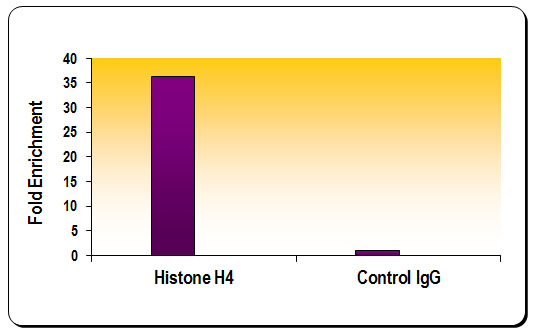
Histone H4 antibody (pAb)
Host / Isotype
Rabbit / IgG
Reactivity
Human, Wide Range Predicted
Applications
ChIP, ChIP-Seq, WB
Cat No : 61299,61300 61299
Synonyms
验证数据展示
产品信息
| Tested Applications |
ChIP, ChIP-Seq, WB
Applications Validated by Active Motif: ChIP: 2 - 10 ul per ChIP WB*: 1:500 - 1:2,000 dilution *Note: many chromatin-bound proteins are not soluble in a low salt nuclear extract and fractionate to the pellet. Therefore, we recommend a High Salt / Sonication Protocol when preparing nuclear extracts for Western Blot. For Histone H4, we also offer AbFlex Histone H4 Recombinant Antibody (rAb). For details, see Catalog No. 91295. |
| Tested Reactivity | Human, Wide Range Predicted |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | This Histone H4 antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 43- 54 of human histone H4. |
| Full Name | Histone H4 antibody (pAb) |
| Synonyms | Histone H4, H4, Histone, variant, chromatin, nucleosome, antibody, antibodies, polyclonal, chromatin immunoprecipitation, chip, sample, pAb, western blotting |
| Molecular weight | 8 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NP_778224 | RRID | AB_2650524 | Purification Method | Affinity Purified |
| Buffer | Purified IgG in PBS with 30% glycerol and 0.035% sodium azide. Sodium azide is highly toxic. |
| Storage | Some products may be shipped at room temperature. This will not affect their stability or performance. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles by aliquoting items into single-use fractions for storage at -20°C for up to 2 years. Keep all reagents on ice when not in storage. |
背景介绍
Histone H4 is one of the core components of the nucleosome, the basic building block of chromatin. Histones are subject to a variety of chemical modifications, including post-translational modifications of the histone proteins and the methylation of cytosine residues in the DNA. Reported histone modifications include acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitylation, glycosylation, ADP-ribosylation, carbonylation and SUMOylation; these modifications play a major role in regulating gene expression.