Recombinant Human CD33 protein (rFc Tag) (HPLC verified)
种属
Human
纯度
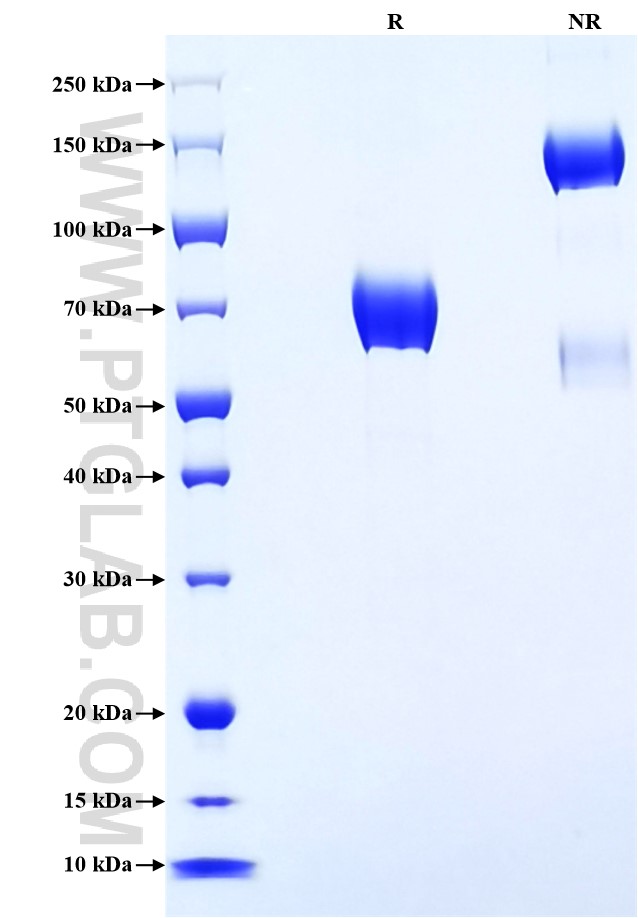
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
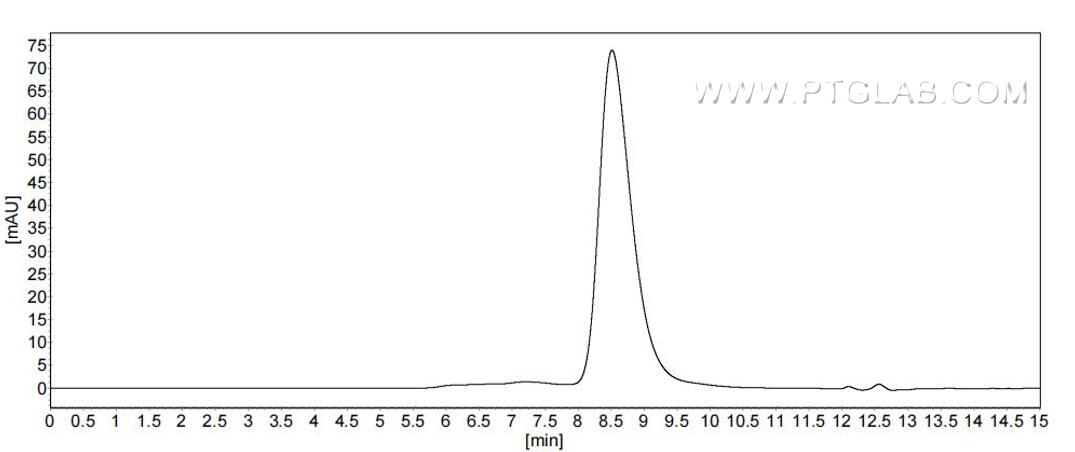
>90 %, SEC-HPLC
标签
rFc Tag
生物活性
未测试
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90 %, SEC-HPLC |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 | Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Human CD33 protein Asp18-His259 (Accession# AAH28152.1) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 945 |
| 蛋白编号 | AAH28152.1 |
| 预测分子量 | 53.0 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 60-85 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
CD33, also known as sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 3 (Siglec-3) or gp67, is a 67-kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein of sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lactic (Siglec) family, a discrete subset of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily molecules. It contains an amino-terminal V-set Ig-like domain and a C2-set Ig-like domain in its extracellular region, a transmembrane region, and two conserved tyrosine-based inhibitory signaling motif in its cytoplasmic region. Alternative splicing of CD33 RNA leads to a shorter isoform. CD33 is expressed on myeloid progenitors, granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells, subsets of activated T- and NK cells. It may mediate cell-to-cell adhesion and act as a receptor that inhibits the proliferation of normal and leukemic myeloid cells.
参考文献:
1. E J Favaloro, et al. (1988) Br J Haematol. 69(2):163-71. 2. S D Freeman, et al. (1995) Blood. 85(8):2005-12. 3. C Vitale, et al. (1999) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 96(26):15091-6. 4. Trinidad Hernández-Caselles, et al. (2006) J Leukoc Biol. 79(1):46-58. 5. George S Laszlo, et al. (2014) Blood Rev. 28(4):143-53.