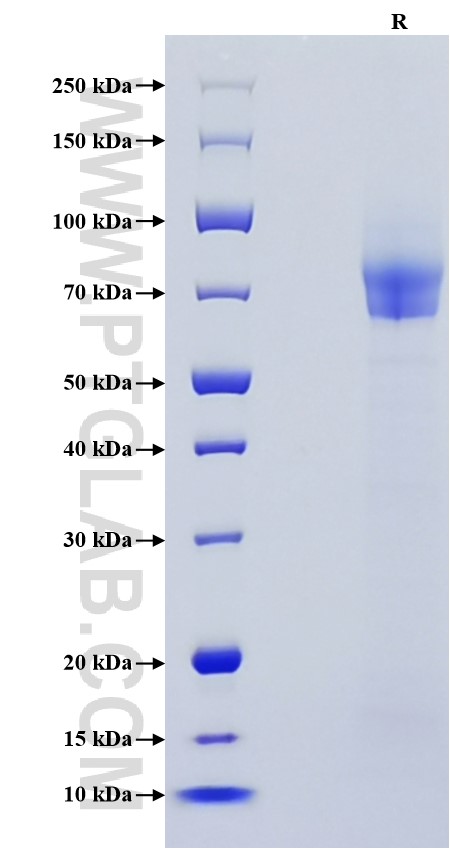
Recombinant Human Thrombomodulin protein (His Tag)
种属
Human
纯度
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
标签
His Tag
生物活性
未测试
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 | Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Human Thrombomodulin protein Ala19-Ser515 (Accession# P07204) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 7056 |
| 蛋白编号 | P07204 |
| 预测分子量 | 52.9 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 70-100 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
Thrombomodulin, also known as CD141, is an endothelial cell surface glycoprotein that forms a 1:1 complex with the coagulation factor thrombin and plays an important role as a natural anticoagulant. Thrombomodulin serves to convert thrombin from a procoagulant protein into the activator for protein C. Once converted to activated protein C (APC), this protein serves as a major anticoagulant in blood. Thrombomodulin is also located in other cells (keratinocytes, osteoblasts, macrophages,...) where it might be involved in cell differentiation or in inflammation. Mutations in the gene of thrombomodulin are a cause of thromboembolic disease, also known as inherited thrombophilia.
参考文献:
1. N L Esmon, et al. (1987) Semin Thromb Hemost. 13(4):454-63. 2. A K Ohlin, et al. (1997) Thromb Haemost. 78(1):396-400. 3. M C Boffa, et al. (1998) Lupus.7 Suppl 2:S120-5. 4. Georgia Anastasiou, et al. (2012) Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 23(1):1-10.