu19-Leu201 (Accession# P02753) with a Myc tag and a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 5950 |
| 蛋白编号 | P02753 |
| 预测分子量 | 26.1 kDa |
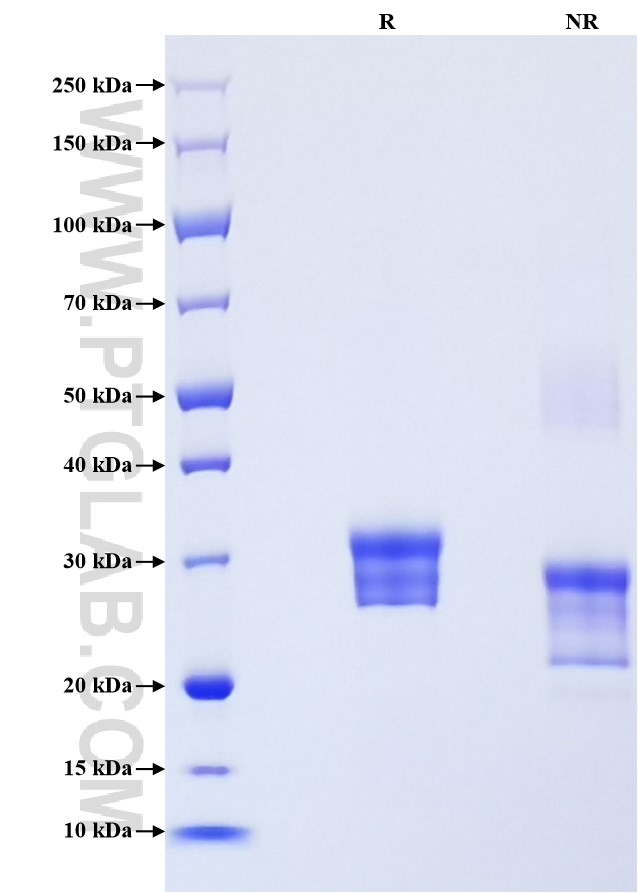
| SDS-PAGE | 26-32 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
RBP4 (retinol-binding protein 4) is a carrier protein that transports vitamin A (retinol) from the liver to the peripheral tissues. Synthesized primarily by hepatocytes and adipocytes as a 21 kDa non-glycosylated protein, RBP4 is secreted into the circulation as a retinol-RBP4 complex. In plasma the RBP4-retinol complex is bound to transthyretin (TRR), which prevents prevent kidney filtration. Two truncated forms of RBP4, RBP4-L (truncated at Leu-183) and RBP4-LL (truncated at Leu-182 and Leu-183), exist by proteolytic process. RBP4-L and RBP4-LL, which do not bind TTR, are normally excreted into the urine but accumulate in the serum during renal failure. Urinary RBP4 has been reported as marker for glomerular disease. RBP4 also was identified as an adipokine that elevated in some INS-resistant states. Measurement of serum RBP4 could be used to assess the risk of INS resistance, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.
参考文献:
1. Simone K Frey. et al. (2008) Lipids Health Dis. 7:29. 2. Qin Yang. et al. (2005) Nature. 436(7049):356-62.