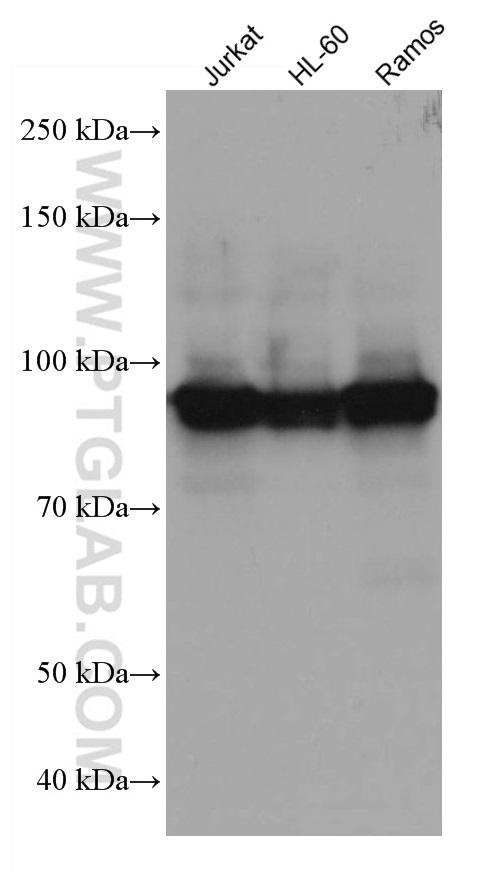
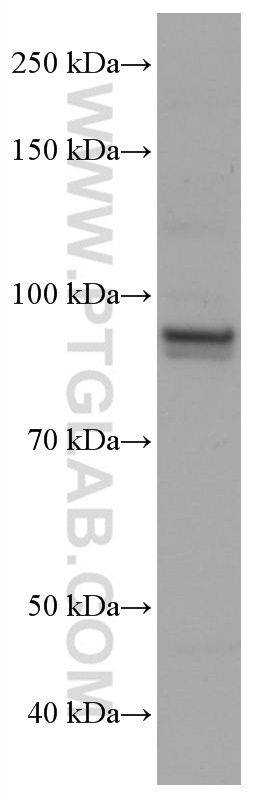
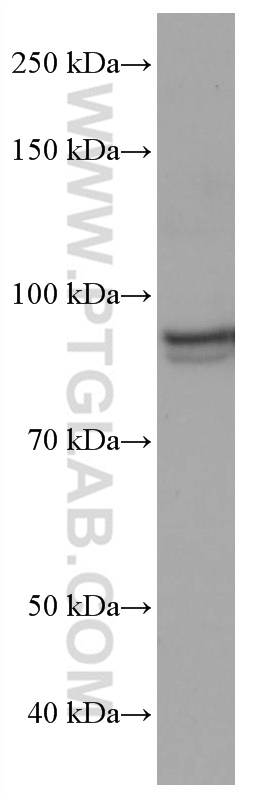
验证数据展示
产品信息
67138-1-PBS targets ELF1 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | Human |
| 免疫原 | ELF1 fusion protein Ag14689 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG1 |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | E74-like factor 1 (ets domain transcription factor) |
| 别名 | E74 like factor 1, ELF1 |
| 计算分子量 | 619 aa, 67 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 93-97 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC030507 |
| 基因名称 | ELF1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1997 |
| RRID | AB_2882437 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P32519 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
ELF1, also named as ETS-related transcription factor Elf-1, is originally cloned from a human T-cell cDNA library by hybridization with a probe encoding the DNA binding domain (ETS domain) of the human Ets-1 cDNA. Based on its preferential expression in embryonic lymphoid organs (thymus and spleen), a wide variety of epithelial cells and fetal liver as well as in adult haematopoietic tissues, including thymus, spleen and bone marrow, Elf-1 emerged as a potential key regulator of haematopoietic gene expression. Consistent with this notion, Elf-1 has been shown to be a direct upstream regulator of genes important for haematopoiesis such as Scl, Fli-1, Lyl-1, Runx1 and Lmo2 . Elf-1 has also been shown to be important for blood vessel development, a process that is closely linked to early haematopoiesis during embryonic development. Elf-1 has been reported to take part in the transcriptional control of major regulators of blood vessel development such as Tie1, Tie2, angiopoietin-2, the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR1), the endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS) and endoglin . Functional activity of Ets proteins is modulated at multiple levels. It is known that ELF-1 appears in the cytoplasm as a 80 KDa protein that is O -glycosylated and phosphorylated in order to be translocated into the nucleus where it can be detected as a 98 KDa protein. After dephosphorylation, the protein is degraded through the proteasome pathway. The inactive form of Elf-1 is an 80-kDa protein that lacks DNA-binding activity and is confined to the cytoplasm of the cell. Phosphorylation and O-linked glycosylation increase the molecular weight of Elf-1 to 98 kDa, the active form; 98 kDa Elf-1 binds to the promoter of the gene that codes for CD3ζ inducing its transcription.