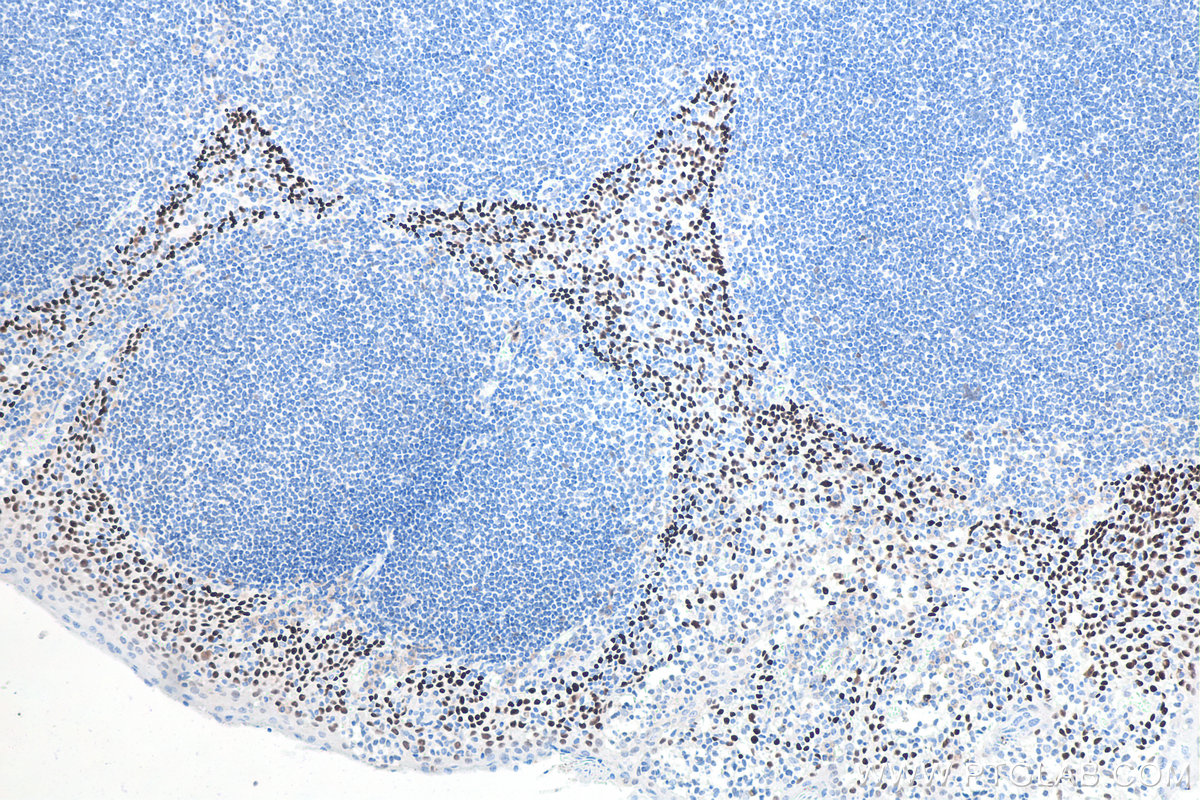
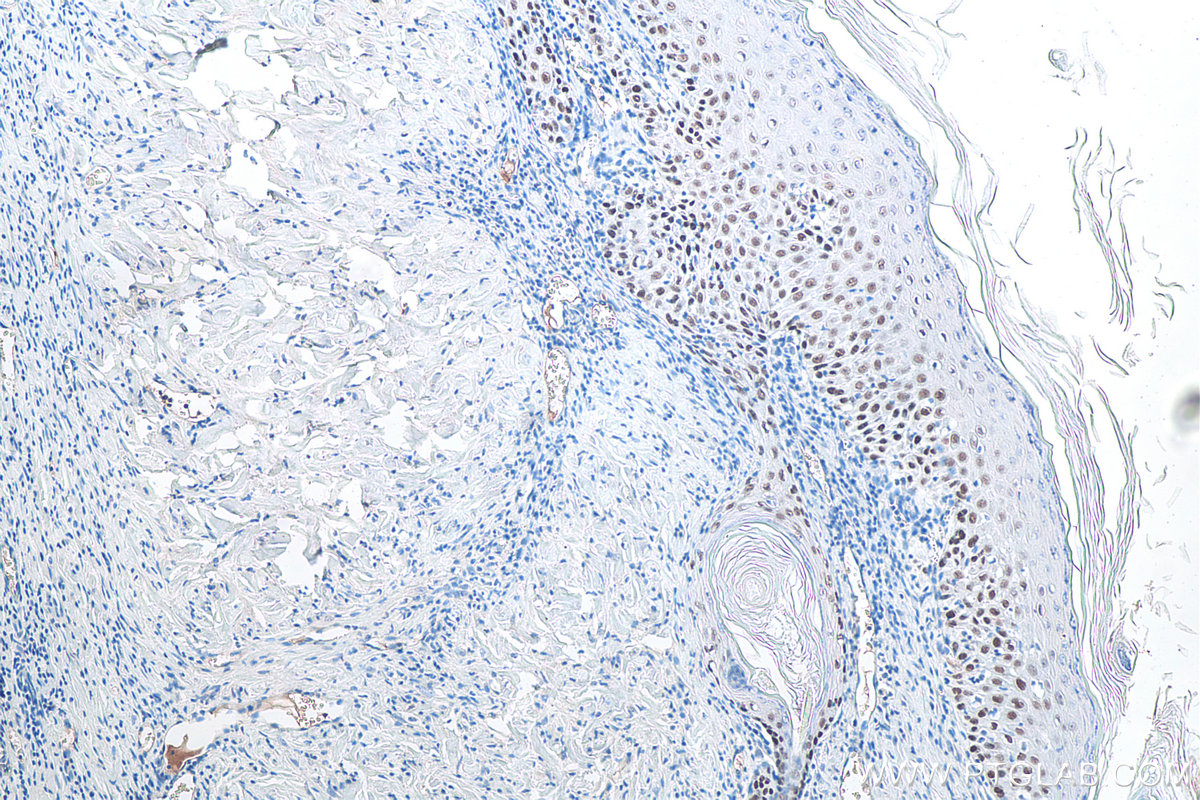
