验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
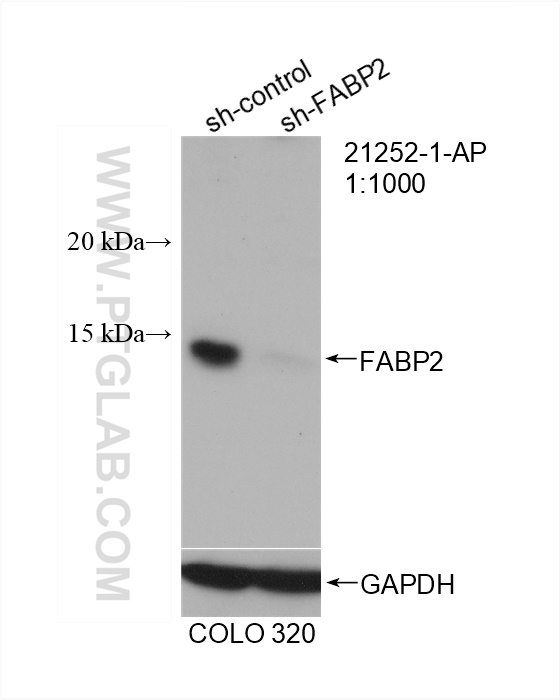
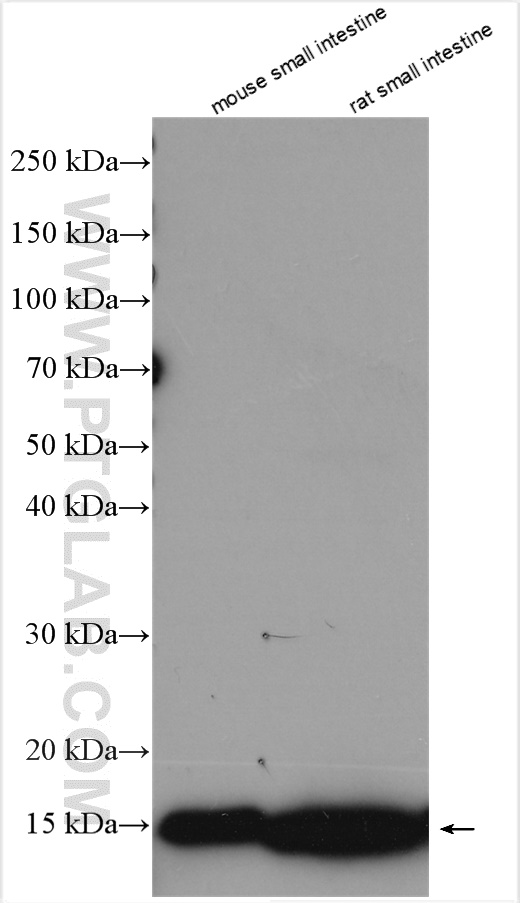
| Positive WB detected in | COLO 320 cells, mouse small intestine tissue, rat small intestine tissue |
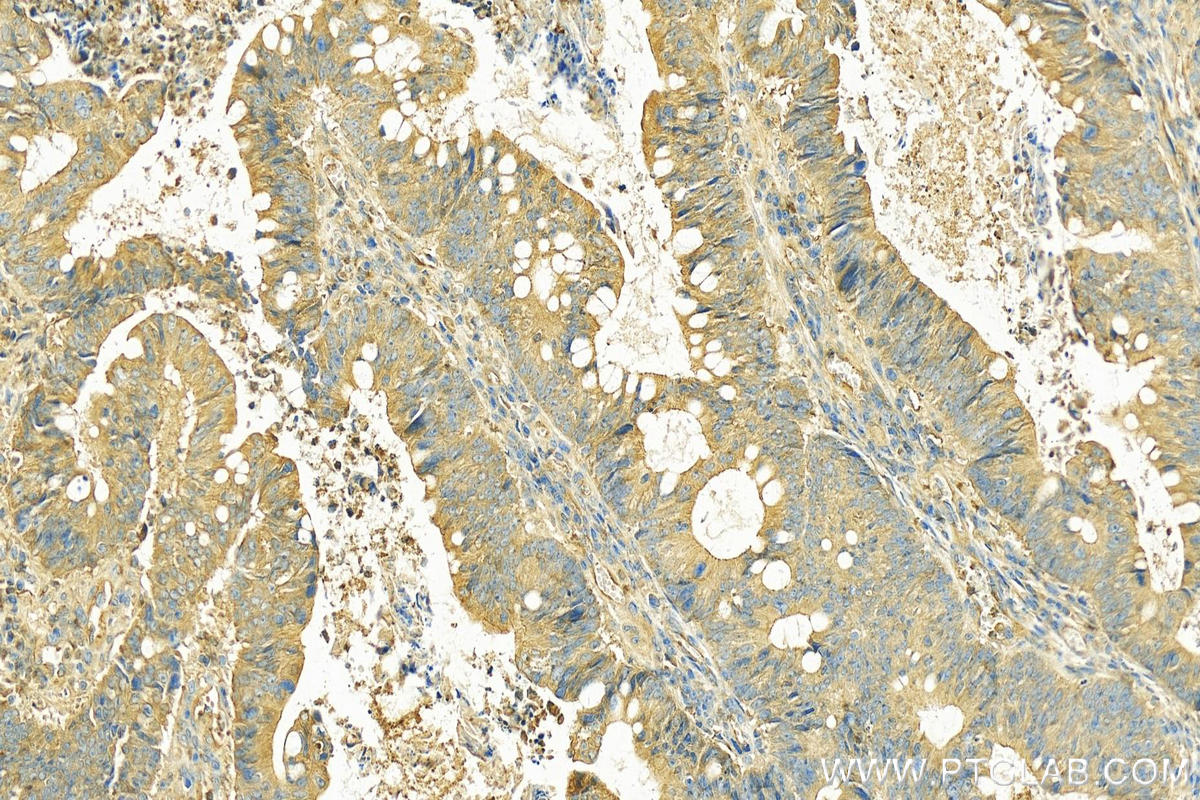
| Positive IHC detected in | human stomach cancer tissue, human colon cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
发表文章中的应用
| WB | See 16 publications below |
产品信息
21252-1-AP targets FABP2 in WB, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, ELISA Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | WB |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat |
| 文献引用反应性 | mouse, rat, pig, chicken |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag15793 Product name: Recombinant human FABP2 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-132 aa of BC069617 Sequence: MAFDSTWKVDRSENYDKFMEKMGVNIVKRKLAAHDNLKLTITQEGNKFTVKESSAFRNIEVVFELGVTFNYNLADGTELRGTWSLEGNKLIGKFKRTDNGNELNTVREIIGDELVQTYVYEGVEAKRIFKKD 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | fatty acid binding protein 2, intestinal |
| 别名 | Intestinal-type fatty acid-binding protein, I-FABP, Fatty acid-binding protein, intestinal, Fatty acid-binding protein 2, Fatty acid binding protein 2 |
| 计算分子量 | 132 aa, 15 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 15 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC069617 |
| 基因名称 | FABP2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2169 |
| RRID | AB_10734425 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P12104 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
