验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
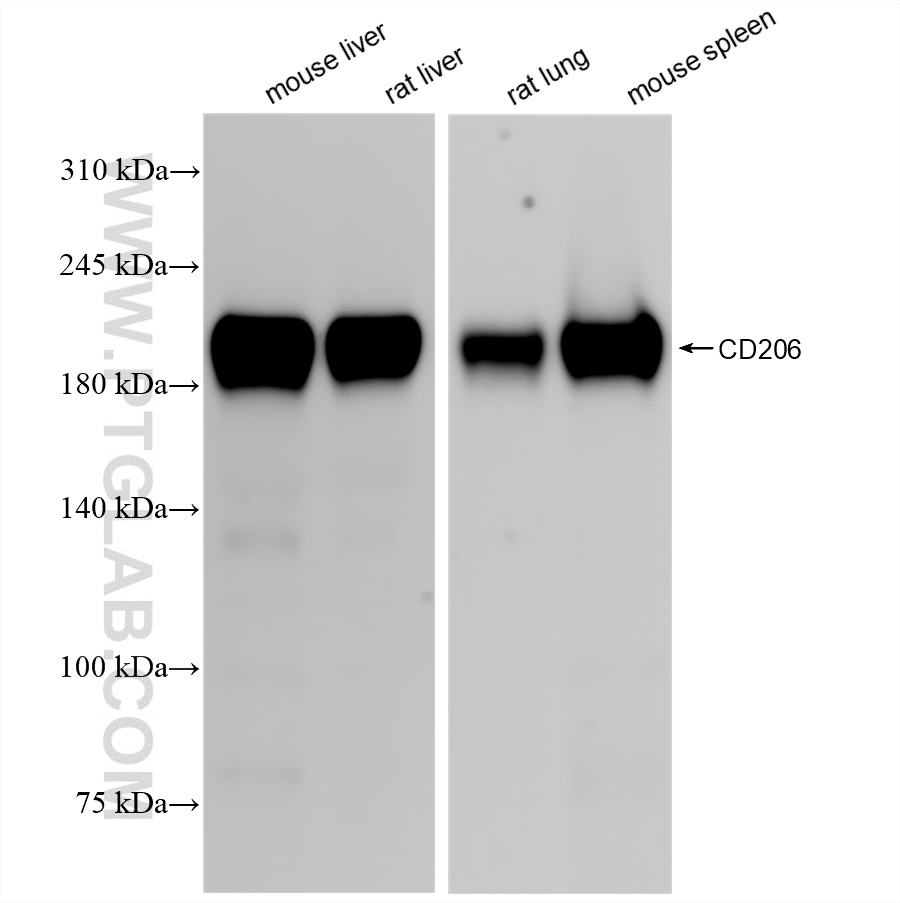
| Positive WB detected in | mouse liver tissue, rat liver tissue, rat lung tissue, mouse spleen tissue |
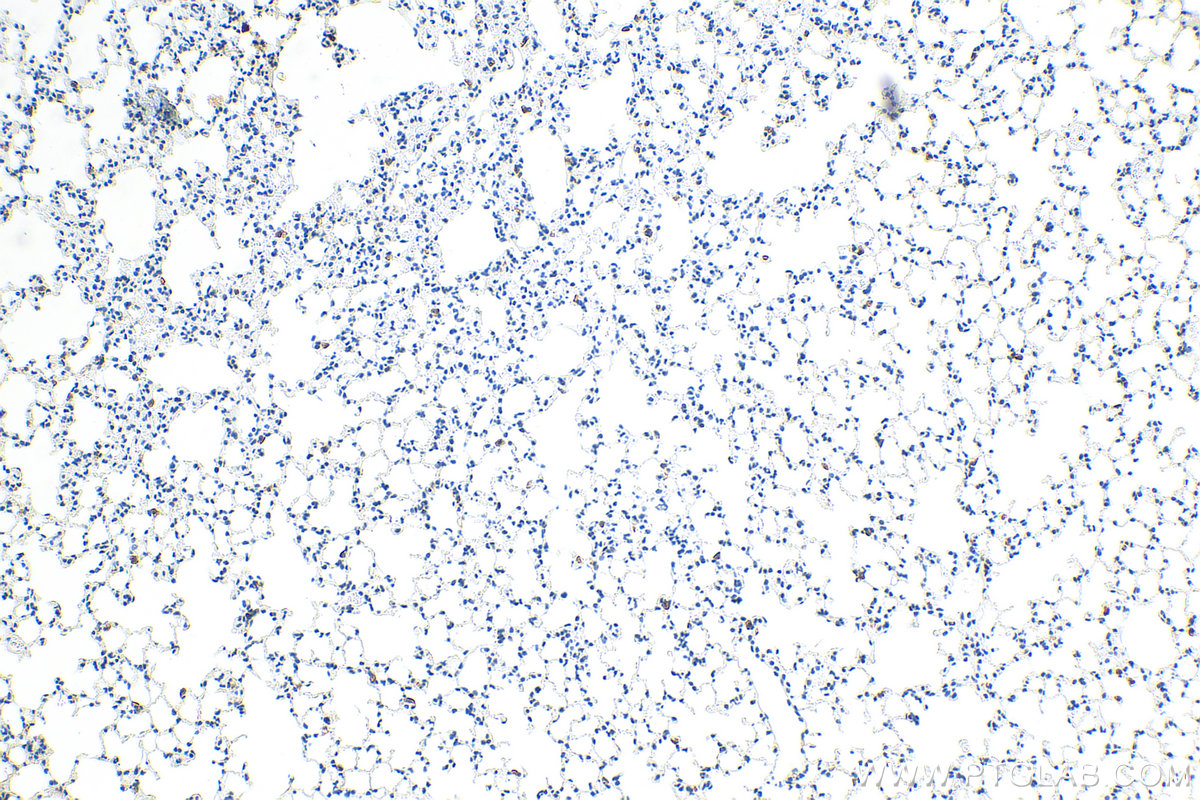
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse lung tissue, mouse liver tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
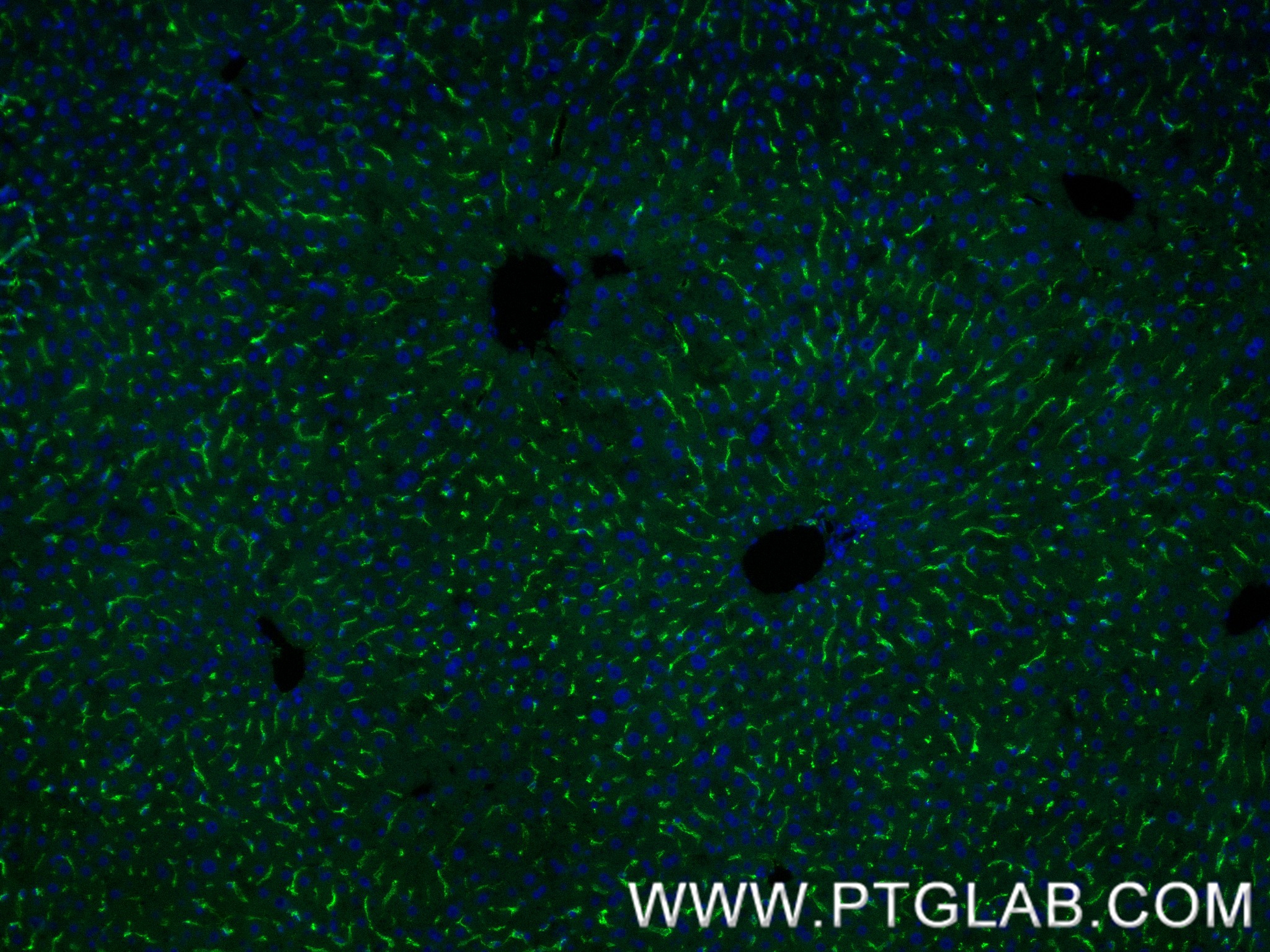
| Positive IF-P detected in | mouse liver tissue |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:500-1:2000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
产品信息
83485-1-RR targets CD206 in WB, IHC, IF-P, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with mouse, rat samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF-P, ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | mouse, rat |
| 免疫原 | Recombinant protein 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Recombinant |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | mannose receptor, C type 1 |
| 别名 | Mrc1, MR, MMR, mannose receptor, C type 1, 240344B9 |
| 计算分子量 | 165 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 200 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | NM_008625.2 |
| 基因名称 | CD206 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 17533 |
