验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
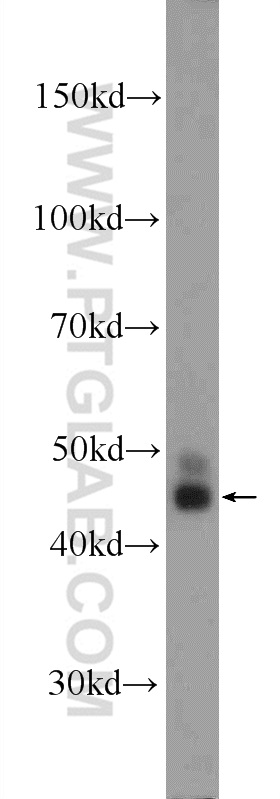
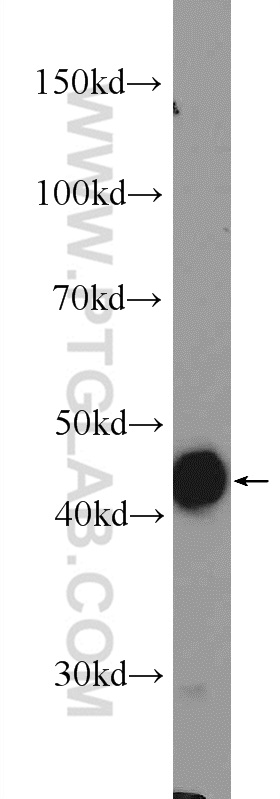
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, MCF-7 cells, NIH/3T3 cells |
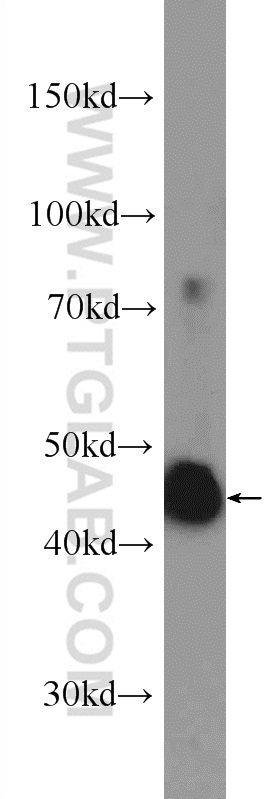
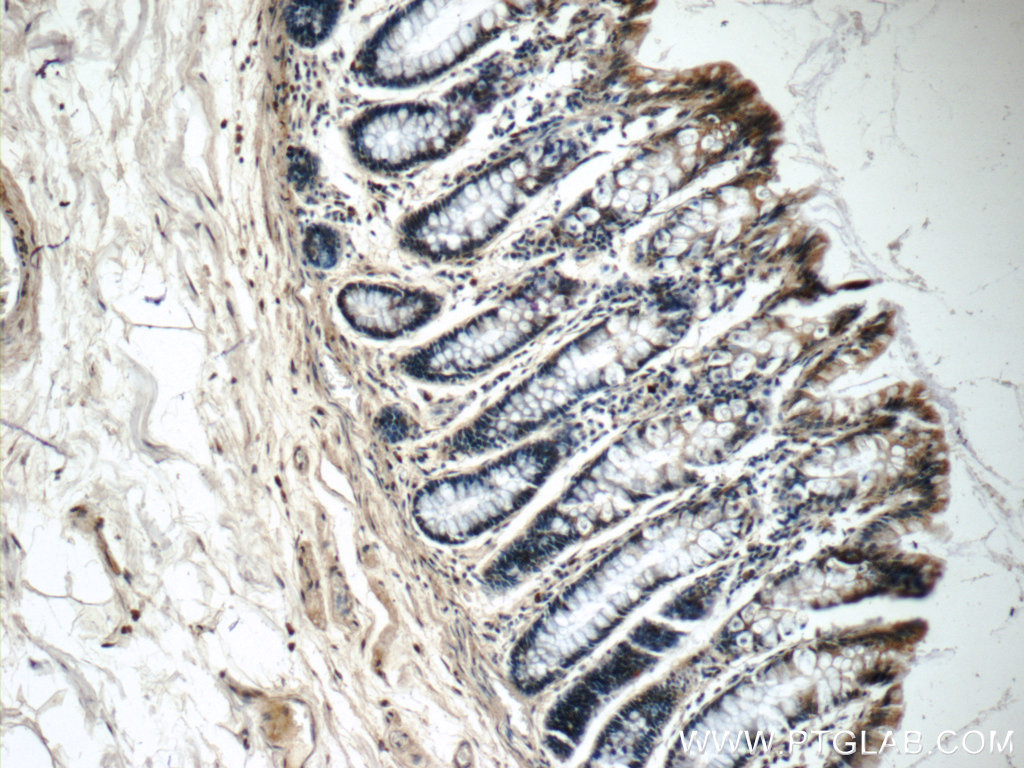
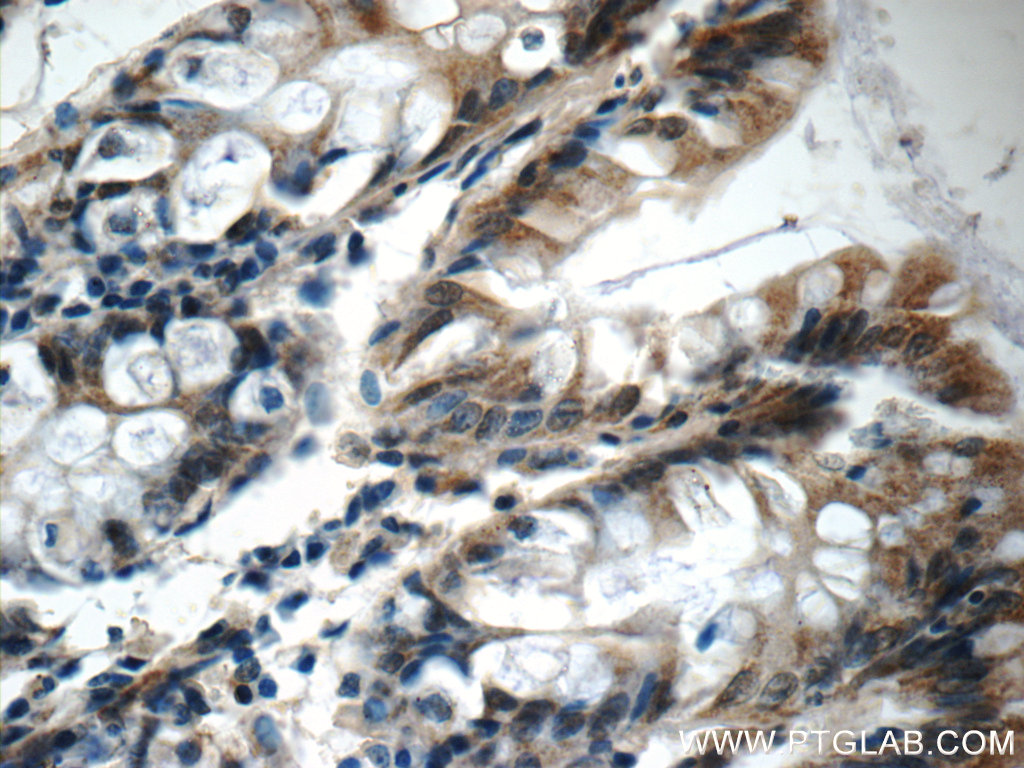
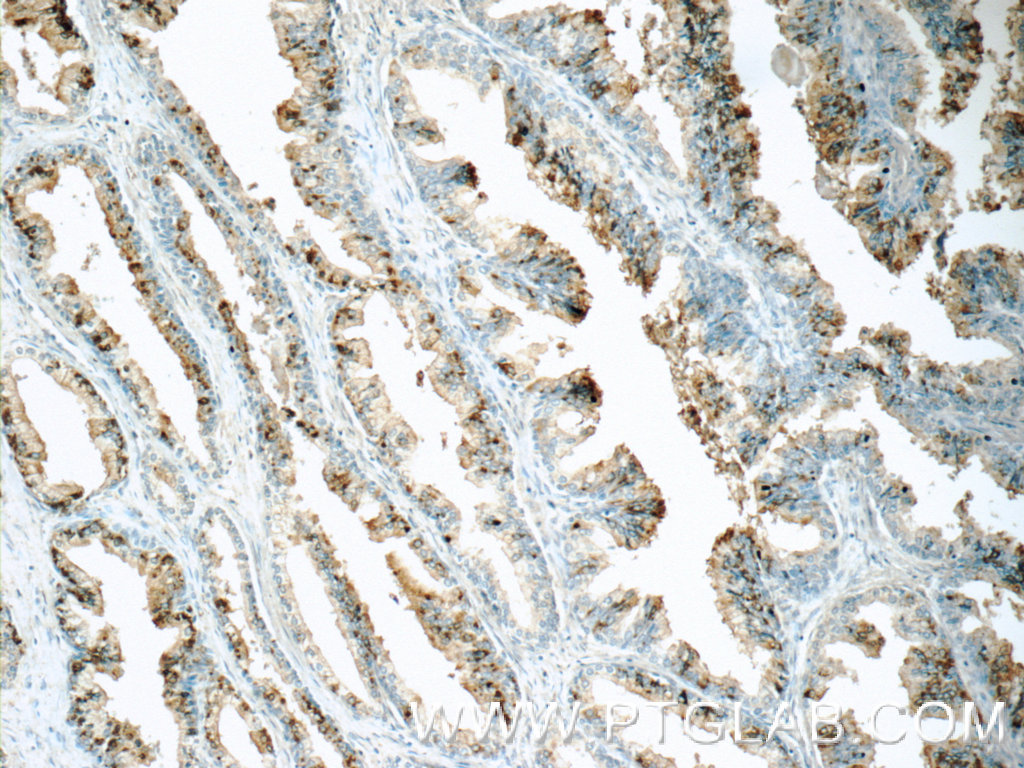
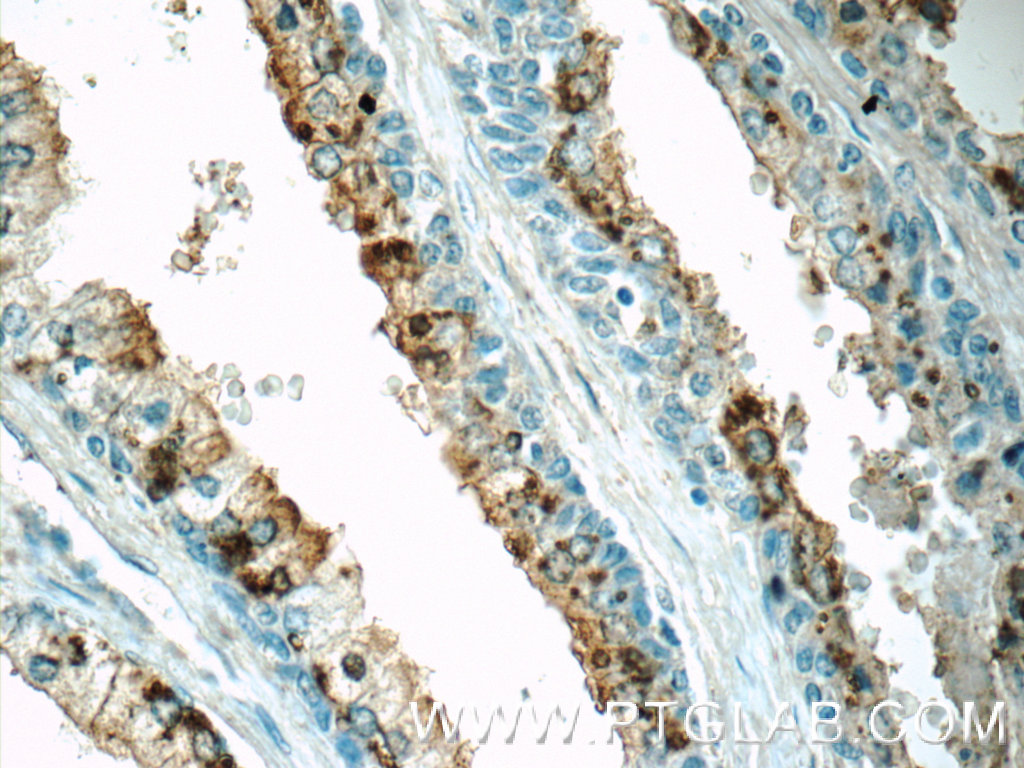
| Positive IHC detected in | human colon tissue, human prostate hyperplasia tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
发表文章中的应用
| WB | See 1 publications below |
产品信息
25694-1-AP targets OSGEPL1 in WB, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, ELISA Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | WB |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse |
| 文献引用反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 | OSGEPL1 fusion protein Ag22204 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | O-sialoglycoprotein endopeptidase-like 1 |
| 别名 | OSGEPL1 |
| 计算分子量 | 414 aa, 45 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 45 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC011904 |
| 基因名称 | OSGEPL1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 64172 |
| RRID | AB_2880198 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9H4B0 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for OSGEPL1 antibody 25694-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for OSGEPL1 antibody 25694-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |