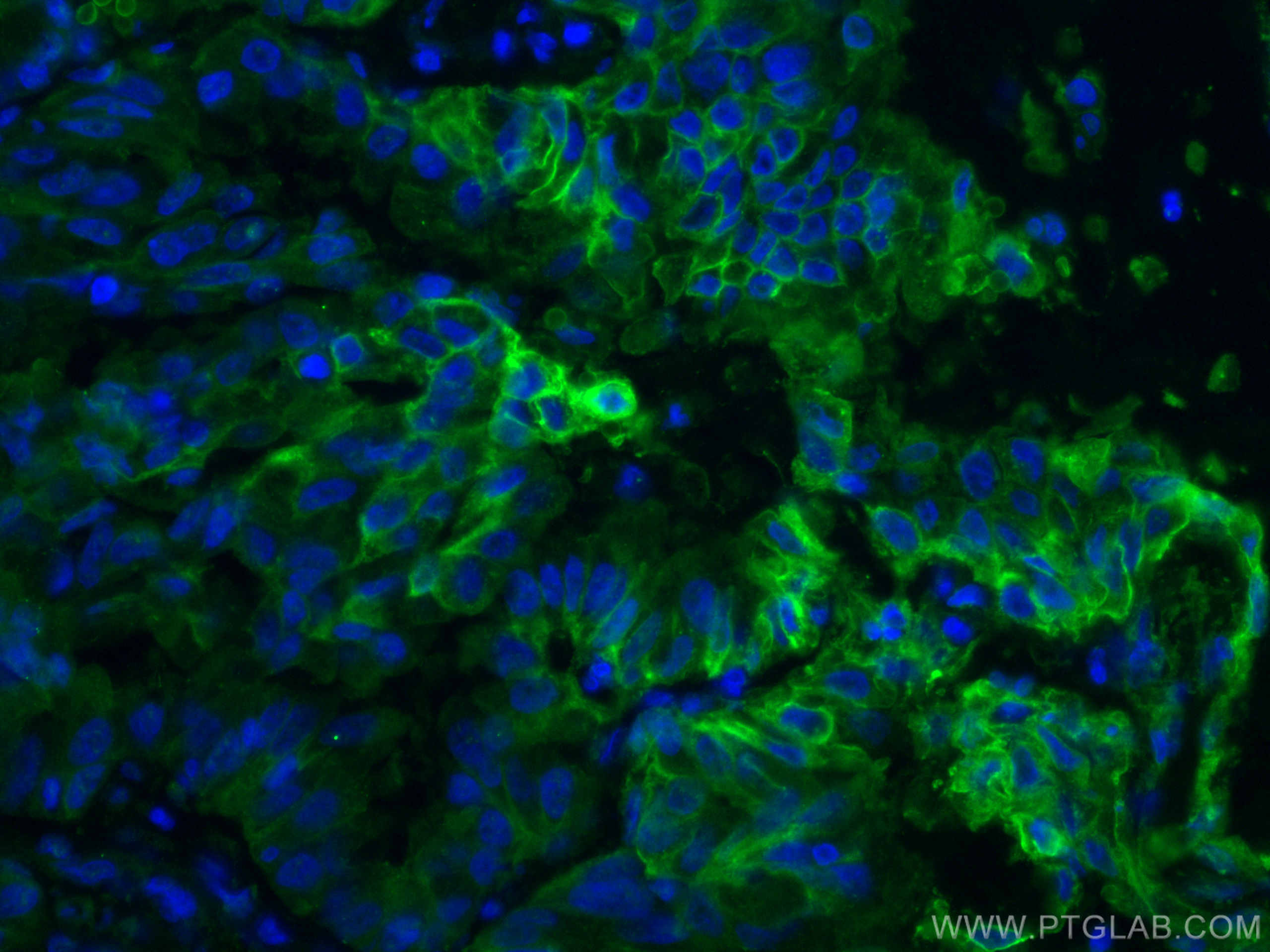
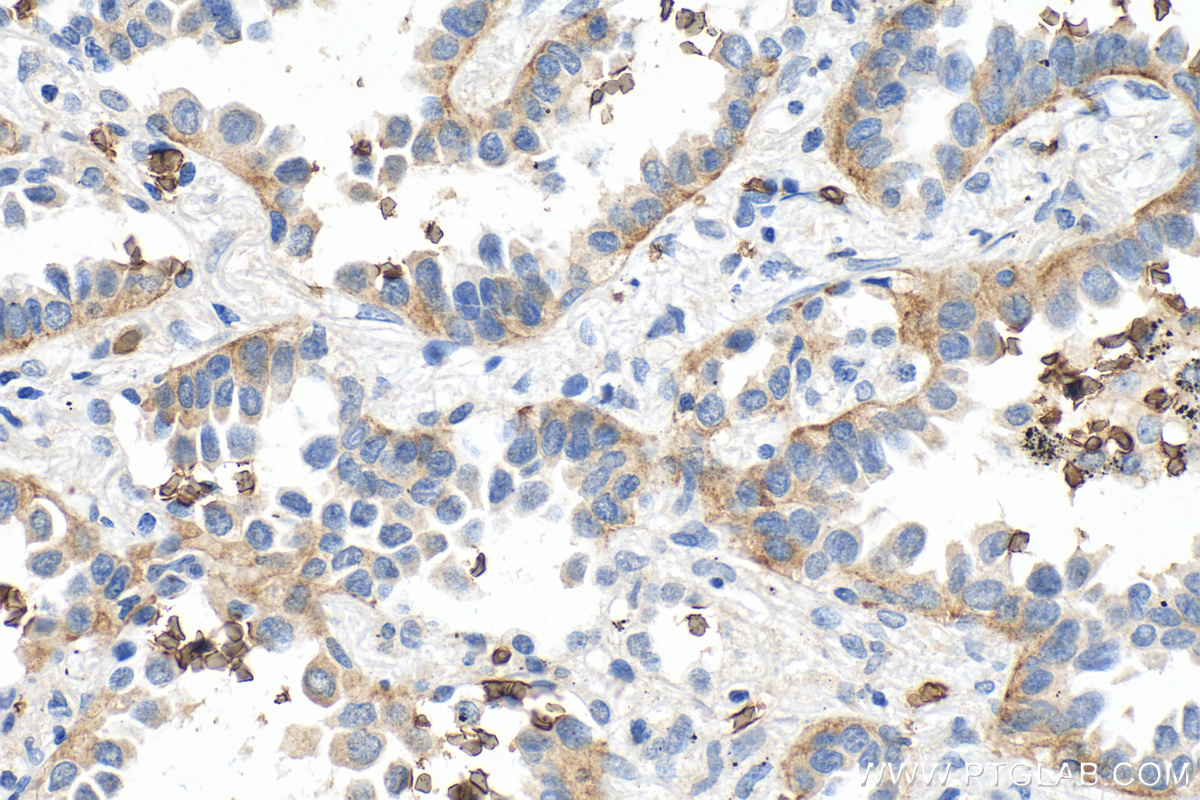
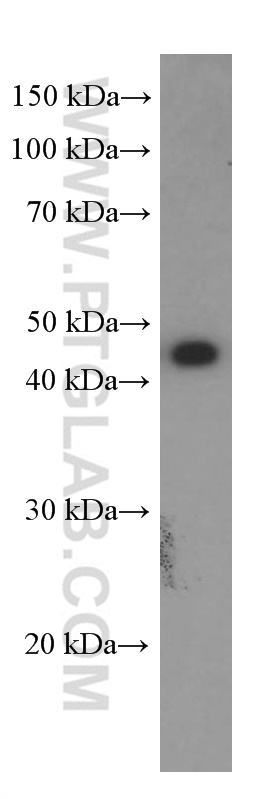
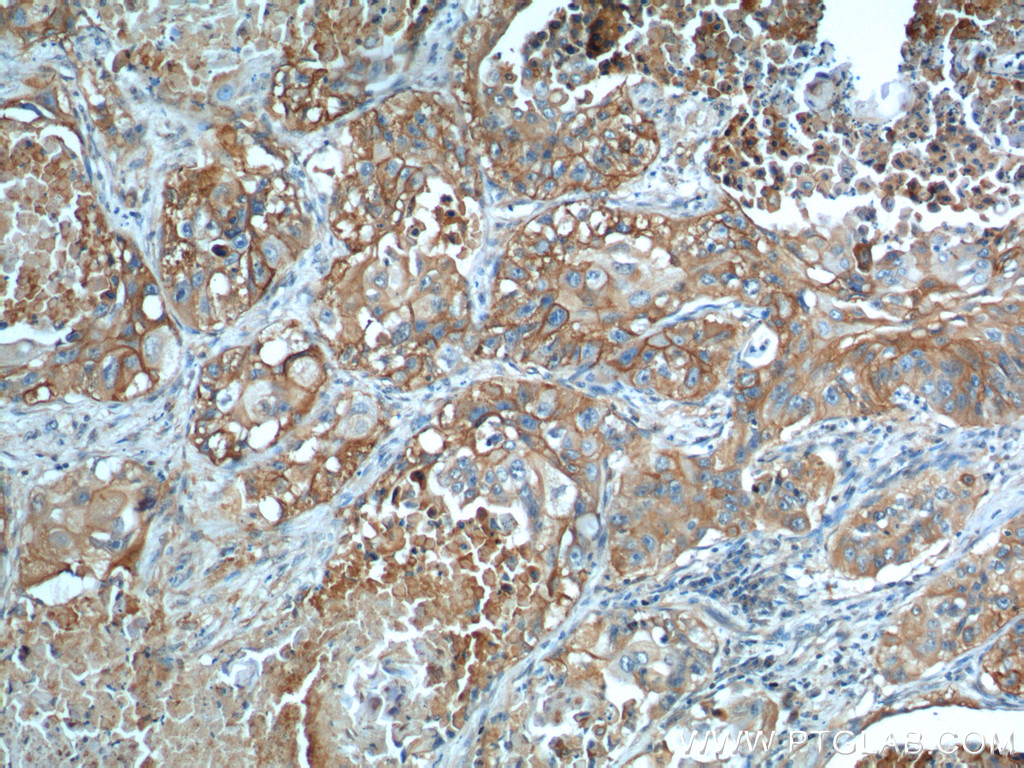
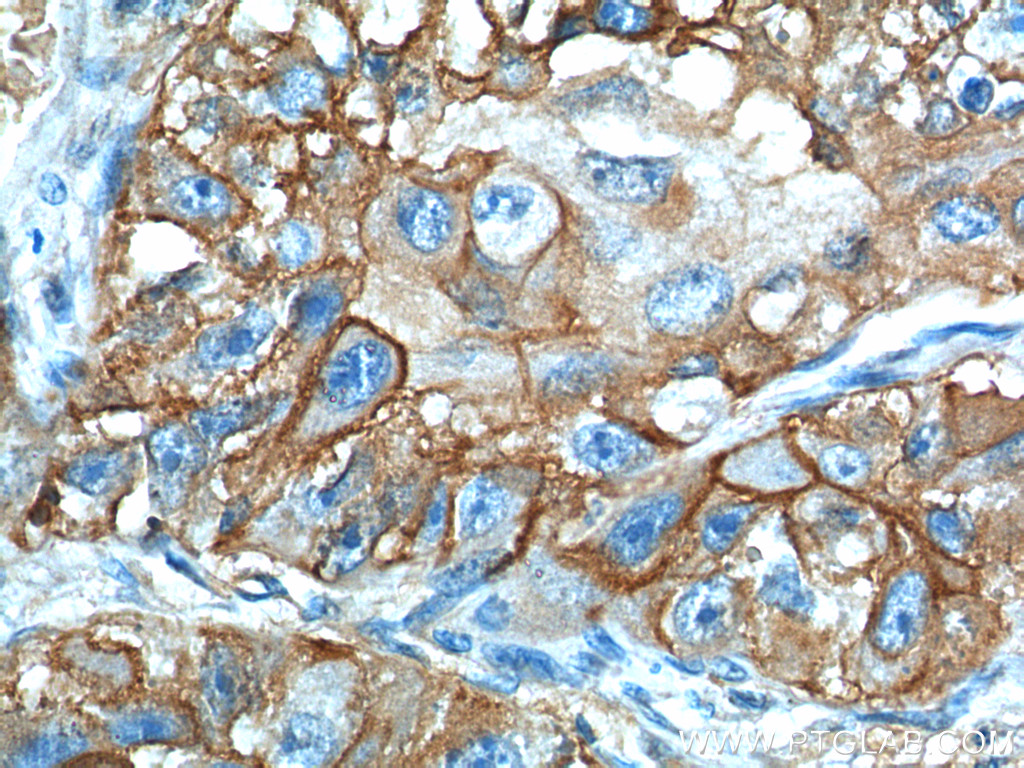
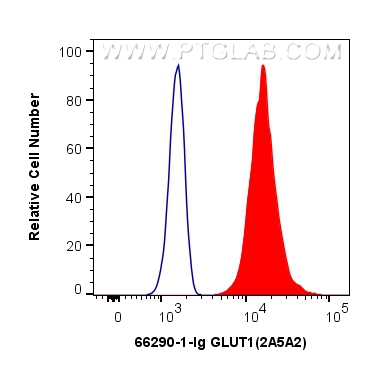
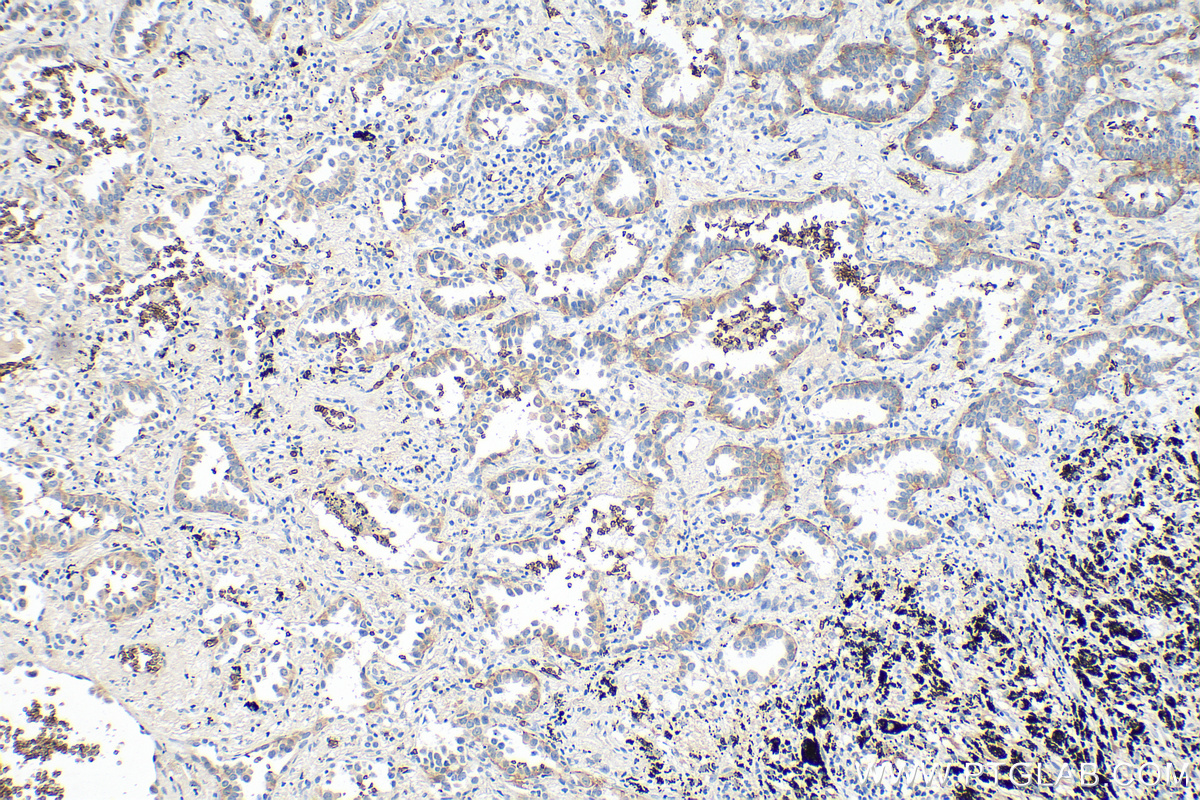
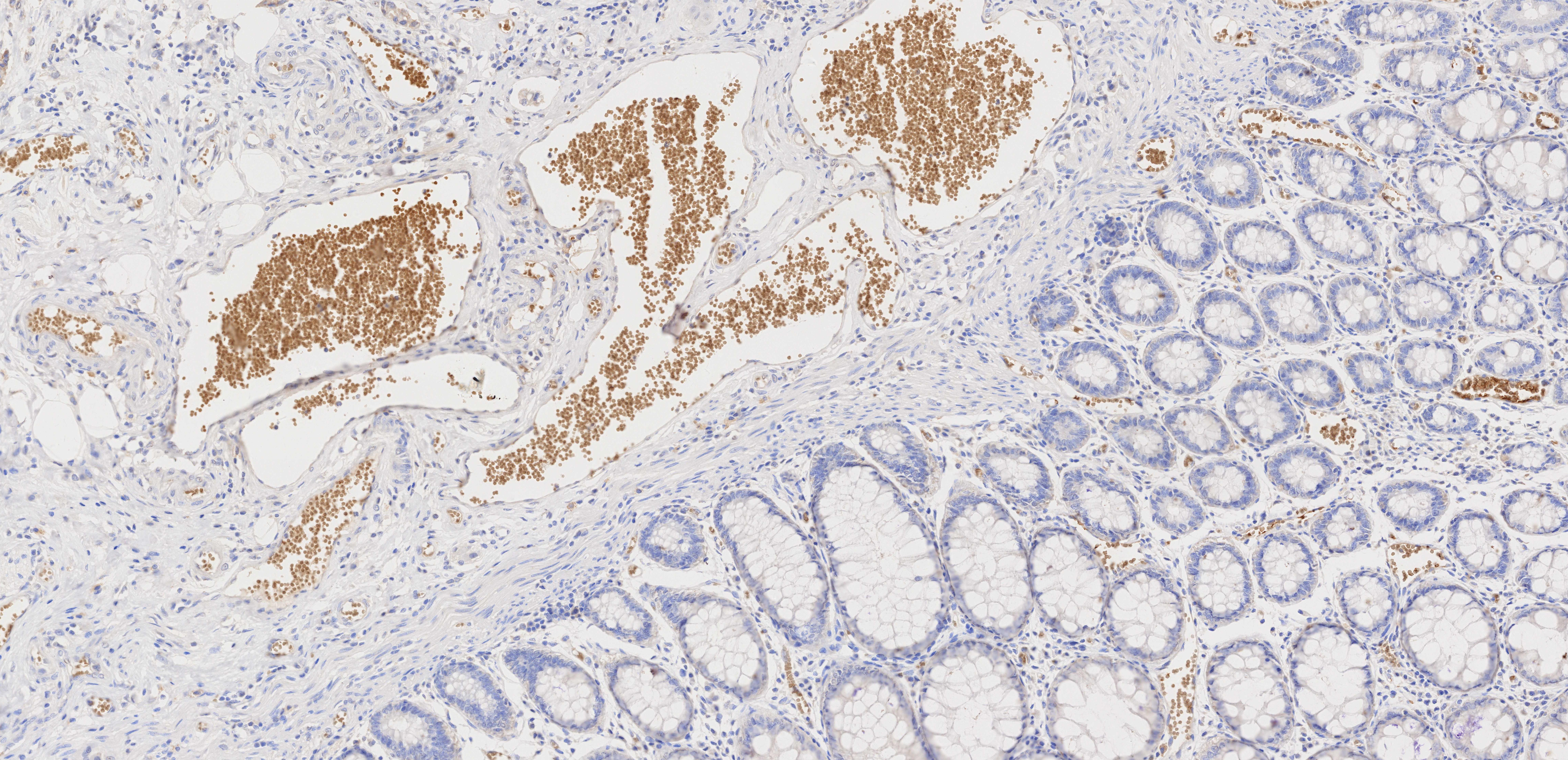
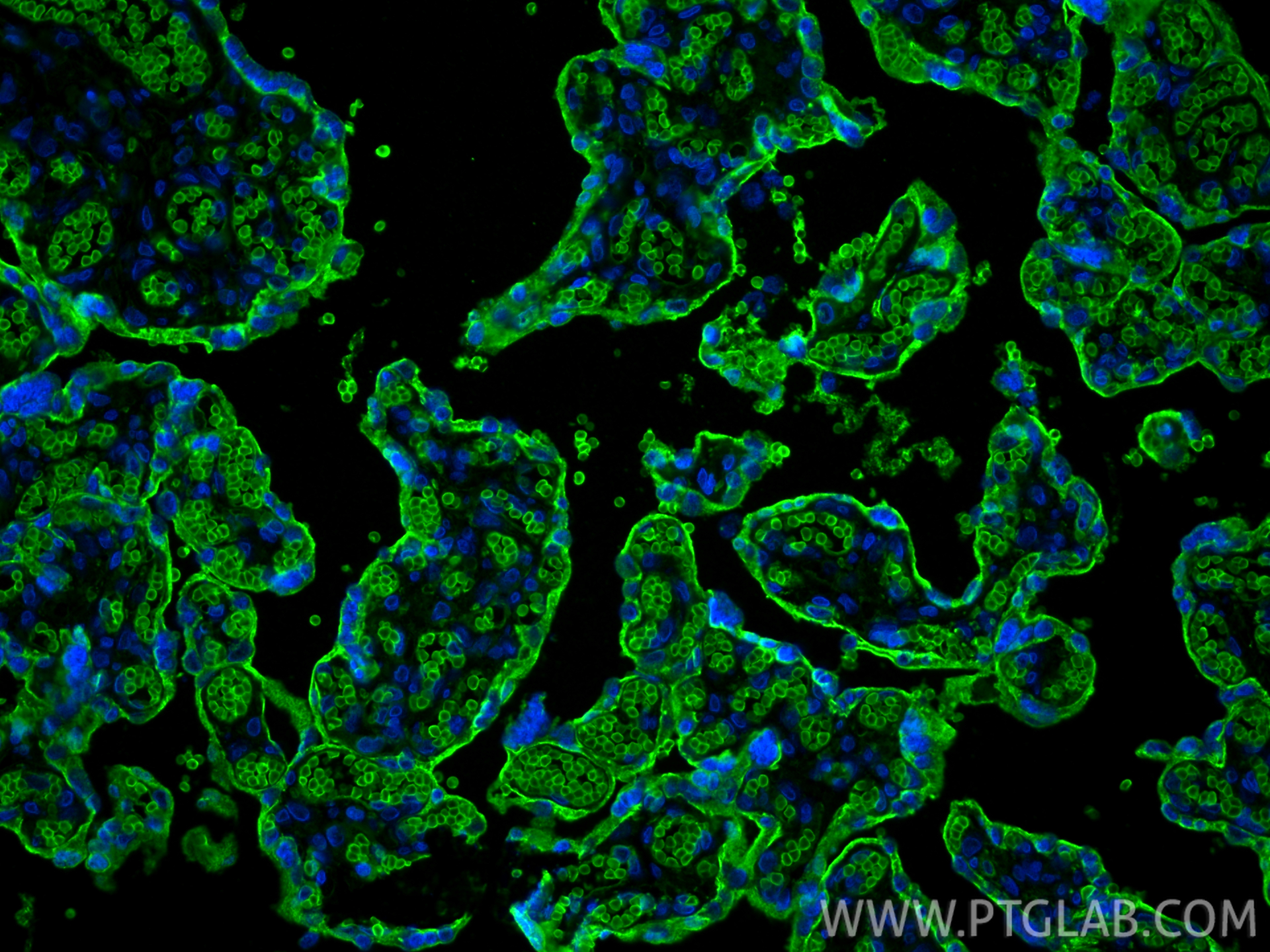
验证数据展示
产品信息
