Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a protein (His Tag)
种属
Human
纯度
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
标签
His Tag
生物活性
未测试
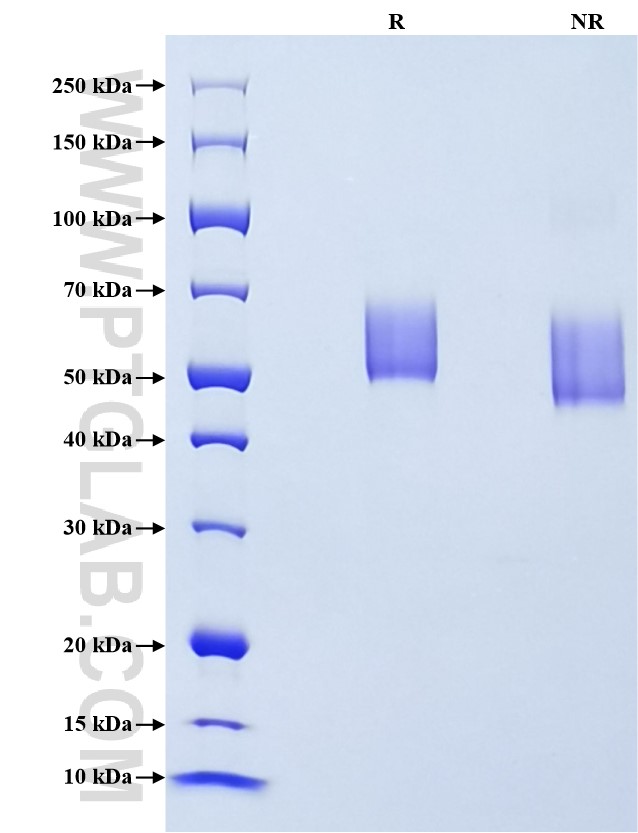
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 | Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Human SIRP alpha protein Glu31-Arg370 (Accession# P78324-1) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 140885 |
| 蛋白编号 | P78324-1 |
| 预测分子量 | 38.1 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 50-70 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
SIRP Alpha, also known as CD172a or SHPS-1, is a transmembrane glycoprotein that belongs to the SIRP family. SIRP Alpha is a receptor with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs in its cytoplasmic domain expressed by myeloid cells, including monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, and a subset of dendritic cells. After activation of SIRP Alpha, Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) is recruited and regulates receptor tyrosine kinase coupled signaling, participating in the regulation of phagocytosis and polarization of macrophages. SIRP Alpha binds to CD47, a receptor present on all cells (and frequently overexpressed in cancer cells), and this interaction provides a ‘do-not-eat-me’ signal to prevent phagocytosis.
参考文献:
1. Sarfati M, et al. (2008) Curr Drug Targets. 9(10):842-50. 2. Barclay AN, et al. (2014) Annu Rev Immunol. 32:25-50. 3. de Vos AF, et al. (2020) Nat Immunol. 21(6):601-603. 4. Shen Q, et al. (2022) Front Immunol. 13:865579.