Recombinant Human Cathepsin D protein (His Tag)
种属
Human
纯度
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
标签
His Tag
生物活性
未测试
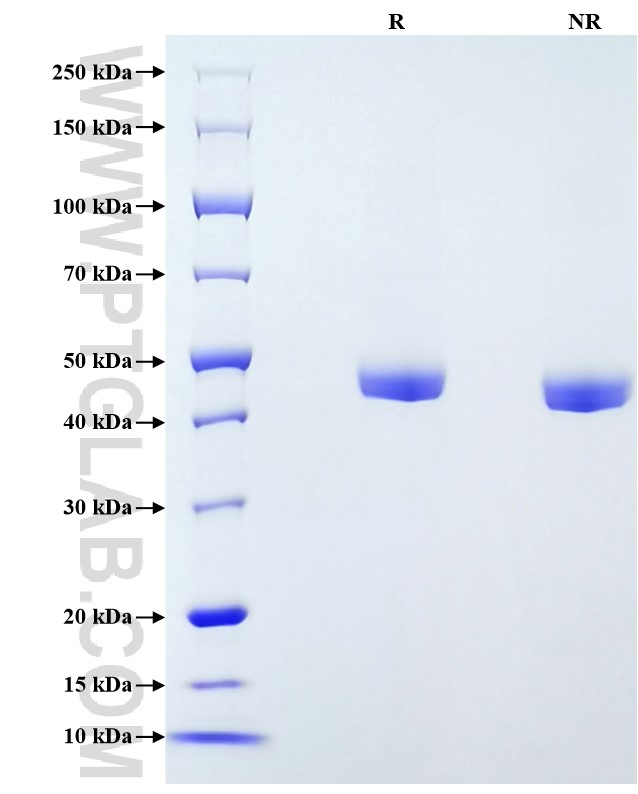
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 | Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Human Cathepsin D protein Leu21-Leu412 (Accession# P07339) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 1509 |
| 蛋白编号 | P07339 |
| 预测分子量 | 43.4 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 43-49 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
CTSD (Cathepsin D), also named CPSD, belongs to the peptidase A1 family. It is ubiquitously expressed and is involved in proteolytic degradation, cell invasion, and apoptosis. Human CTSD is synthesized as a 52-kDa precursor that is converted into an active 48-kDa single-chain intermediate in the endosomes, and then into a fully active mature form, composed of a 34-kDa heavy chain and a 14-kDa light chain, in the lysosomes. It is a lysosomal acid protease found in neutrophils and monocytes and involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases such as breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer disease (PMID: 27114232, PMID: 30717773, PMID: 30051532).
参考文献:
1. Vidoni C, et al. (2016). Med Res Rev. 36(5):845-70. 2. Ashraf Y, et al. (2019). J Immunother Cancer. 7(1):29. 3. Chai YL, et al. (2019). Brain Pathol. 29(1):63-74. 4. Mijanovic O, et al. (2021). Pharmaceutics. 5;13(6):837.