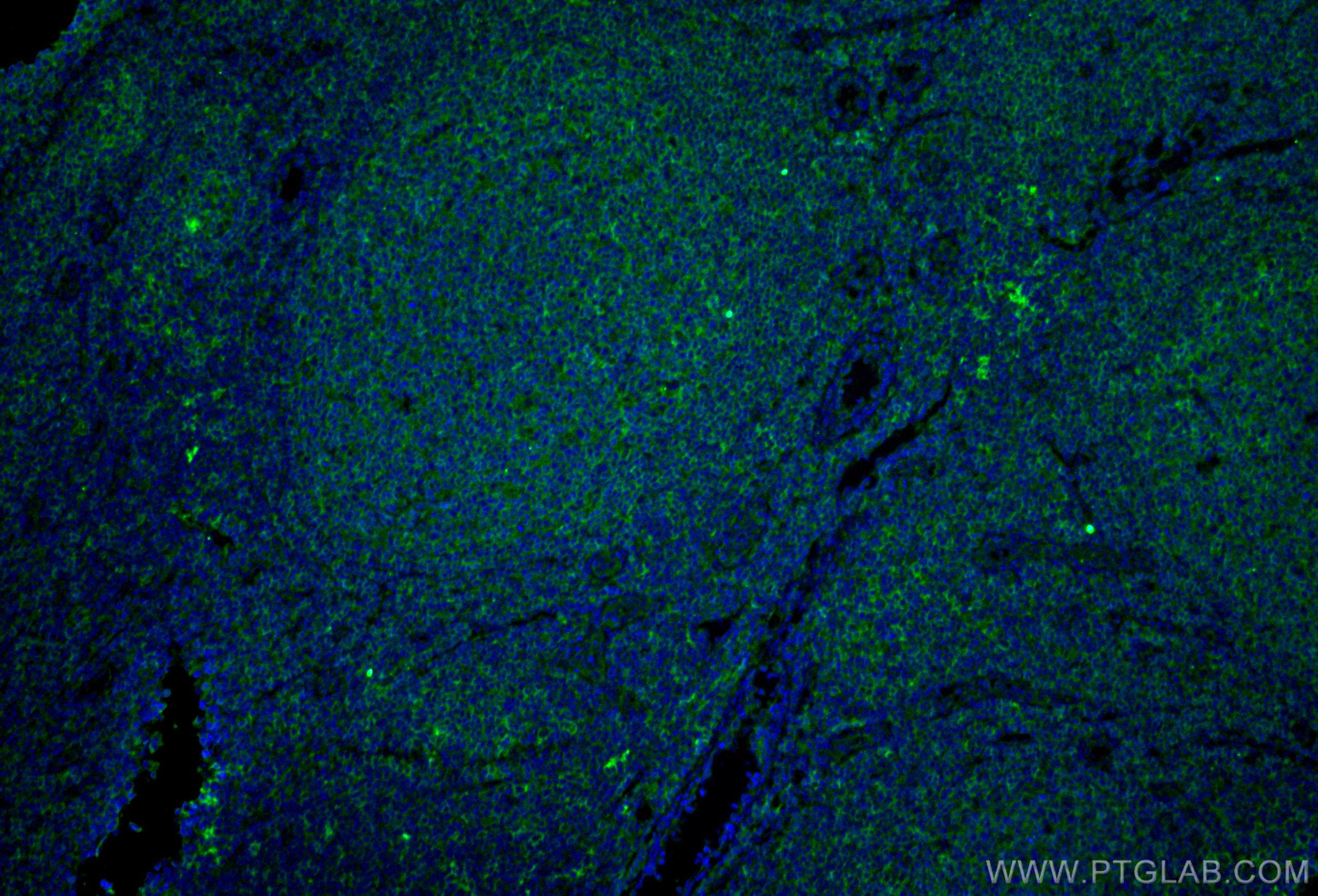
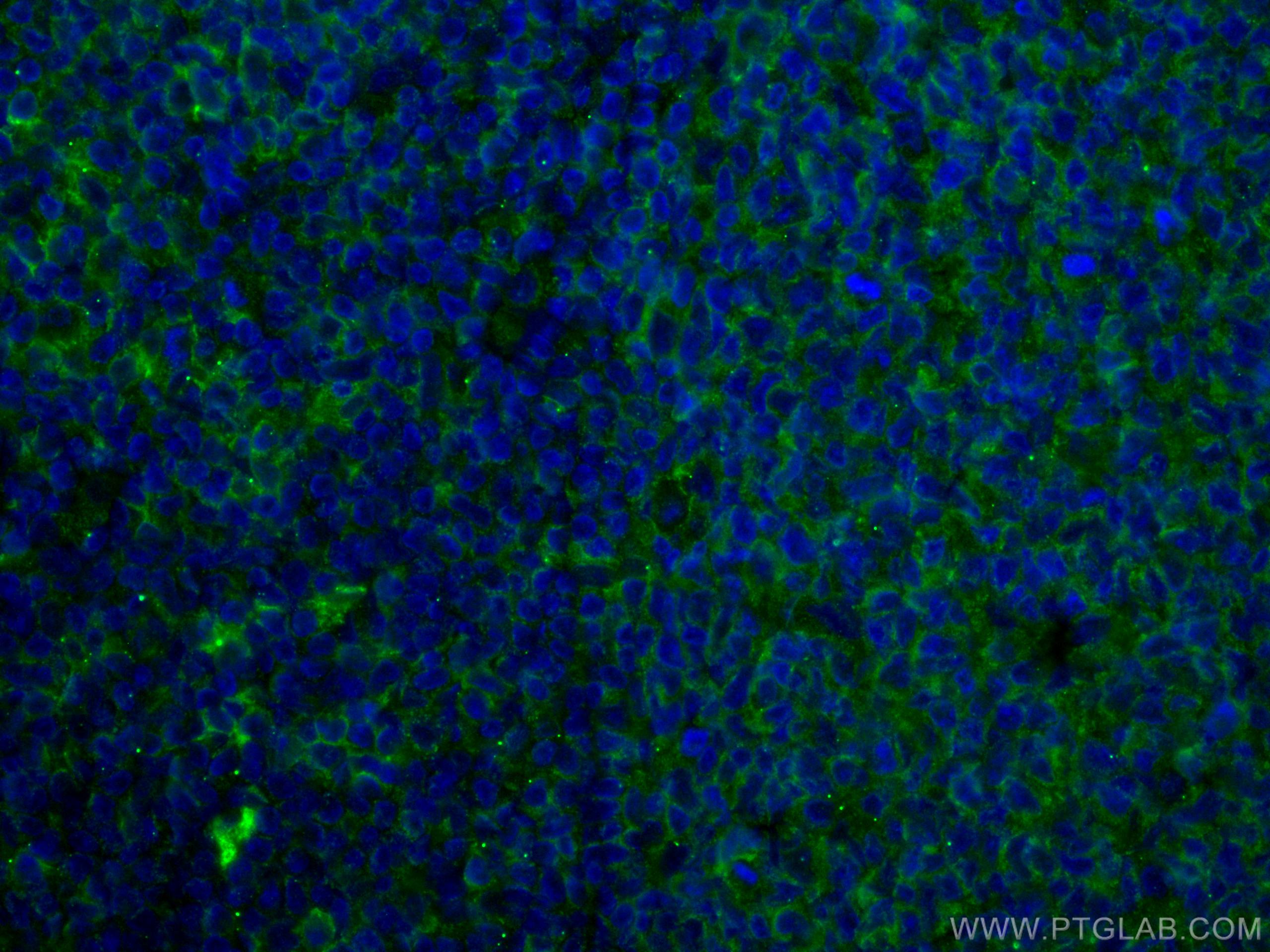
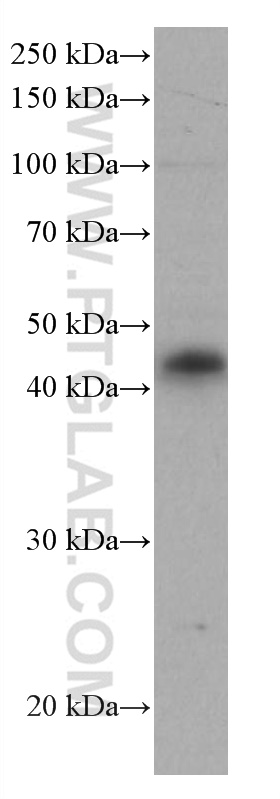
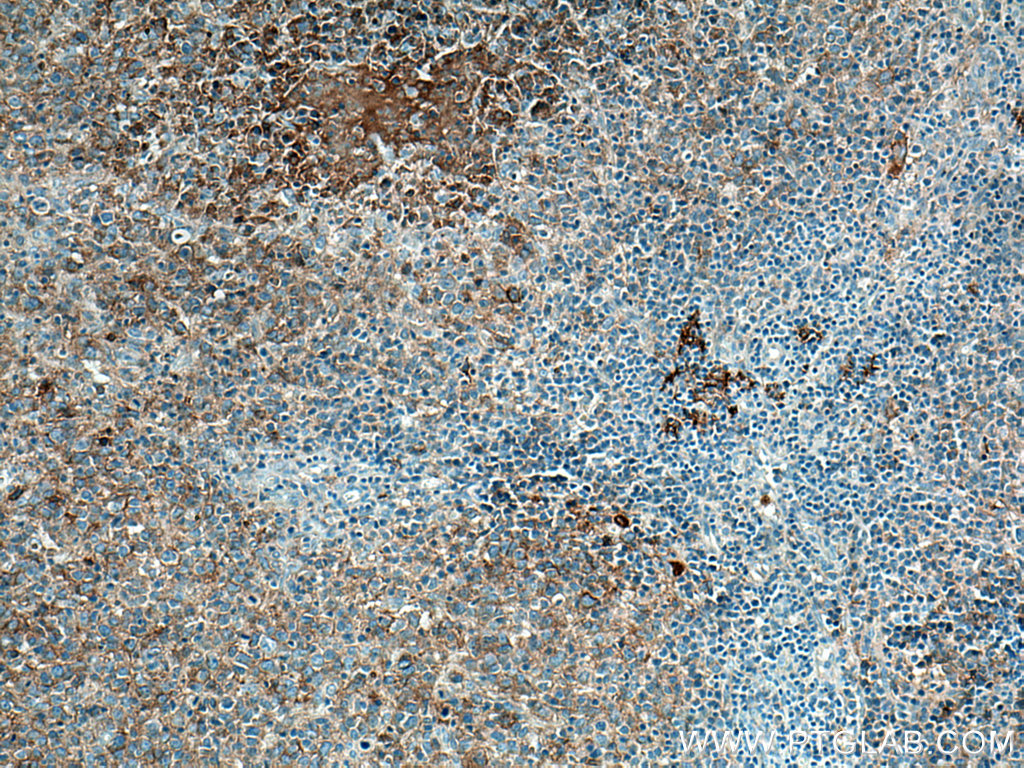
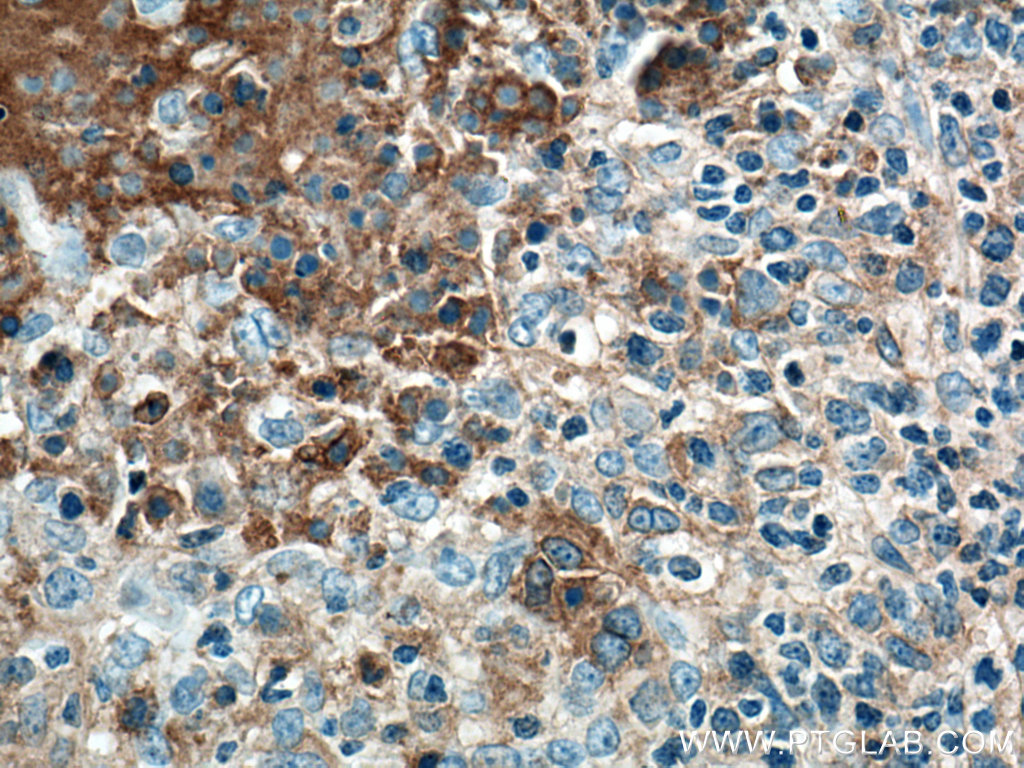
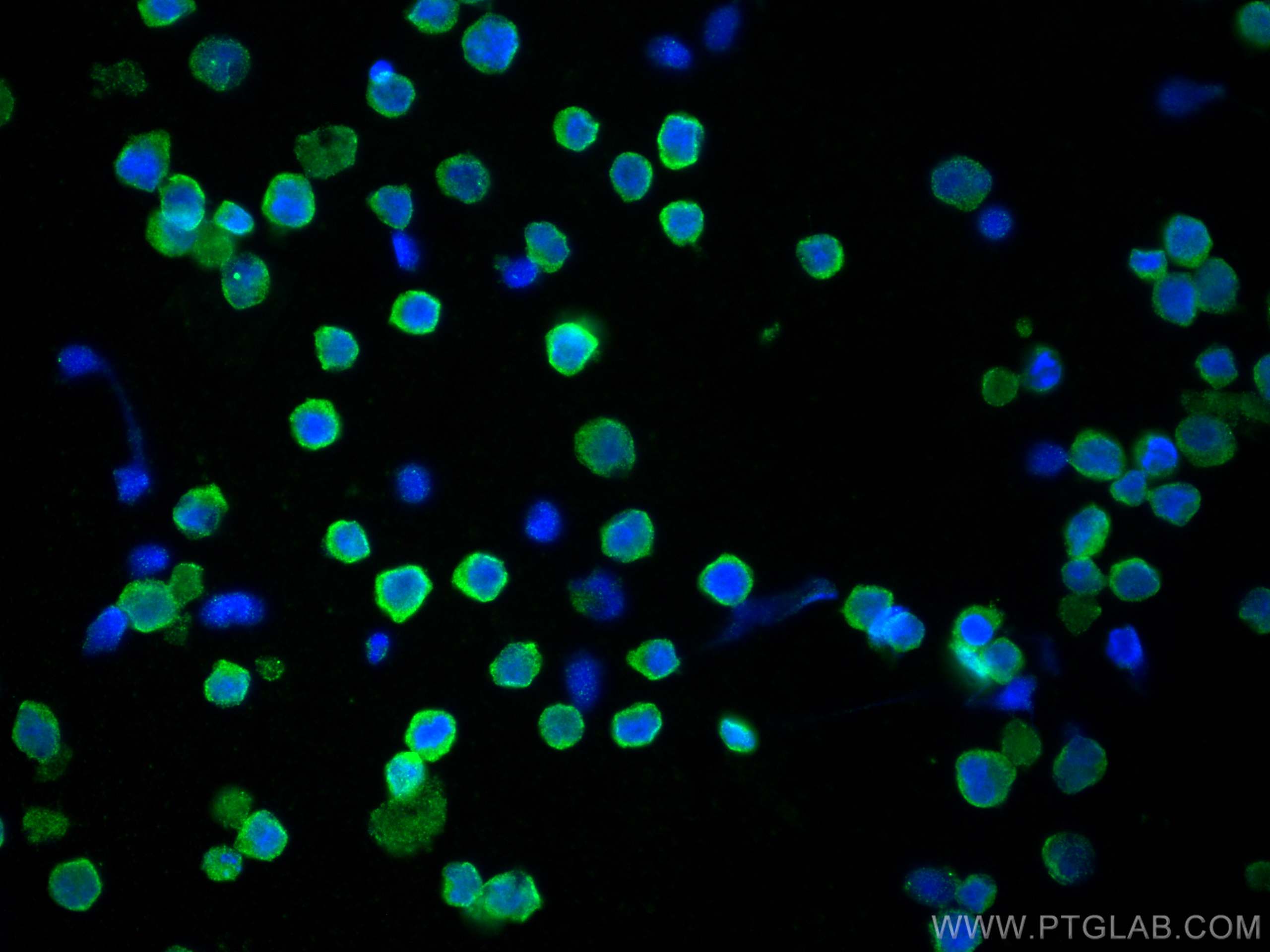
验证数据展示
产品信息
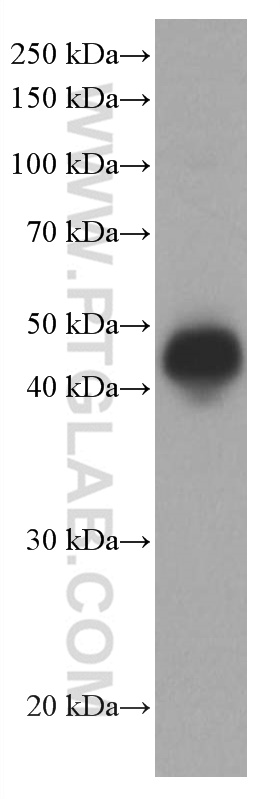
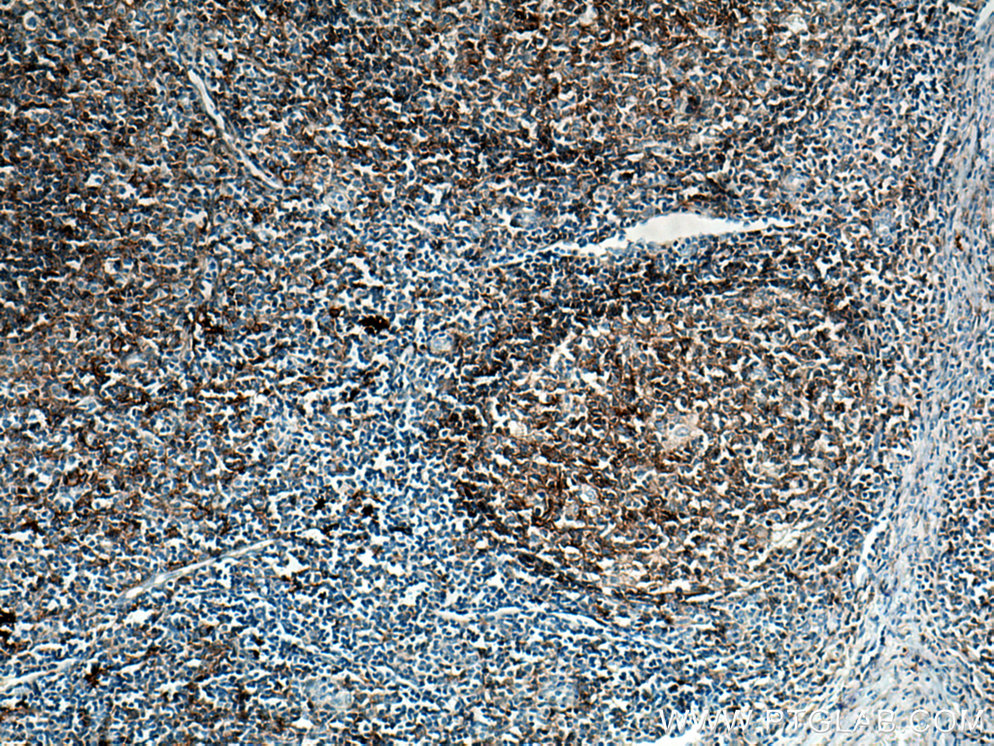
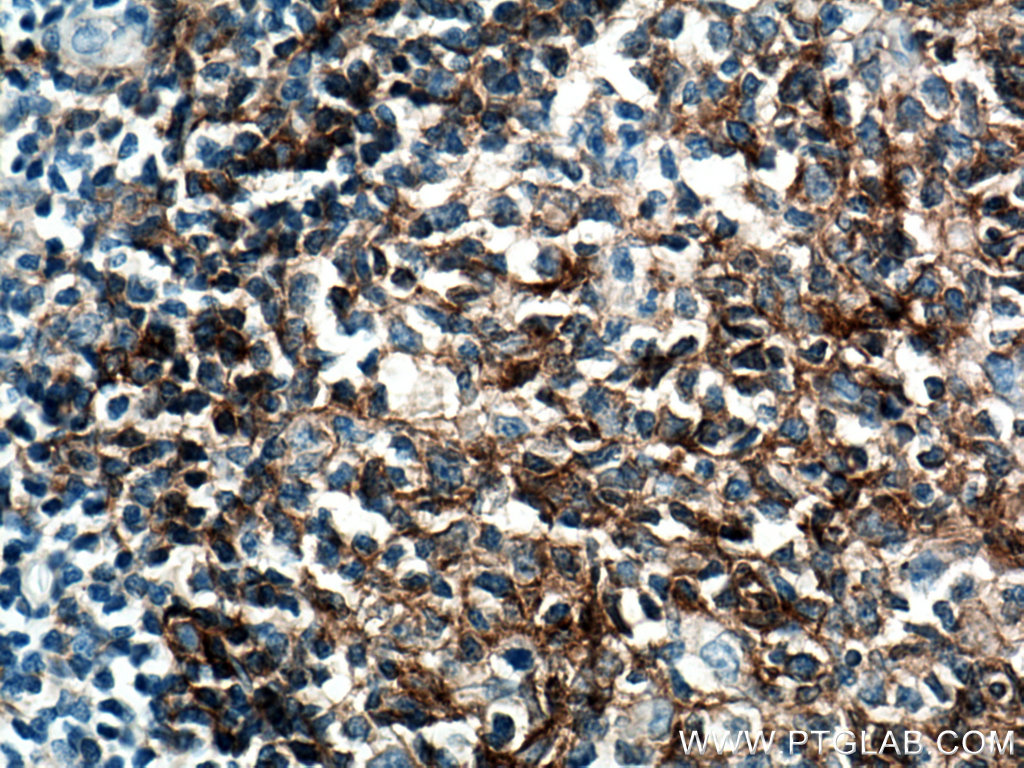