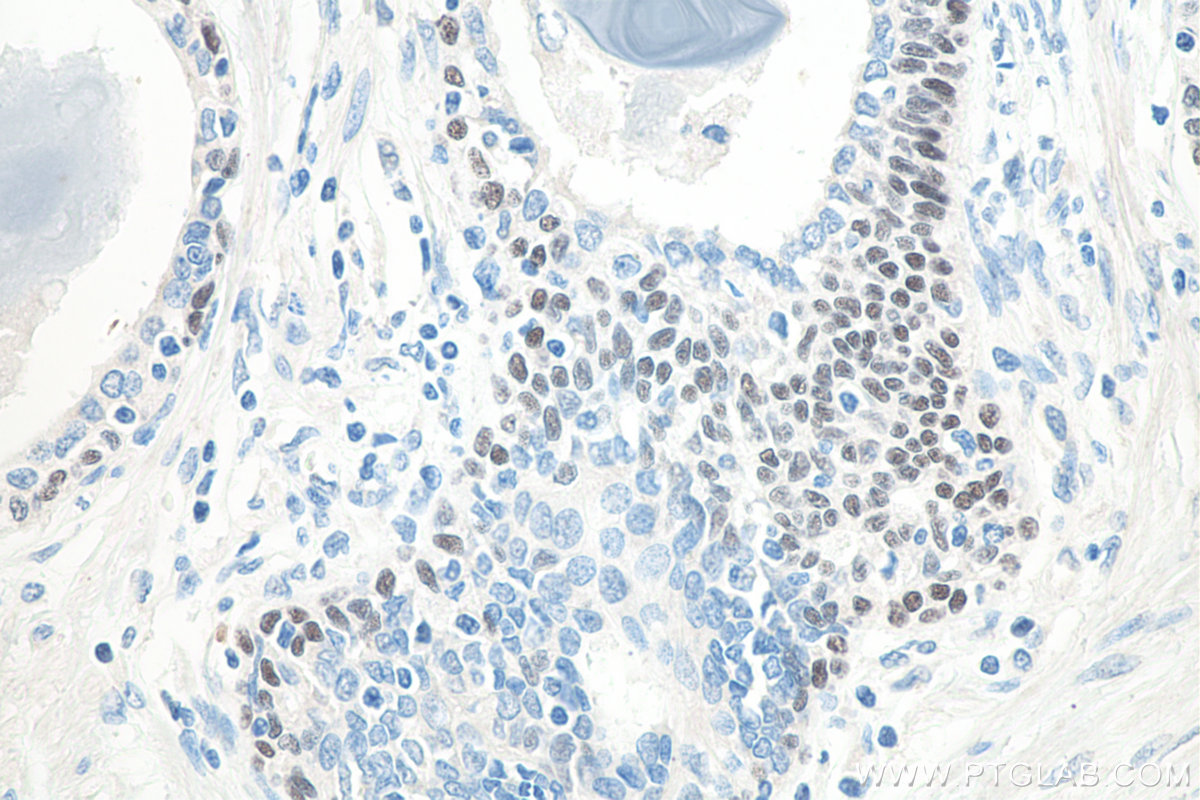
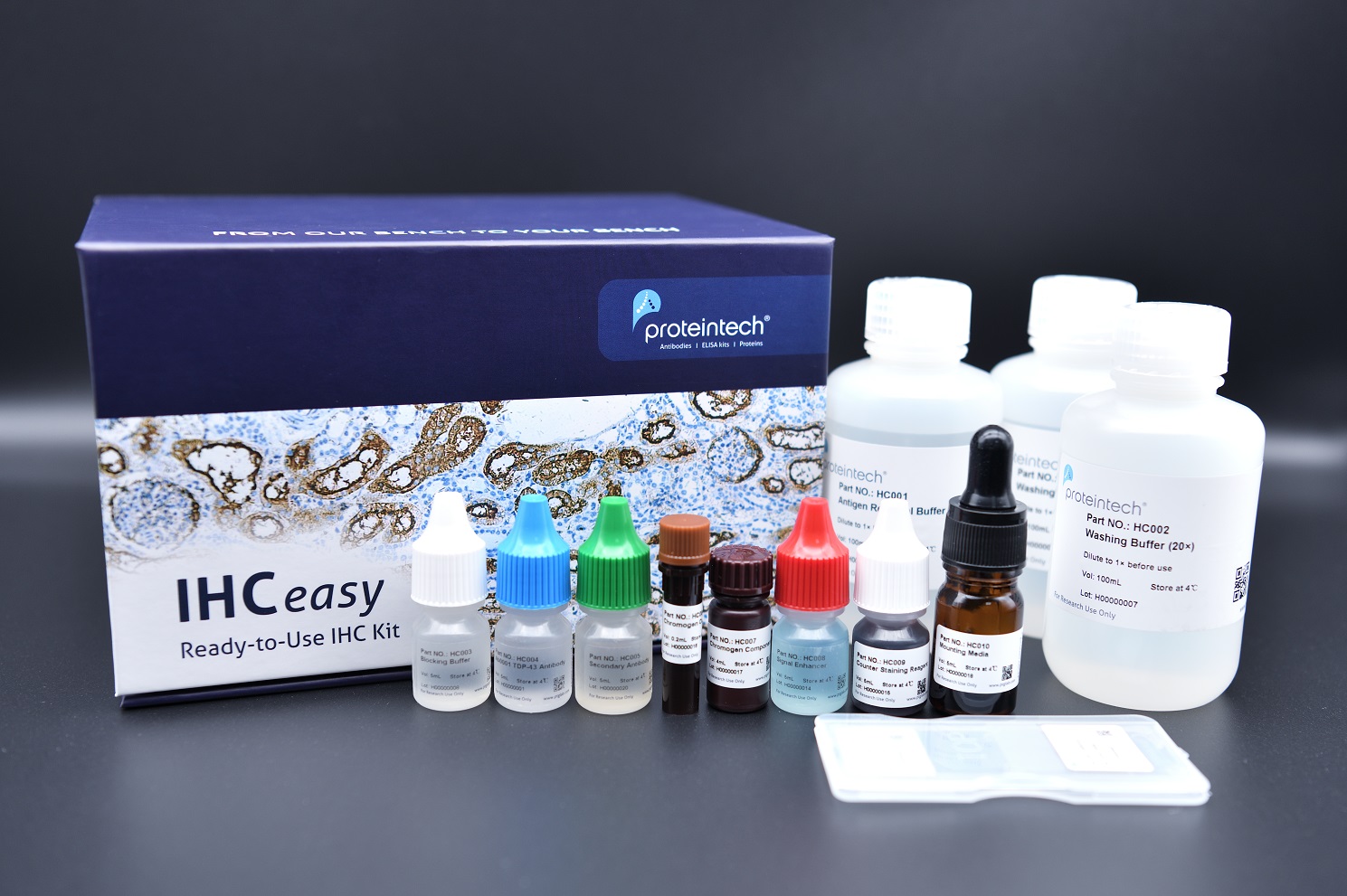
IHCeasy® TP63 Ready-To-Use IHC Kit
TP63 Ready-to-use reagent kit for IHC.
Cat no : KHC0086
Synonyms
AIS, B(p51A), B(p51B), CUSP, DNp63, EEC3, KET, LMS, NBP, OFC8, p53CP, p63, RHS, SHFM4, TP53CP, TP63, Tumor protein 63
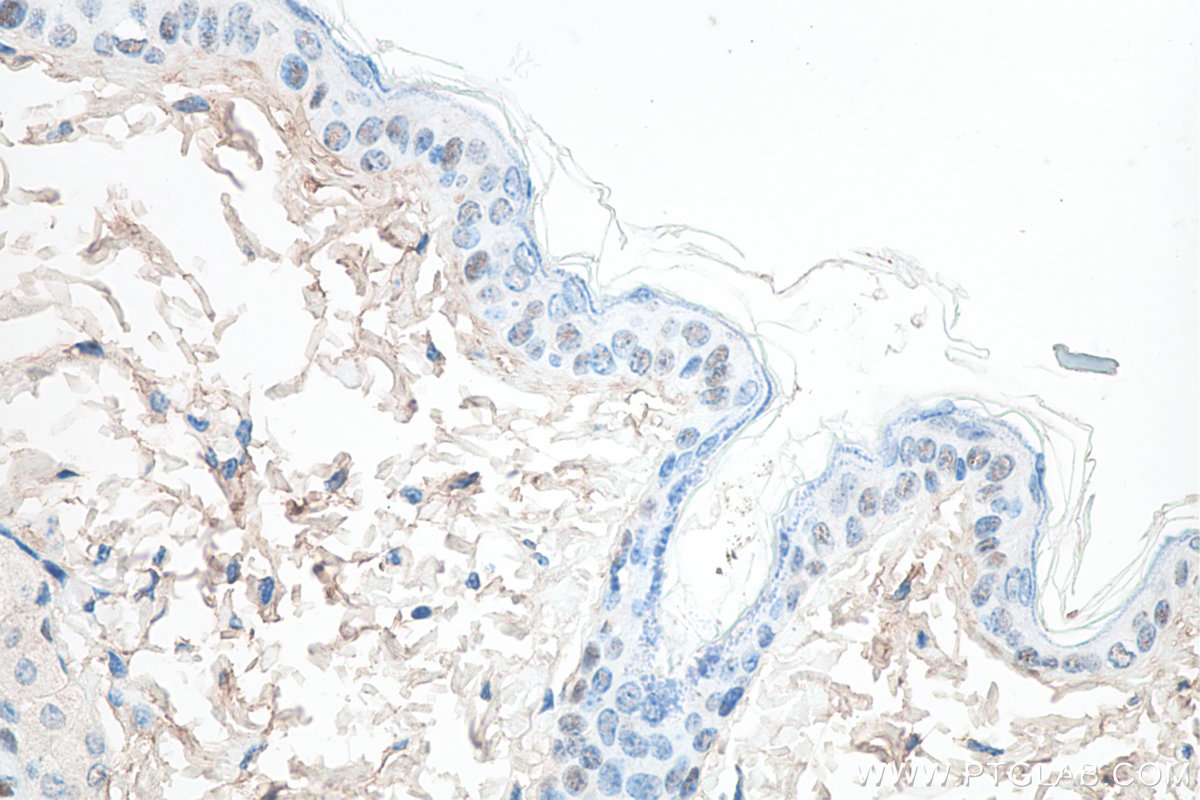
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
KHC0086 is a ready-to-use IHC kit for staining of TP63. The kit provides all reagents, from antigen retrieval to cover slip mounting, that require little to no diluting or handling prior to use. Simply apply the reagents to your sample slide according to the protocol and you're steps away from obtaining high-quality IHC data.
| Product name | IHCeasy TP63 Ready-To-Use IHC Kit |
| Sample type | FFPE tissue |
| Assay type | Immunohistochemistry |
| Primary antibody type | Mouse Monoclonal |
| Secondary antibody type | Polymer-HRP-Goat anti-Mouse |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Kit components
| Component | Size | Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Antigen Retrieval Buffer | 100 mL | 50× |
| Washing Buffer | 100 mL ×2 | 20× |
| Blocking Buffer | 5 mL | RTU |
| Primary Antibody | 5 mL | RTU |
| Secondary Antibody | 5 mL | RTU |
| Chromogen Component A | 0.2 mL | RTU |
| Chromogen Component B | 4 mL | RTU |
| Signal Enhancer | 5 mL | RTU |
| Counter Staining Reagent | 5 mL | RTU |
| Mounting Media | 5 mL | RTU |
| Datasheet | 1 Copy | |
| Manual | 1 Copy |
Background Information
TP63, also named KET, P63, P73H, P73L and TP73L, belongs to the p53 family. It is a homologue of the tumor suppressor p53 and p73 genes. It is involved in malignancy acquisition and maintenance of cells. Unlike p53, the p63 gene encodes multiple isotypes with remarkably divergent abilities to transactivate p53 reporter genes and induce apoptosis. TP63 acts as a sequence specific DNA binding transcriptional activator or repressor.
Properties
| Storage Instructions | All the reagents are stored at 2-8°C. The kit is stable for 6 months from the date of receipt. |
| Synonyms | AIS, B(p51A), B(p51B), CUSP, DNp63, EEC3, KET, LMS, NBP, OFC8, p53CP, p63, RHS, SHFM4, TP53CP, TP63, Tumor protein 63 |
Publications
| Application | Title |
|---|---|
Nat Commun UPP1 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression through the induction of an immunosuppressive microenvironment |