ChromoTek PD-L1 VHH, recombinant binding protein for 2x Cys conjugation
Alpaca anti-PD-L1 VHH, purified recombinant binding protein. Suitable for for cysteine conjugation with thiol-reactive reagents, e.g. maleimides. Note: unconjugated VHHs are not suited for usage without prior labeling, since they contain reactive Cysteines. Shipment and storage buffers contain TCEP to keep Cysteins reduced.
Host/Type
Alpaca VHH
Reactivity
Human
Applications
Conjugation
Conjugate
Unconjugated
Cat No : pdloCys2
Synonyms
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
Alpaca anti-PD-L1 VHH, purified recombinant binding protein. Suitable for for cysteine conjugation with thiol-reactive reagents, e.g. maleimides. Note: unconjugated VHHs are not suited for usage without prior labeling, since they contain reactive Cysteines. Shipment and storage buffers contain TCEP to keep Cysteins reduced.
| Applications | Conjugation |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Type | Nanobody |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Host | Alpaca |
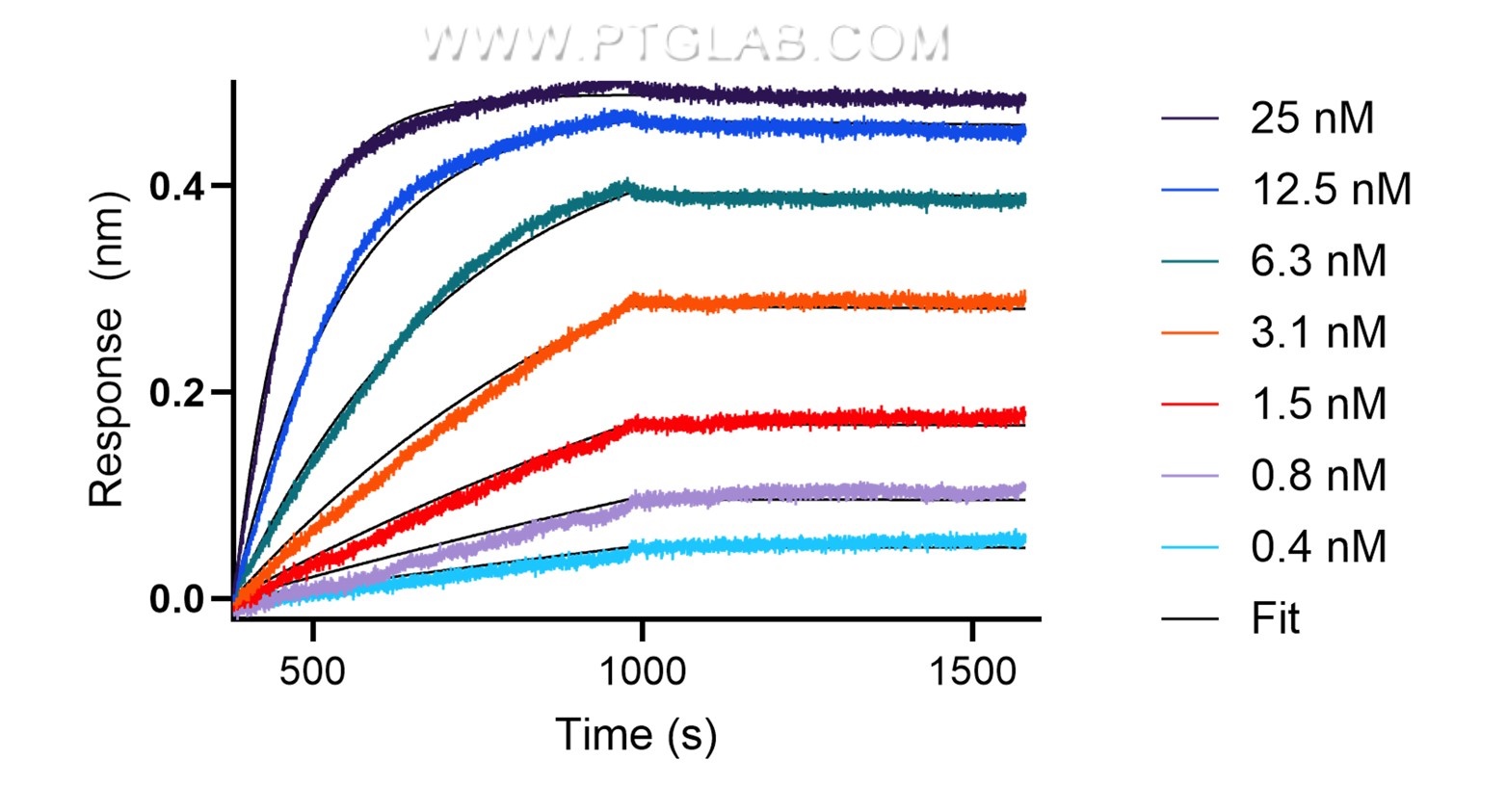
| Affinity | Picomolar range, below the assay limit (biolayer interferometry) |
| Molecular Weight | 13.887 kDa |
| Form | Liquid |
| RRID | AB_3661833 |
| Storage Buffer | 10 mM HEPES, 500 mM NaCl, pH 7.0, 1 mM TCEP, 0.09% sodium azide |
| Storage Condition | Store at -20°C |
| Background | PD-L1, also known as CD274 or B7H1, stands for programmed cell death ligand 1. It is a type I transmembrane protein that is thought to repress immune responses by binding to its receptor (PD1), thus inhibiting T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. It contains V-like and C-like immunoglobulin domains. PD-L1 expression is regulated by various cytokines, such as TNF-α or LPS (ISSN: 1848-7718). Increased expression of this protein in certain types of cancers, e.g., renal cell carcinoma or colon cancer, correlates with poor prognosis. D-L1 is critical for the induction and maintenance of immune self-tolerance during infection or inflammation in normal tissues. The interaction of PD-L1 and its receptors is responsible for preventing auto-immune phenotypes and balancing the overall immune response in situations such as pregnancy or tissue allografts. The interaction between PD-L1 and PD-1 or B7.1 starts an inhibitory signaling cascade, which results in the decreased proliferation of antigen-specific T-cells and increased survival of regulatory T-cells (PMID: 15240681). |
Documentation
| SDS |
|---|
| SDS_Immuno-Oncology VHHs (grouped) |