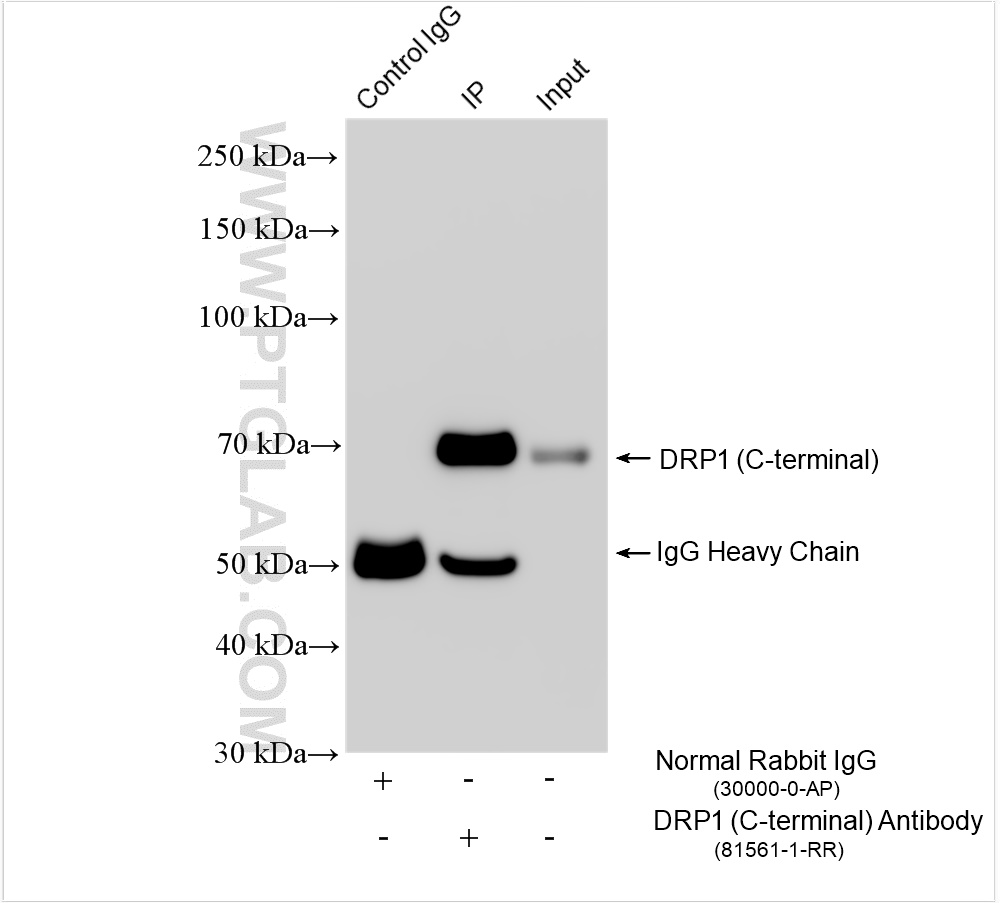
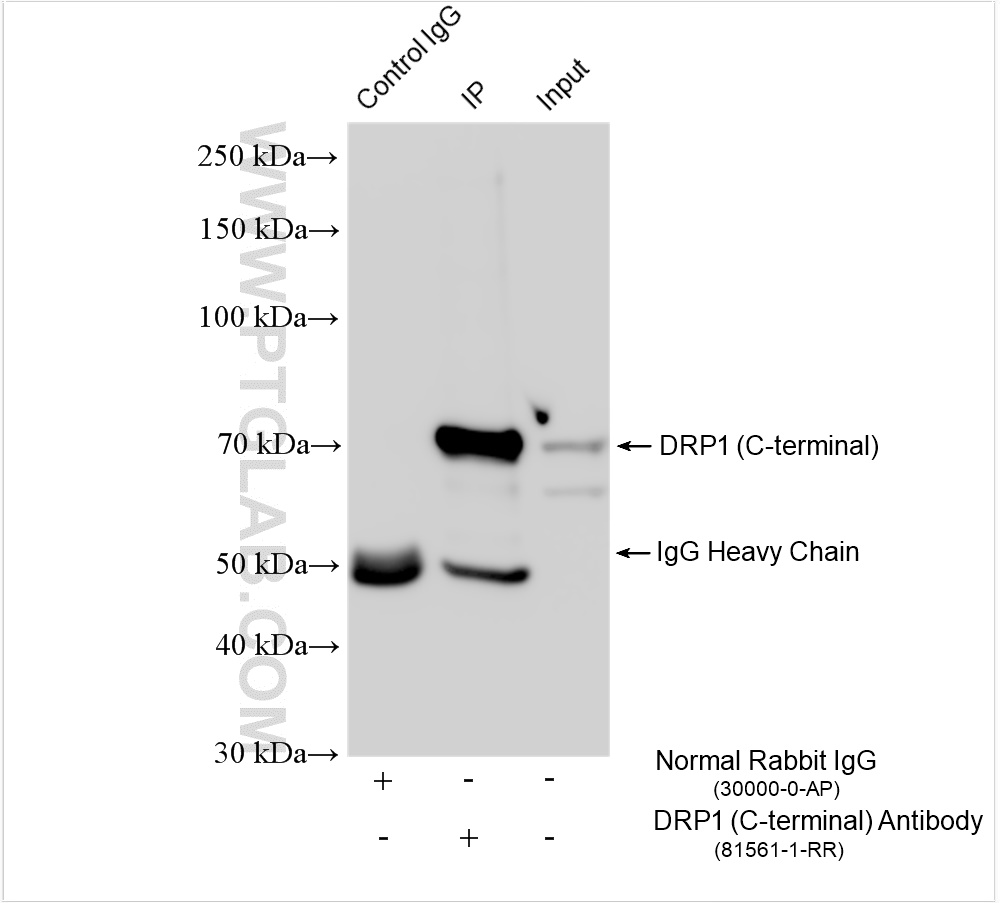
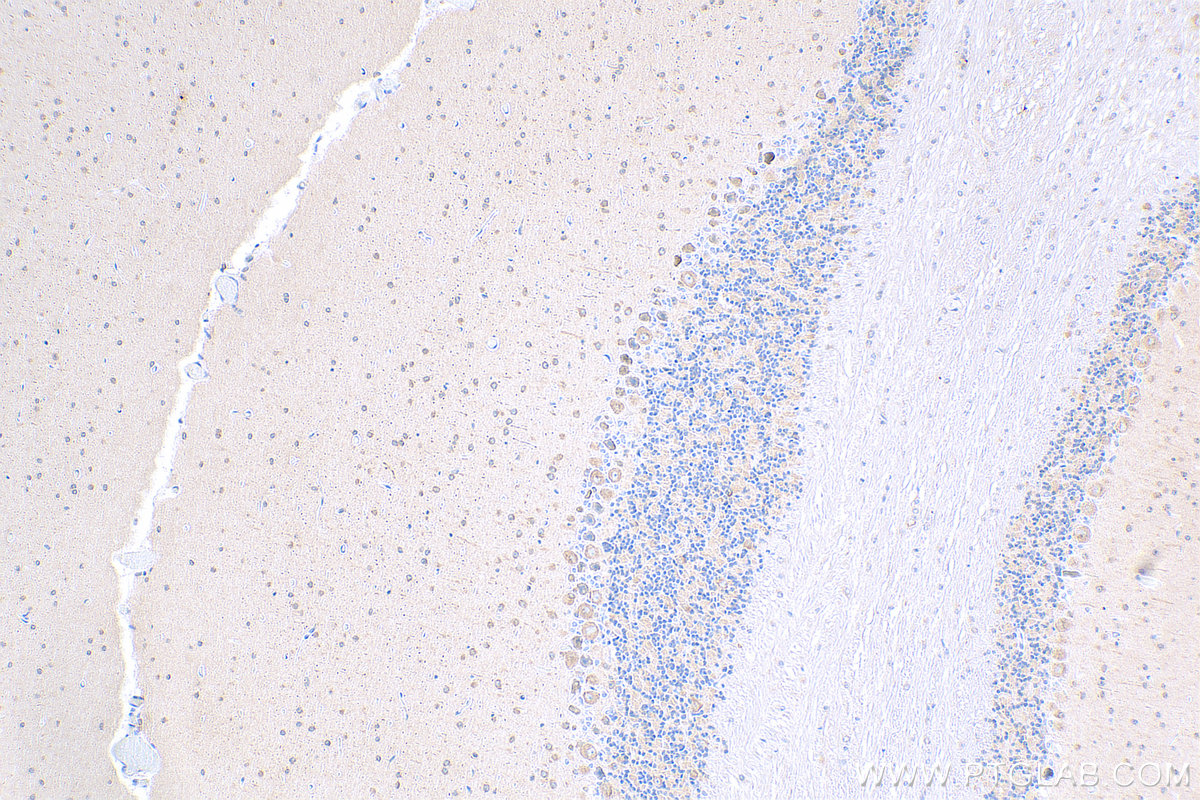
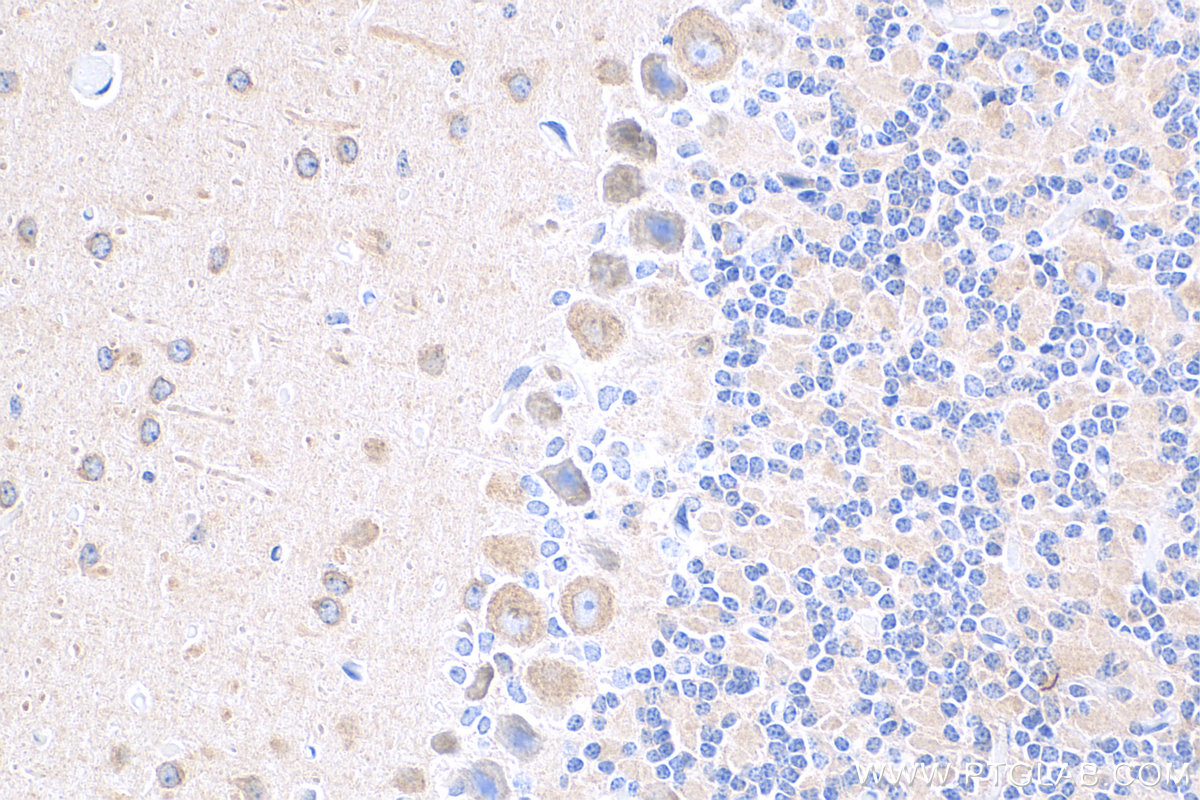
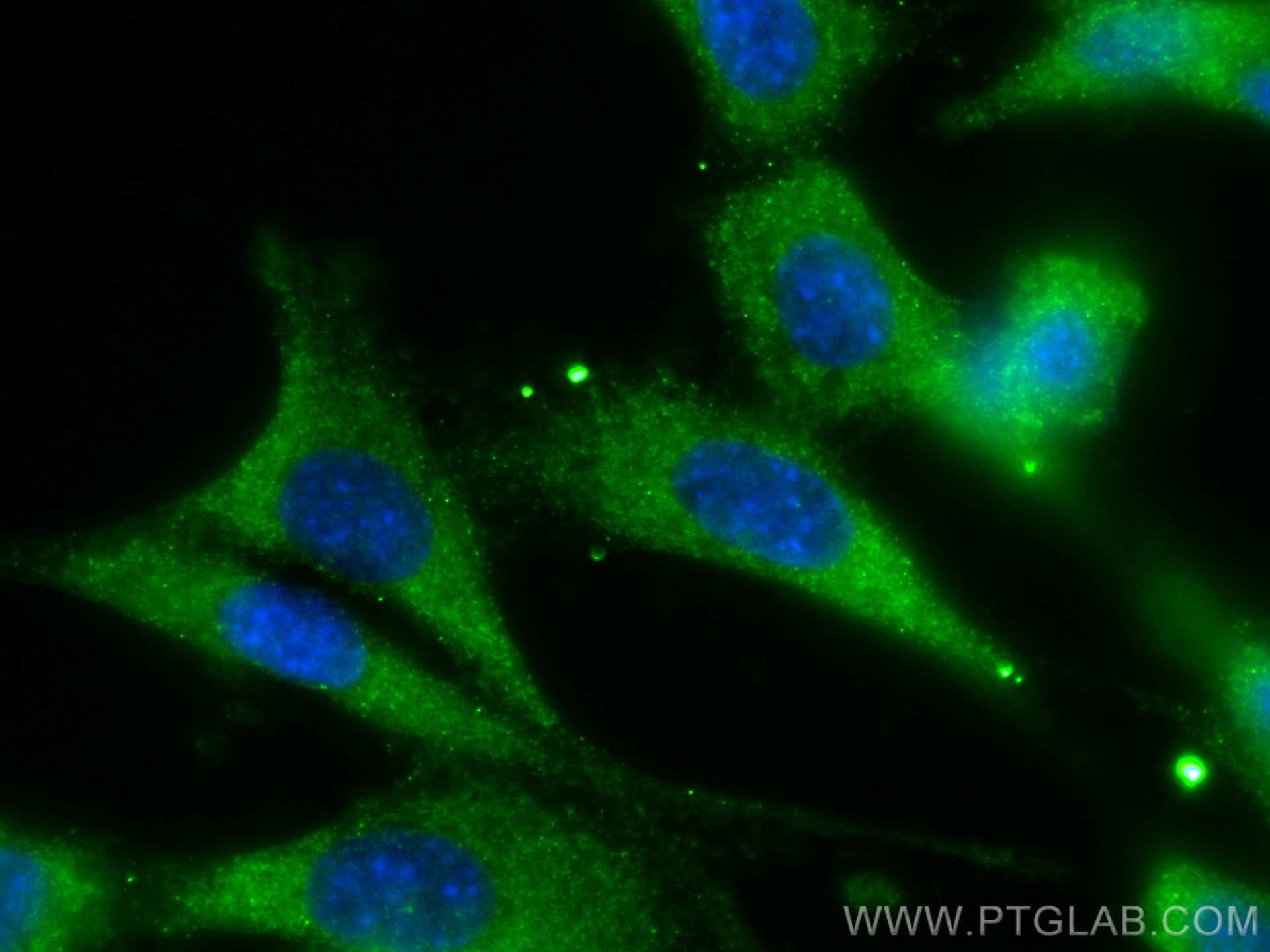
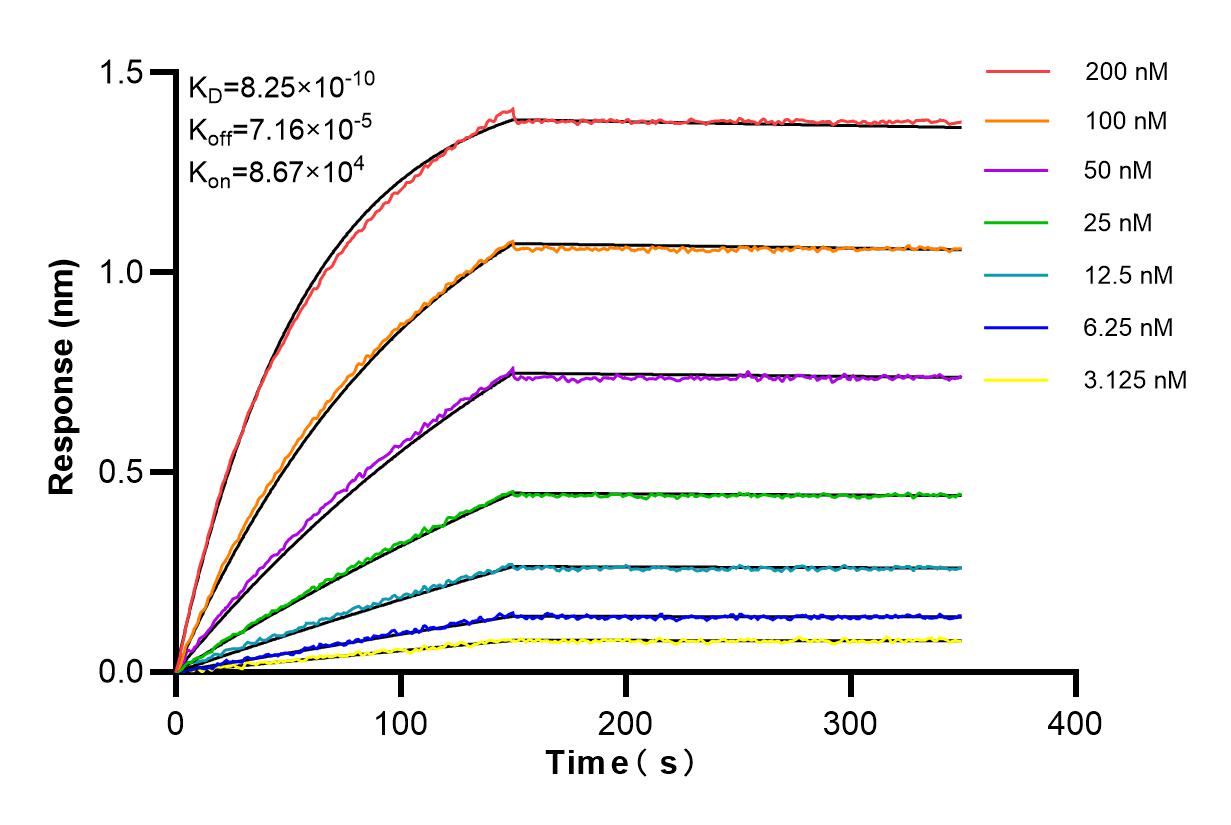
验证数据展示
产品信息
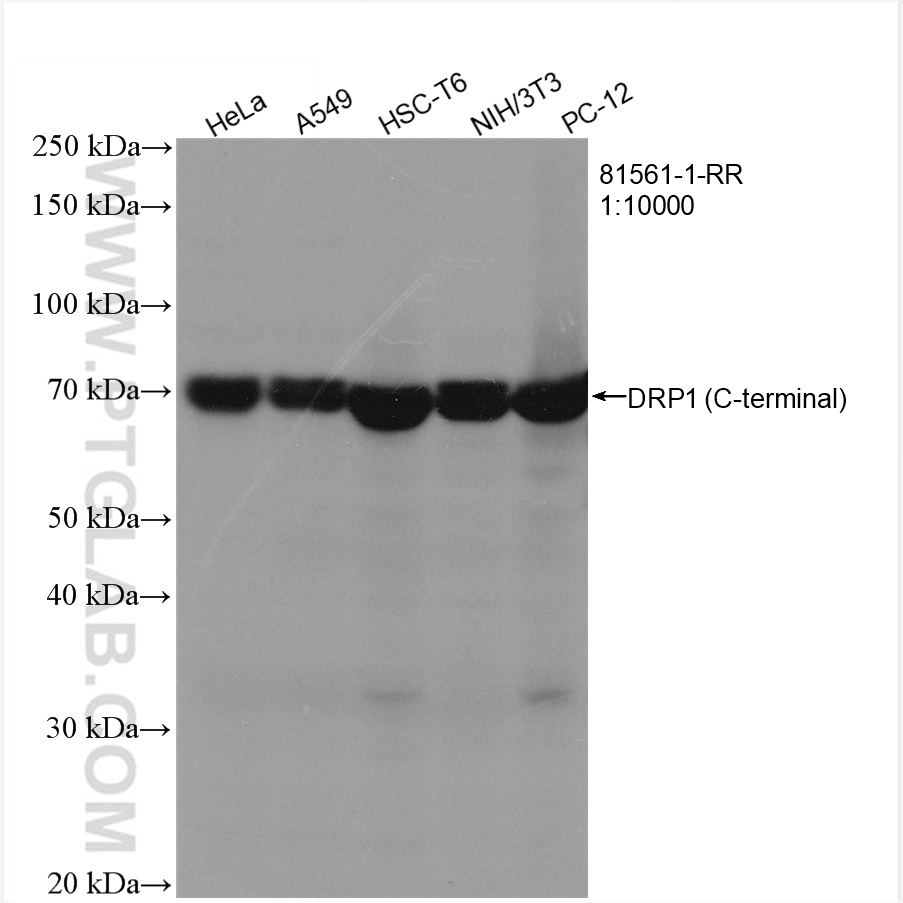
