验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
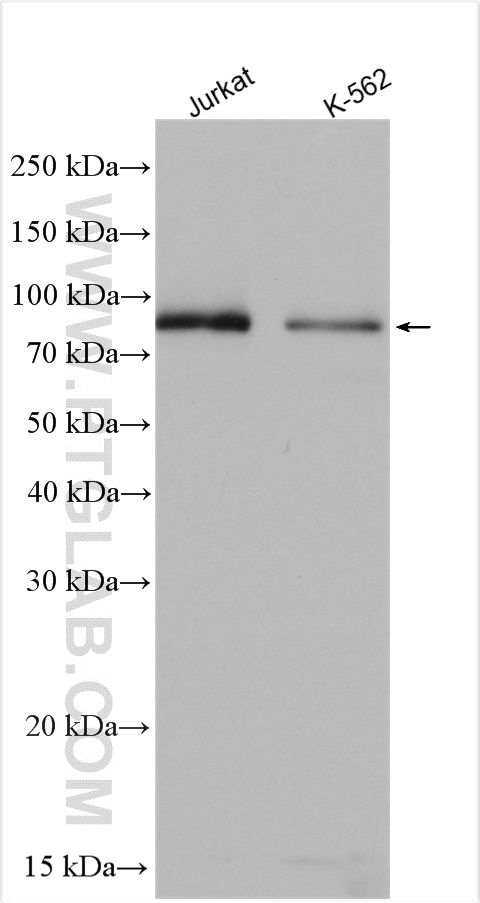
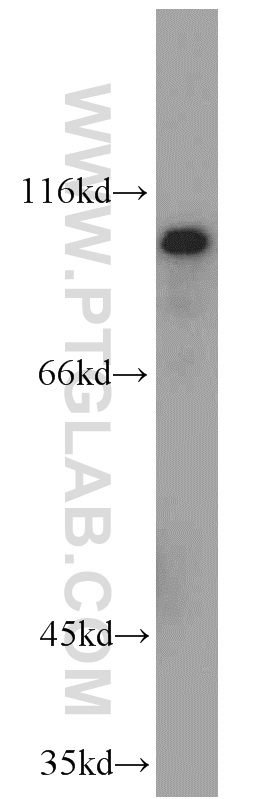
| Positive WB detected in | Jurkat cells, A375 cells, HeLa cells, K-562 cells |
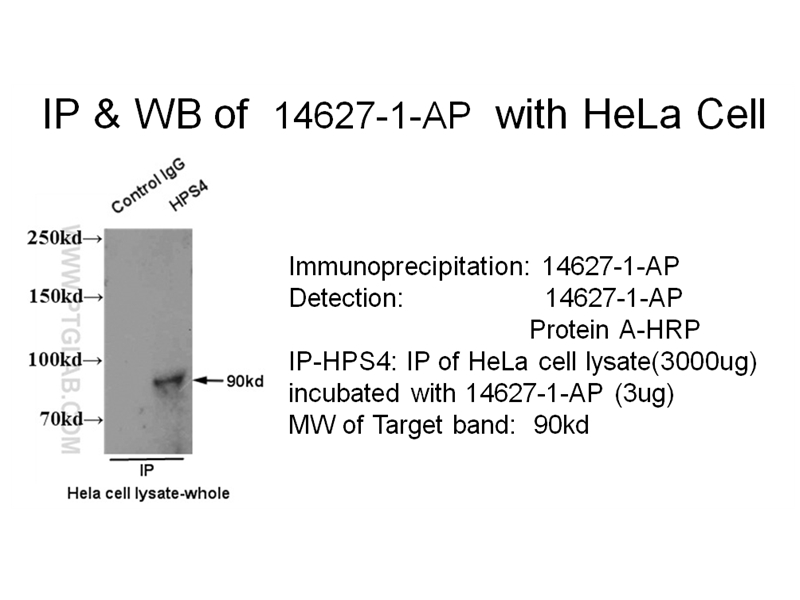
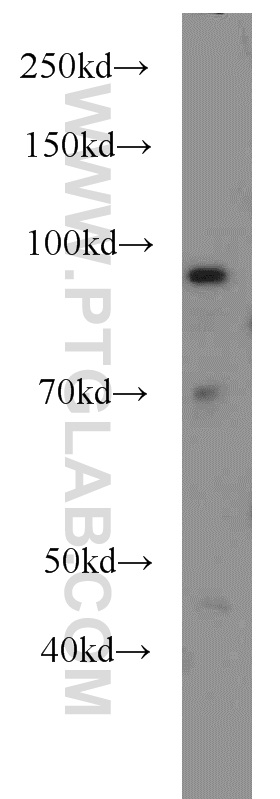
| Positive IP detected in | Hela cells, IP result of anti-HPS4 (14267-1-AP for IP and Detection) with HeLa cell lysate. |
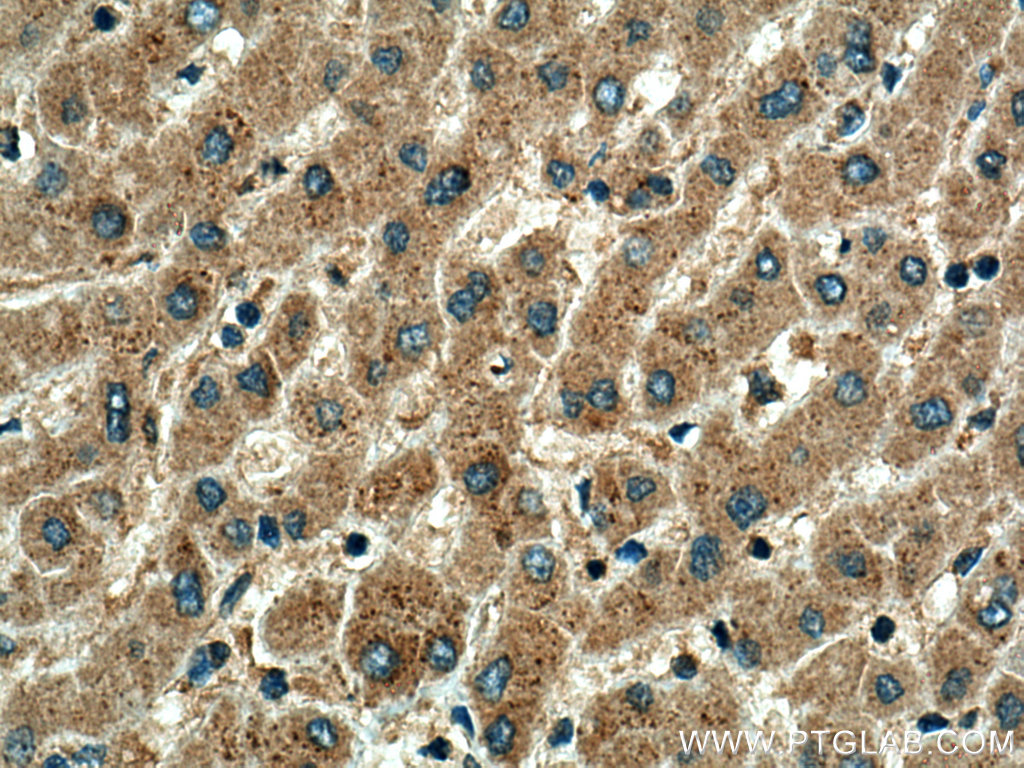
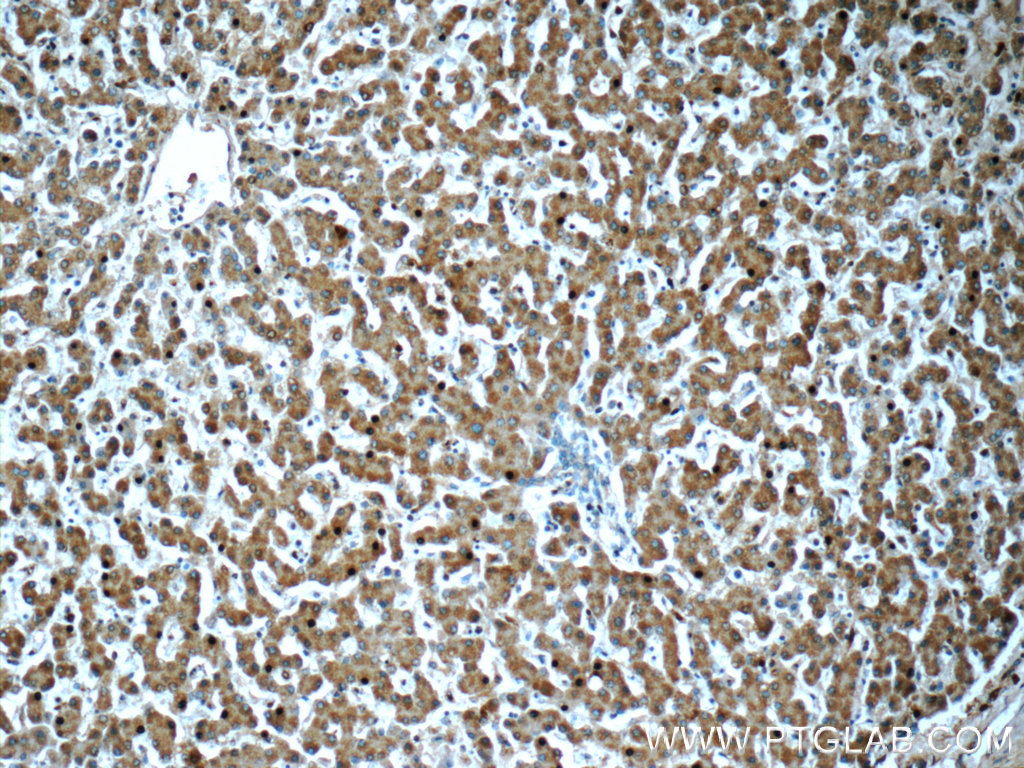
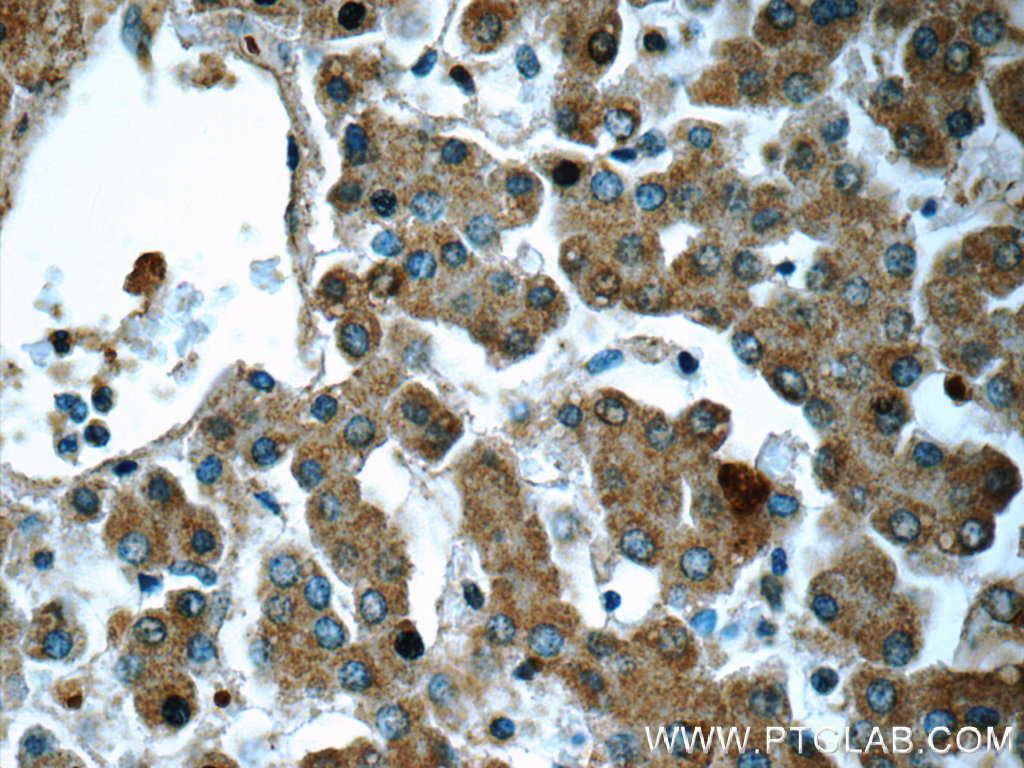
| Positive IHC detected in | human liver tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
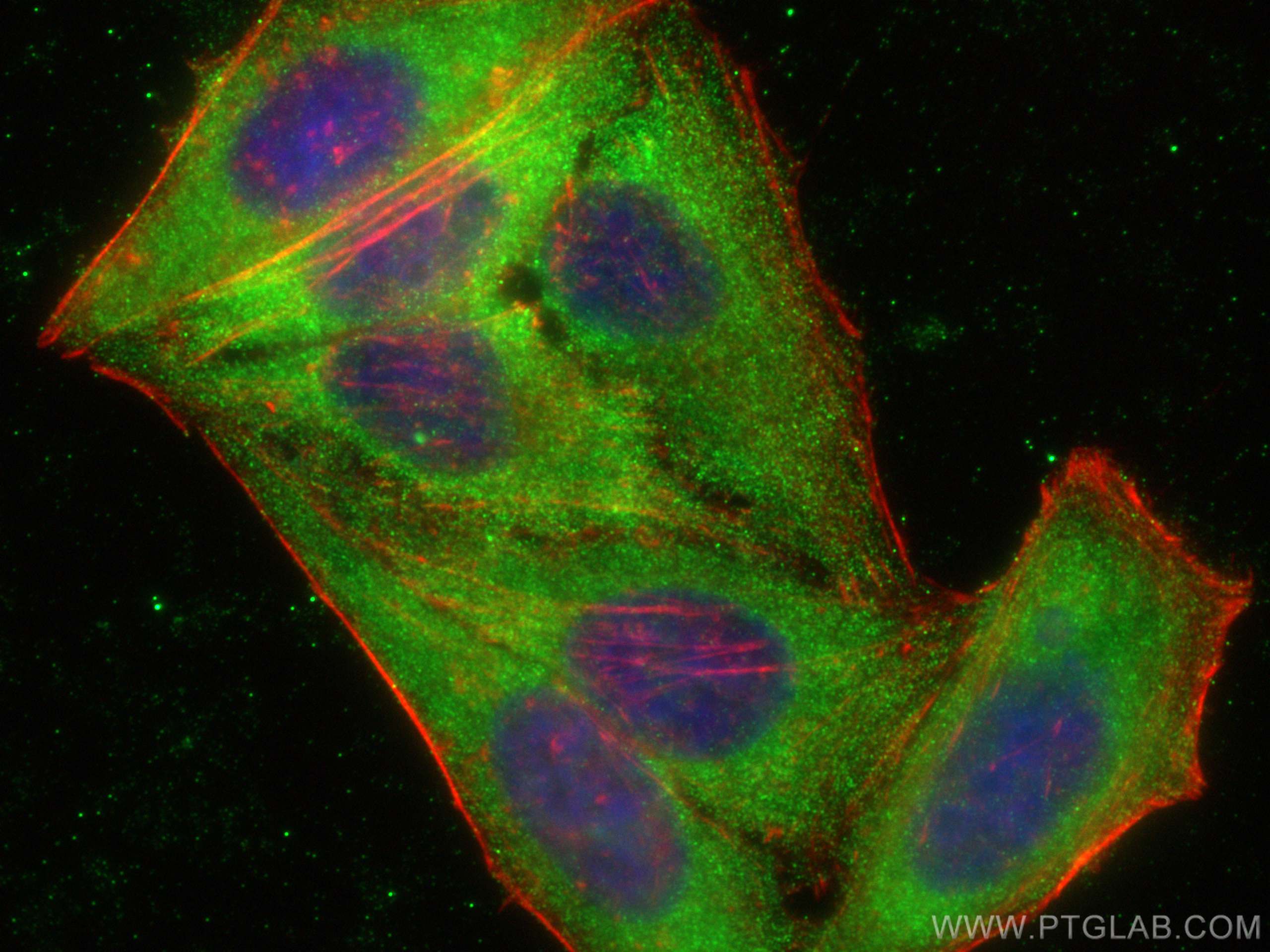
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells |
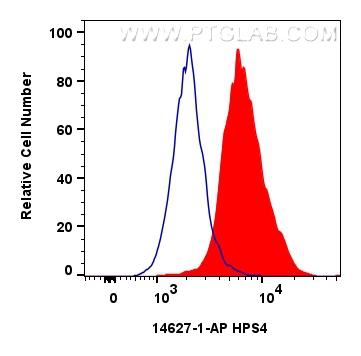