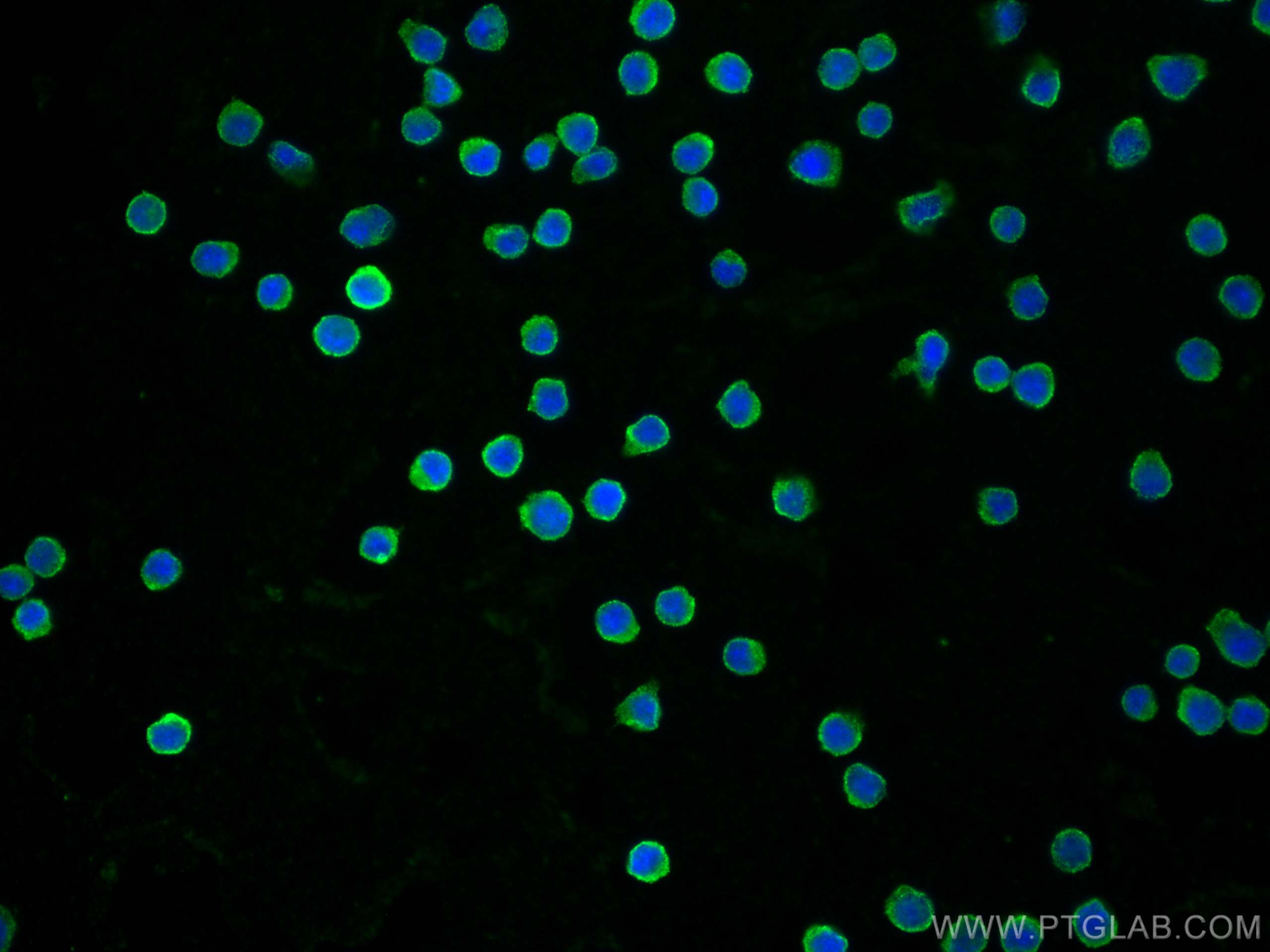
66965-1-PBS targets CD40 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 | CD40 fusion protein Ag28040 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG1 |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | CD40 molecule, TNF receptor superfamily member 5 |
| 别名 | p50, CD40L receptor, Bp50, B-cell surface antigen CD40, B cell surface antigen CD40 |
| 计算分子量 | 277 aa, 31 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 43 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC012419 |
| 基因名称 | CD40 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 958 |
| ENSEMBL Gene ID | ENSG00000101017 |
| RRID | AB_2882288 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P25942 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
Cluster of differentiation 40 (CD40) is a costimulatory protein located on antigen presenting cells and is required for their activation. CD40 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor (TNFR) family.
What is the molecular weight of CD40?
The molecular weight of CD40 is 43 kDa.
What is the cellular localization of CD40?
CD40 can be secreted by cells or found in the cell membrane.
What is the tissue specificity of CD40?
CD40 is expressed in B cells and primary carcinoma cells but is also found in dendritic cells and macrophages (PMID: 10209159).
What is the function of CD40?
CD40 acts as a receptor for TNFSF5/CD40LG, which is expressed on activated T cells. This interaction is essential for B cell proliferation, expression of activation markers, immunoglobulin production, and isotype switching (PMID: 8809473). This interaction is also crucial for the formation of memory B cells and germinal centers, and signaling through CD40 prevents apoptosis of germinal center B cells.
What is the role of CD40 in disease?
Defects in CD40 lead to hyper-IgM immunodeficiency syndrome type 3 (HIGM3) (PMID: 11675497). This is an autosomal recessive disorder that includes the inability of B cells to undergo isotype switching, a key step in the final differentiation of the humoral immune response, and an inability to mount an antibody-specific immune response.