产品信息
Cytochalasin B is a mycotoxin binding to the barbed end of actin filaments. It can disrupt the formation of actin polymers (Kd: 1.4-2.2 nM for F-actin).
|
CAS号
|
14930-96-2 |
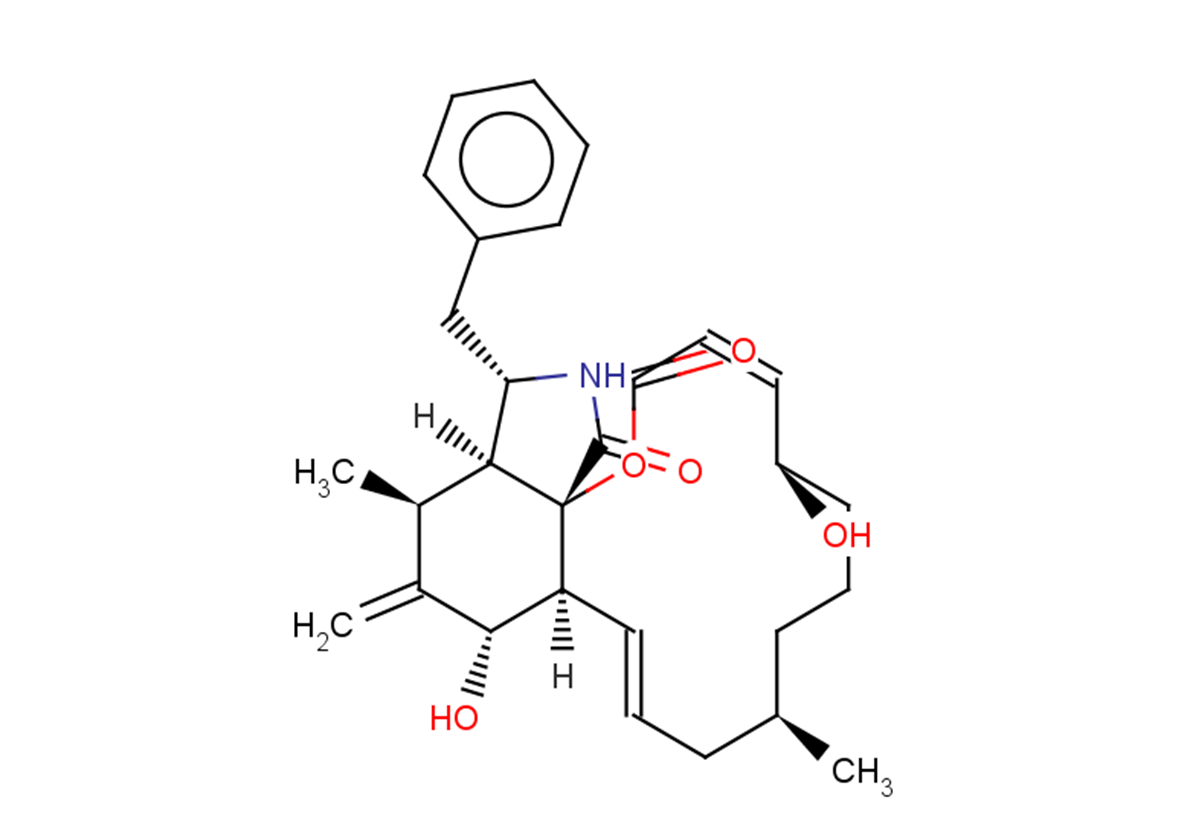
| 分子式 |
C29H37NO5 |
| 主要靶点 |
Arp2/3 Complex |
| 主要通路 |
细胞骨架 |
| 分子量 |
479.617 |
| 纯度 |
, 此纯度可做参考,具体纯度与批次有关系,可咨询客服 |
| 储存条件 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year |
| 别名 |
细胞松弛素 B|Phomin|细胞松弛素B |
靶点活性
F-actin (Mg2+):2.2 nM (Kd)|F-actin (Mg2+/K+):1.4 nM (Kd)
体内活性
Cytochalasin B (10, 25, 50 mg/kg, i.p.) dose-dependently increases the life expectancy of Balb/c mice bearing with P388/ADR leukemias. Cytochalasin B at 50 mg/kg produces 10 % long-term survival in the multidrug-resistant P388/ADR cohort, and 40 % long-term survival in the drug-sensitive P388/S cohort [3].
体外活性
Cytochalasin B is a cell-permeable mycotoxin binding to the barbed end of actin filaments, inhibits the enlongation and shortening of actin filaments, with Kds of 2.2 nM and 1.4 nM for F-actin in the presence of MgCl2 (2 mM) or MgCl2 (2 mM) plus KCl, respectively [1]. Cytochalasin B (6 μM) increases the myofibrillar fragmentation index, which is attributed to the intensely breaking of myofibrillar proteins into short segments. Cytochalasin B also accelerates the disruption of actin filaments. In addition, Cytochalasin B accelerates the transformation from F-actin to G-actin, lowering the content of F-actin and significantly increasing G-actin bands during postmortem conditioning [2]. Cytochalasin B (0.1-10 μM) shows inhibitory effect on multiple murine cancer cell lines, with IC50s of 2.56 μM (M109c), 10.46 μM (B16BL6), 105.5 μM (P388/ADR), 51.9 μM (P388/S) and IC80s of 12.23 μM (M109c), 44.86 μM (B16BL6), 188.4 μM (P388/ADR), 84.1 μM (P388/S) after treatment for 3 h, with IC50s of 0.25 μM (M109c), 0.37 μM (B16F10), 0.87 μM (B16BL6), and IC80s of 0.75 μM (M109c), 1.21 μM (B16F10) after treatment for 4 days [3].
溶解度
DMSO:20 mg/mL (41.7 mM),Ethanol:20 mg/mL (41.7 mM)
细胞实验
The attached cell lines M109c, B16BL6, and B16F10 are seeded at 1 to 4?×?10^4 cells/mL in 2 mL volumes in 24-well culture plates 1 day prior to treatment with Cytochalasin B. The suspension culture of P388/ADR cells is seeded at 5?×?10^4 cells/mL and allowed to grow overnight before Cytochalasin B treatment. Cells are treated with Cytochalasin B for 3 h, as well as 2, 3, or 4 days. In the case of continuous exposure for 2, 3, or 4 days, attached cells are trypsinized and counted with a hemacytometer. Leukemia cell suspensions are counted with a Coulter Counter. In the case of short-term exposure, cells are washed twice with fresh medium, then trypsinized (except for P388/ADR cells), reseeded, and allowed to regrow for 3 days, at which time they are counted. Growth results are calculated as the number of cells generated above the seeding density compared to the untreated control cells and graphically presented as a percent of control increase [3].
动物实验
For chemotherapy testing, Balb/c mice under isoflurane anesthesia are challenged with 2?×?10^5 trypan blue negative P388/S or P388/ADR cells subcutaneously (s.c.) in a volume of 200 μL. Untreated mice are kept in order to determine the lethality of the challenge without chemotherapeutic intervention. Long-term survival is defined as challenged mice that survive the duration of the observation period. Cytochalasins B and D are prepared in suspension form in 2 % carboxymethyl cellulose 1 % tween 20 (CMC/Tw) for intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration. The congeners or the vehicle are administered to leukemia-challenged mice on Days 1-8 following the initial challenge [2].