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | HepG2 cells |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
发表文章中的应用
| WB | See 5 publications below |
产品信息
14627-1-AP targets HPS4 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | WB |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 文献引用反应性 | human, mouse |
| 免疫原 | HPS4 fusion protein Ag6202 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 4 |
| 别名 | Light-ear protein homolog, KIAA1667, Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 4 protein, BLOC-3 complex member HPS4 |
| 计算分子量 | 77 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 70-90 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC065030 |
| 基因名称 | HPS4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 89781 |
| RRID | AB_2878071 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9NQG7 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) is a genetic disease characterized by oculocutaneous albinism, bleeding due to platelet storage pool deficiency, and lysosomal storage defects. This syndrome results from defects of diverse cytoplasmic organelles including melanosomes, platelet dense granules and lysosomes. HPS1 and HPS4 are the most frequently mutated genes associated with HPS in humans. Both of HPS1 and HPS4 are components of two complexes involved in biogenesis of melanosome and lysosome-related organelles: BLOC-3 and BLOC-4. HPS4 is supposed to interact with HPS1 and stabilize HPS1. The human HPS4 migrates at about 90 kDa on SDS-PAGE, versus its predicated molecular mass of 77 kDa.
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for HPS4 antibody 14627-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for HPS4 antibody 14627-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for HPS4 antibody 14627-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol Gene-edited MLE-15 Cells as a Model for the Hermansky Pudlak Syndromes. | ||
PLoS One Cellular and molecular defects in a patient with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 5. | ||
Gene Intron retention is a stress response in sensor genes and is restored by Japanese herbal medicines: A basis for future clinical applications. | ||
Mol Genet Metab In vitro functional correction of Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome type-1 by lentiviral-mediated gene transfer. | ||