| RRID | AB_3671113 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | Q2HZ94 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
Background
CD206 (macrophage mannose receptor 1) is a lectin-type endocytic receptor expressed on selected macrophages, dendritic cells, and non-vascular endothelium and plays a role in antigen processing and presentation, phagocytosis, and intracellular signaling.
1. What is the molecular weight of CD206?
The molecular size of full-length CD206 is 170-180 kDa, depending on the exact tissue-specific glycosylation pattern (PMID: 19427834). Additionally, CD206 can be cleaved off and a soluble form (sMR) lacking the tail, with a slightly lower molecular weight, can be released to the cell medium (PMID: 9722572).
2. What is the subcellular localization of CD206?
CD206 is a type I membrane protein composed of a large extracellular multidomain, a transmembrane domain, and a short cytoplasmic tail. It is present at the plasma membrane and in endosomes, as CD206 undergoes constant recycling between the plasma membrane and endosomal compartment.
3. Is CD206 post-translationally modified?
CD206 undergoes quite extensive post-translational modifications, predominantly N-linked glycosylation that affects ligand binding recognition and affinity (PMID: 22966131).
4. Can CD206 marker be used as a marker of M2 macrophages?
The activation of macrophages with various stimuli leads to their polarization into classical (M1) or alternatively activated (M2) subtypes spectrums and both subtypes differ in their regulatory and effector functions (PMID: 24669294). Pathogens and IFN-γ promote M1 polarization, while IL-4 released during parasite infections and allergen response promotes M2 polarization. Classically, the markers of M2 macrophages include CD206, as well as arginase-1 (ARG1; https://www.ptglab.com/products/ARG1-Antibody-16001-1-AP.htm), CD163 (https://www.ptglab.com/products/CD163-Antibody-16646-1-AP.htm), and thrombospondin 1 (TSP1/ THBS1; https://www.ptglab.com/products/TSP1-Antibody-18304-1-AP.htm).
5. How can you polarize macrophages into M2 direction?
One of the most commonly used methods is stimulation by the addition of IL-4 cytokine. We recommend using our animal-free human IL-4 (https://www.ptglab.com/products/recombinant-human-il-4.htm).
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CD206 antibody 83485-1-RR | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for CD206 antibody 83485-1-RR | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for CD206 antibody 83485-1-RR | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |