验证数据展示
产品信息
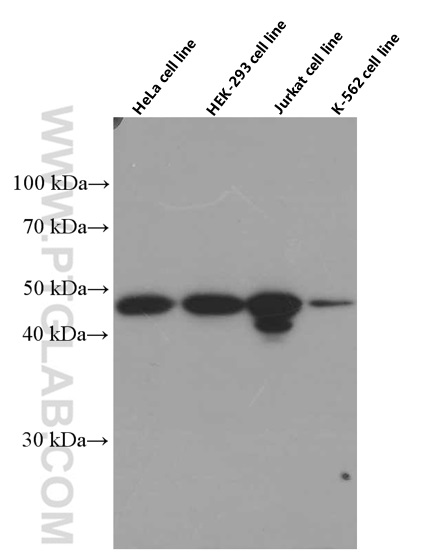
66460-1-PBS targets IKBKG in WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 | IKBKG fusion protein Ag13358 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG1 |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells, kinase gamma |
| 别名 | AMCBX1, FIP 3, FIP3, Fip3p, I kappa B kinase subunit gamma, IkB kinase subunit gamma, IKBKG, IKK gamma, IKKAP1, IKKG, IP, IP1, IP2, IPD2, NEMO, NF kappa B essential modifier, NF kappa B essential modulator |
| 计算分子量 | 48 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 48 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC012114 |
| 基因名称 | IKBKG |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8517 |
| RRID | AB_2881829 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9Y6K9 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
IKBKG, also named as FIP3, NEMO, IKKAP1 and IKKG, is specifically phosphorylate serine or threonine residues that are followed by a proline residue. IKBKG is regulatory subunit of the IKK core complex which phosphorylates inhibitors of NF-kappa-B thus leading to the dissociation of the inhibitor/NF-kappa-B complex and ultimately the degradation of the inhibitor. Its binding to scaffolding polyubiquitin seems to play a role in IKK activation by multiple signaling receptor pathways.