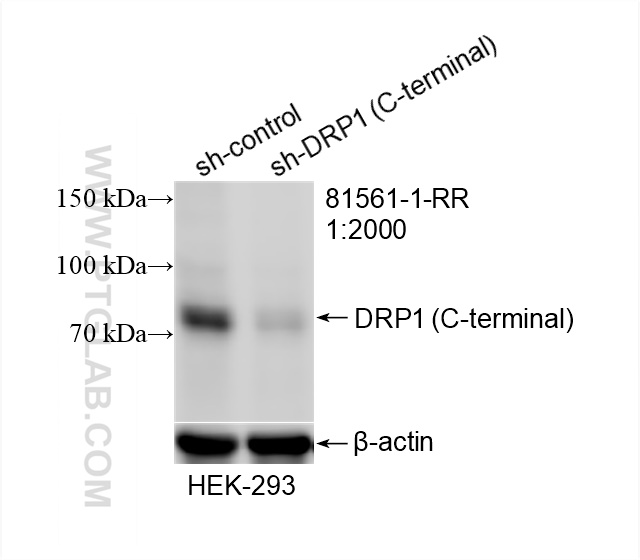
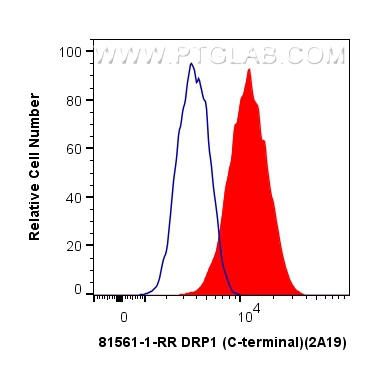
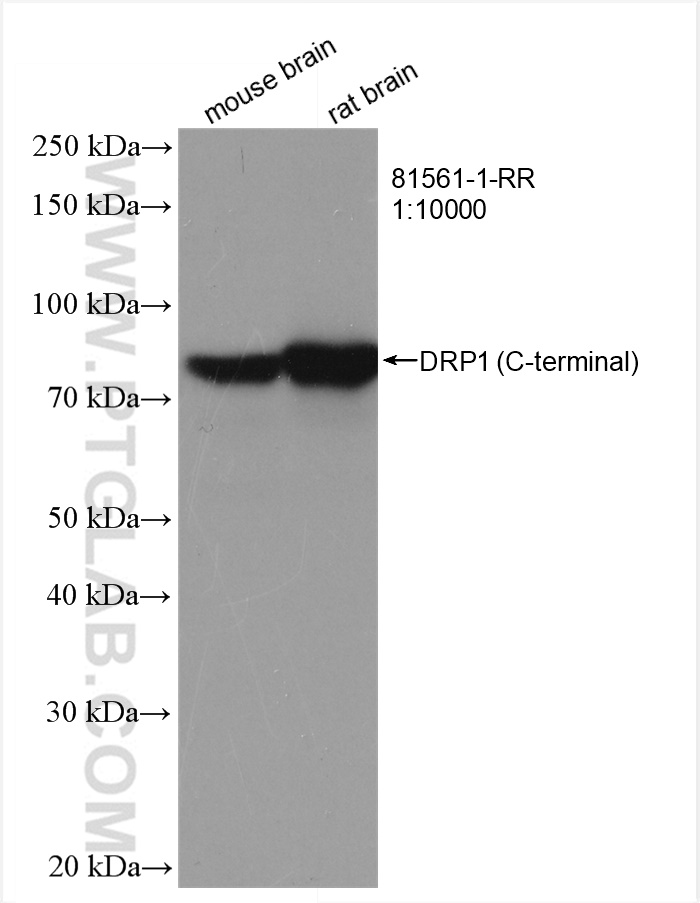
81561-1-PBS targets DRP1 (C-terminal) in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag3644 Product name: Recombinant human DNM1L,DLP1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 