66290-1-PBS targets GLUT1 in WB, IHC, IF-P, FC (Intra), ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF-P, FC (Intra), ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag17108 Product name: Recombinant human SLC2A1,GLUT1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 216-280 aa of BC121804 Sequence: INRNEENRAKSVLKKLRGTADVTHDLQEMKEESRQMMREKKVTILELFRSPAYRQPILIAVVLQL 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG1 |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 1 |
| 别名 | SLC2A1, 2A5A2, GLUT-1, SLC2A1,GLUT1 |
| 计算分子量 | 492 aa, 54 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 45-55 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC121804 |
| 基因名称 | GLUT1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6513 |
| RRID | AB_2881673 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P11166 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (SLC2A1), is a uniporter protein responsible for the transport of glucose in many cell types and across the blood-brain barrier.
What is the molecular weight of GLUT1? Is GLUT1 post-translationally modified?
There are two forms of GLUT1 transporter that differ in their molecular weight. The 45-kDa form is found in glial cells, while the 55-kDa form is present in the endothelial cells regulating glucose transport over the blood-brain and blood-tissue barriers (PMID: 9630522). N-glycosylation of asparagine at position 42 is the only known post-translation modification of GLUT1 (PMID: 3839598).
What is the subcellular localization of GLUT1?
Glucose transporters, including GLUT1, are multiple-pass integral membrane proteins. GLUT1 is present at the plasma membrane but is also a subject of recycling between plasma membrane and endosomes.
What molecules can be transported by GLUT1?
The main substrate of GLUT1 transport is glucose, but it can also transport galactose, mannose, glucosamine, and reduced ascorbate.
What is the tissue expression pattern of GLUT1?
GLUT1 is expressed by many cell types but the highest levels are observed in erythrocytes and in the central nervous system (astrocytes). GLUT1 is responsible for glucose transfer across the blood-brain and blood-tissue barriers, including placental transport.