HRP-conjugated Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L)
Applications
ELISA, WB, Dot blot
Conjugate
HRP
Host
Donkey
Reactivity
Mouse (Minimal Cross Reactivity: Bovine, Chicken, Goat, Guinea Pig, Syrian Hamster, Horse, Human, Rabbit, Sheep Serum Proteins)
Cat no : SA00001-8
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/mL |
| Applications | ELISA, WB, Dot blot |
| Host Species | Donkey |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse (Minimal Cross Reactivity: Bovine, Chicken, Goat, Guinea Pig, Syrian Hamster, Horse, Human, Rabbit, Sheep Serum Proteins) |
| Physical State | Liquid |
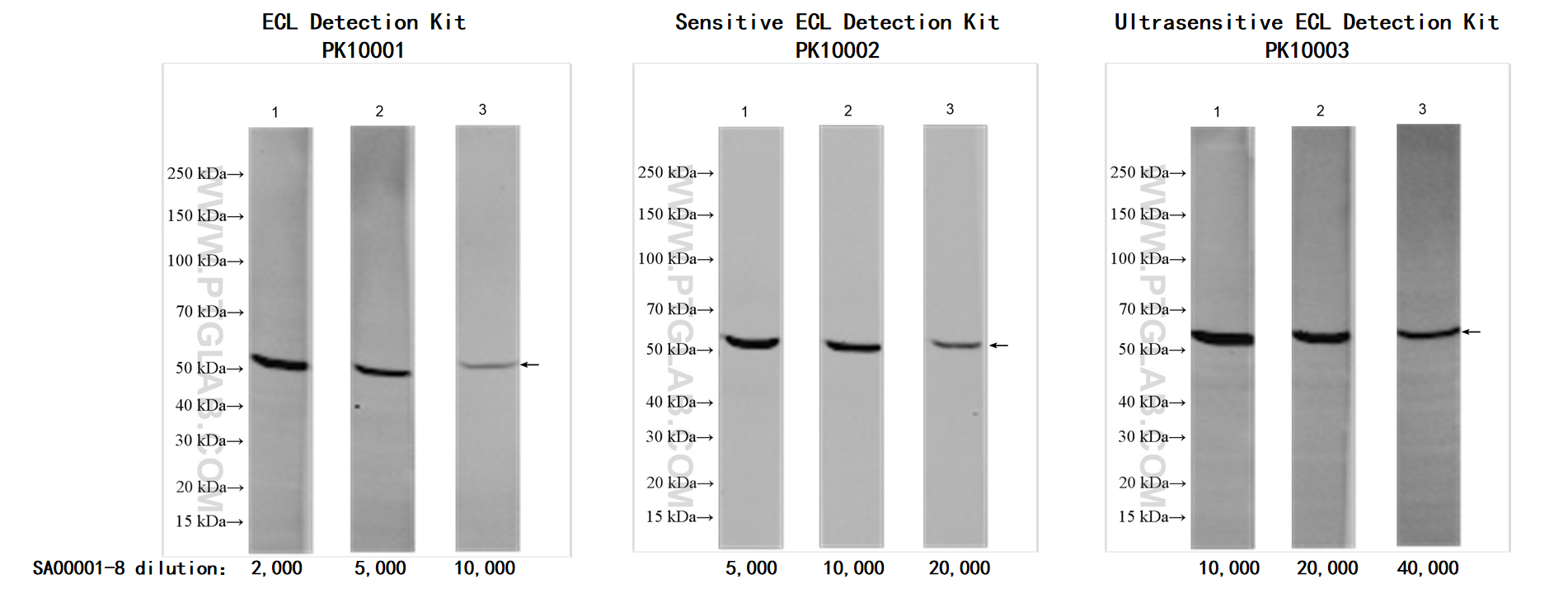
| Suggested Dilution Range | For western blotting with ECL substrates: ECL Detection Kit (PK10001): 1:2,000-1:10,000 Sensitive ECL Detection Kit (PK10002):1:5,000-1:20,000 Ultrasensitive ECL Detection Kit (PK10003): 1:10,000-40,000 For ELISA and Western blotting with chromogenic substrates: 1:1,000-1:20,000 |
| Purity | The antibody was purified from antisera by immunoaffinity chromatography using antigens coupled to agarose beads. |
| Storage Buffer | 0.01 M Sodium phosphate, 0.25 M NaCl, 50% glycerol, 3 mg/ml BSA, pH 7.6. |
| Storage Instructions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. |
| Stabilizer | 3 mg/ml BSA |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| RRID | AB_2890886 |
| Note | This product is for research use only,not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
Publications
| Title |
|---|
Nat Commun Mrg15 stimulates Ash1 H3K36 methyltransferase activity and facilitates Ash1 Trithorax group protein function in Drosophila. |
EMBO Rep A CRISPR-Cas9 screen reveals genetic determinants of the cellular response to decitabine |
Cell Mol Life Sci Soluble RAGE attenuates myocardial I/R injuries via FoxO3-Bnip3 pathway. |
Sci Rep An investigation into the mechanism for Kaempferol improving melanocyte death based on network Pharmacology and experimental verification |
J Biol Chem CDC25B induces cellular senescence and correlates with tumor suppression in a p53-dependent manner. |
Cancer Cell Int Spider venom components decrease glioblastoma cell migration and invasion through RhoA-ROCK and Na+/K+-ATPase β2: potential molecular entities to treat invasive brain cancer. |