361-711 aa of BC024590 Sequence: CGGARICYIFHETFGRTLESVDPLGGLNTIDILTAIRNATGPRPALFVPEVSFELLVKRQIKRLEEPSLRCVELVHEEMQRIIQHCSNYSTQELLRFPKLHDAIVEVVTCLLRKRLPVTNEMVHNLVAIELAYINTKHPDFADACGLMNNNIEEQRRNRLARELPSAVSRDKLIQDSRRETKNVASGGGGVGDGVQEPTTGNWRGMLKTSKAEELLAEEKSKPIPIMPASPQKGHAVNLLDVPVPVARKLSAREQRDCEVIERLIKSYFLIVRKNIQDSVPKAVMHFLVNHVKDTLQSELVGQLYKSSLLDDLLTESEDMAQRRKEAADMLKALQGASQIIAEIRETHLW 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Recombinant |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | dynamin 1-like |
| 别名 | DRP1, 2A19, DLP1, DNM1L, DNM1L,DLP1 |
| 计算分子量 | 736 aa, 82 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 70-80 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC024590 |
| 基因名称 | DRP1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10059 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O00429 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
DNM1L(Dynamin-1-like protein) , also known as dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1), belongs to the dynamin family of large GTPases that mediate membrane remodeling during a variety of cellular processes. DNM1L has an important role in the division of growing mitochondria and peroxisomes and also mediates outer mitochondrial membrane fission in mammalian cells. DNM1L is ubiquitously expressed with abundant expression in skeletal muscle, heart, kidney and brain.Variable isoforms of DNM1L have been reported in a tissue-specific manner due to the alternative splicing.