FABP2, also known as Intestinal Fatty Acid Binding Protein (I-FABP), is a member of the Fatty Acid Binding Proteins (FABPs) family. The cytoplasmic content of FABP2 could be delivered into the systematic circulation once the death of enterocyte happens, thus the elevated FABP2 concentration in the blood has been shown in many human intestinal diseases. FABP2 is a water soluble cytosolic protein with a small molecular weight of 14-15 kDa, and it is initially located in the mature enterocytes of the small intestine (PMID: 26547205).
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for FABP2 antibody 21252-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for FABP2 antibody 21252-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Metab AIDA Selectively Mediates Downregulation of Fat Synthesis Enzymes by ERAD to Retard Intestinal Fat Absorption and Prevent Obesity. | ||
Adv Sci (Weinh) Wogonin Attenuates Atherosclerosis via KLF11-Mediated Suppression of PPARα-YAP1-Driven Glycolysis and Enhancement of ABCA1/G1-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux | ||
Biomaterials MMP-12 siRNA improves the homeostasis of the small intestine and metabolic dysfunction in high-fat diet feeding-induced obese mice. | ||
Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol FACI Is a Novel CREB-H-Induced Protein That Inhibits Intestinal Lipid Absorption and Reverses Diet-Induced Obesity. | ||
Int J Mol Sci INT-767-A Dual Farnesoid-X Receptor (FXR) and Takeda G Protein-Coupled Receptor-5 (TGR5) Agonist Improves Survival in Rats and Attenuates Intestinal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury | ||
Microb Biotechnol Faecal microbiota transplantation-mediated jejunal microbiota changes halt high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice via retarding intestinal fat absorption |