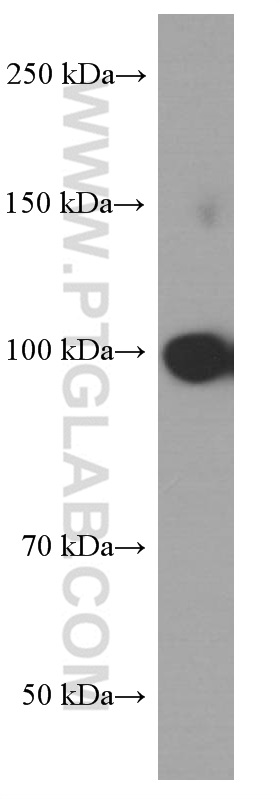
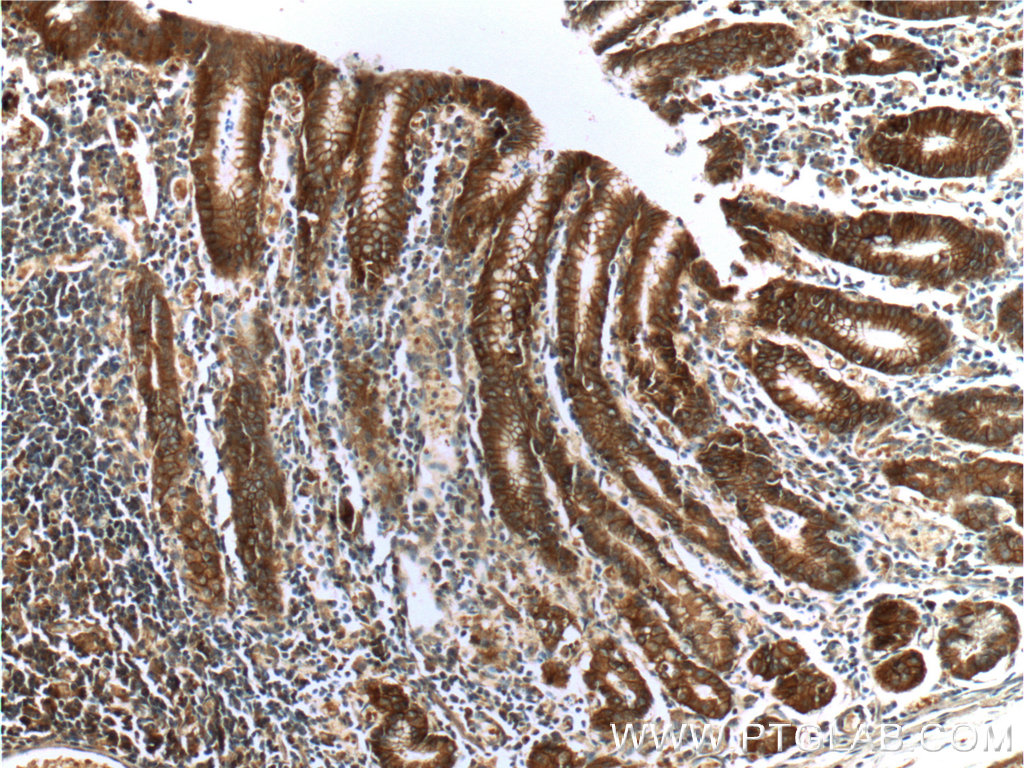
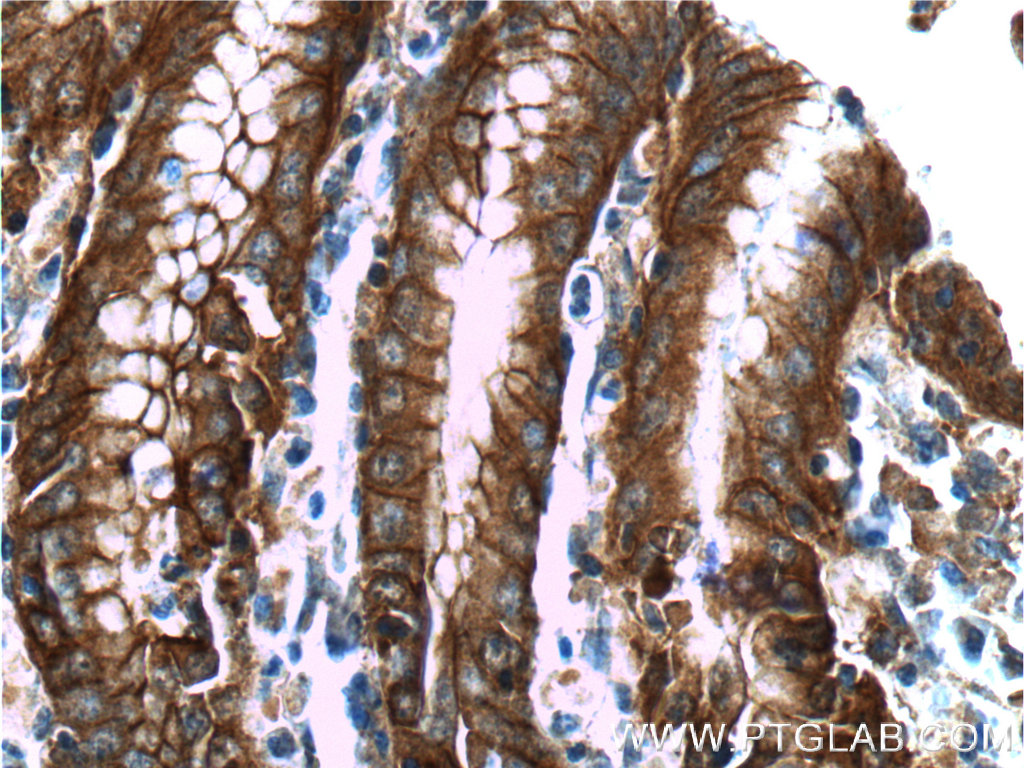
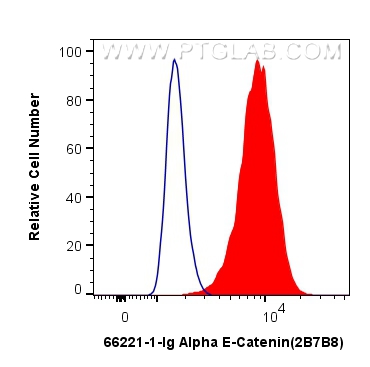
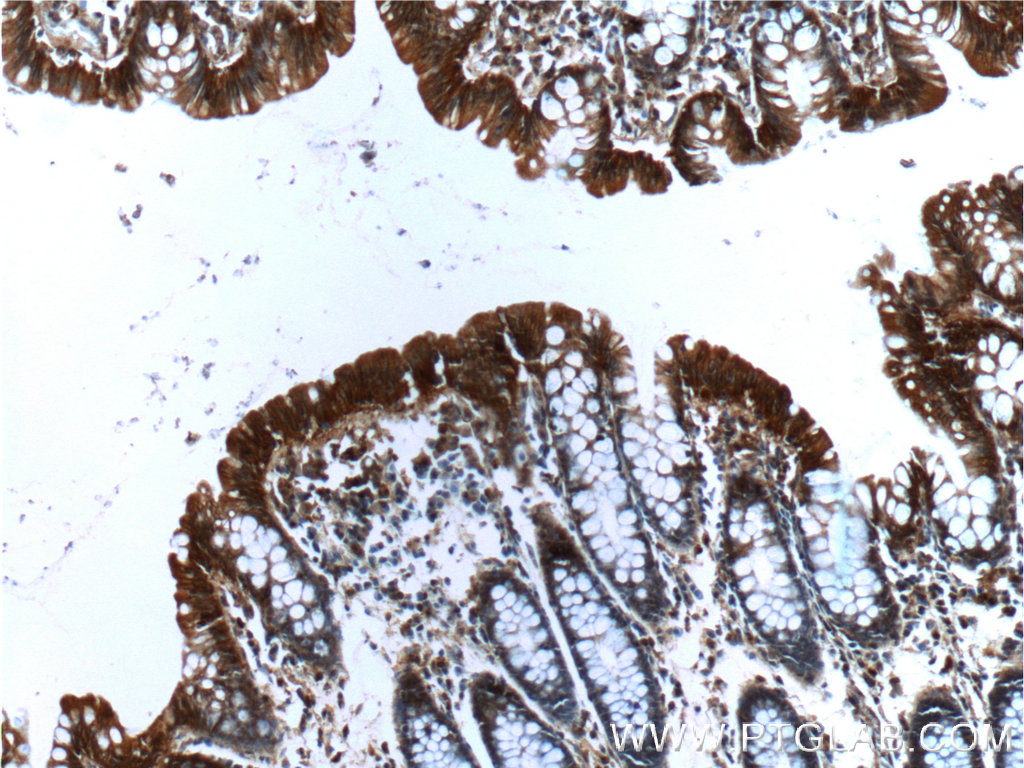
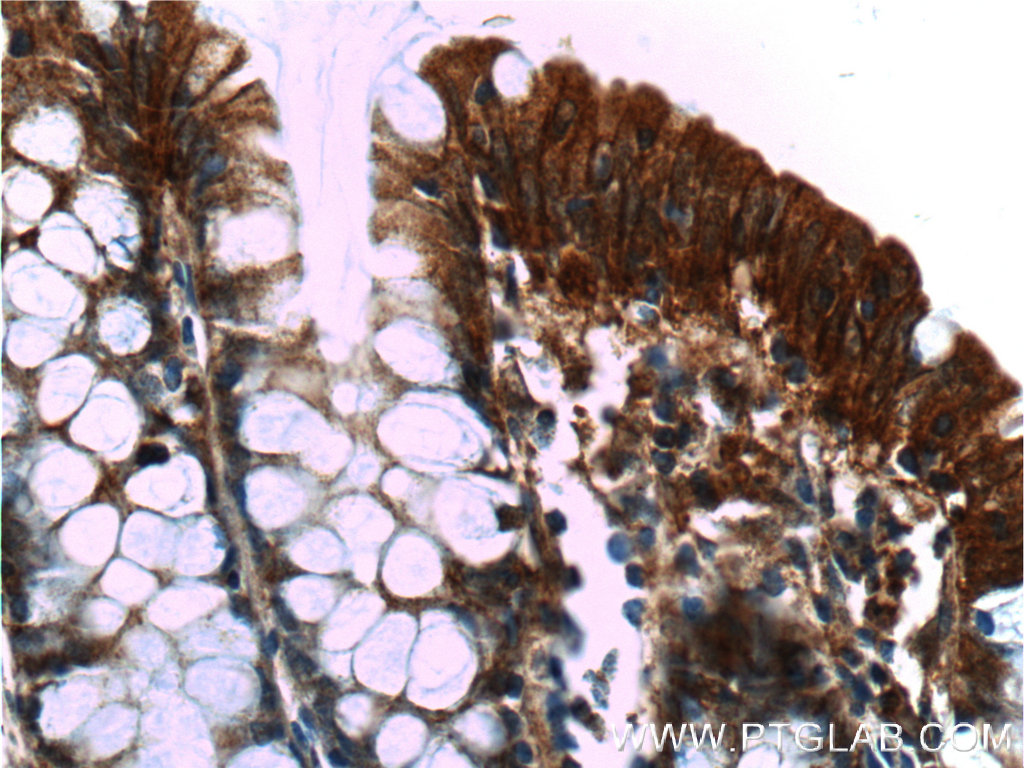
验证数据展示
产品信息
66221-1-PBS targets Alpha E-Catenin in WB, IHC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag23603 Product name: Recombinant human CTNNA1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET30a Tag: 6*His Domain: 188-536 aa of BC031262 Sequence: SEMDNYEPGVYTEKVLEATKLLSNTVMPRFTEQVEAAVEALSSDPAQPMDENEFIDASRLVYDGIRDIRKAVLMIRTPEELDDSDFETEDFDVRSRTSVQTEDDQLIAGQSARAIMAQLPQEQKAKIAEQVASFQEEKSKLDAEVSKWDDSGNDIIVLAKQMCMIMMEMTDFTRGKGPLKNTSDVISAAKKIAEAGSRMDKLGRTIADHCPDSACKQDLLAYLQRIALYCHQLNICSKVKAEVQNLGGELVVSGVDSAMSLIQAAKNLMNAVVQTVKASYVASTKYQKSQGMASLNLPAVSWKMKAPEKKPLVKREKQDETQTKIKRASQKKHVNPVQALSEFKAMDSI 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG1 |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | catenin (cadherin-associated protein), alpha 1, 102kDa |
| 别名 | CTNNA1, 2B7B8, alpha catenin, Alpha E catenin, CAP102 |
| 计算分子量 | 906 aa, 100 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 95-100 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC031262 |
| 基因名称 | Alpha E-Catenin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1495 |
| RRID | AB_2881612 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P35221 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
Alpha catenin is an essential component of adherens junctions that connects E-cadherin-β-catenin complexes with the actin cytoskeleton. It also recruits a range of other important proteins to developing intercellular junctions. Three alpha catenins exist in human: alpha-E-catenin, alpha-N-catenin, and alpha-T-catenin, which share substantial amino-acid sequence similarity but have distinct tissue distribution. alpha-E-catenin is ubiquitously expressed, alpha-N-catenin is restricted to neuronal tissue, and alpha-T-catenin is primarily expressed in heart tissue. Reduced levels of alpha-E-catenin protein seem to be characteristic of many different human cancers, including malignant tumours of the breast, colon, stomach, oesophagus, bladder and liver. In addition, the loss of alpha-E-catenin often correlates with the degree of tumour differentiation and metastasis.