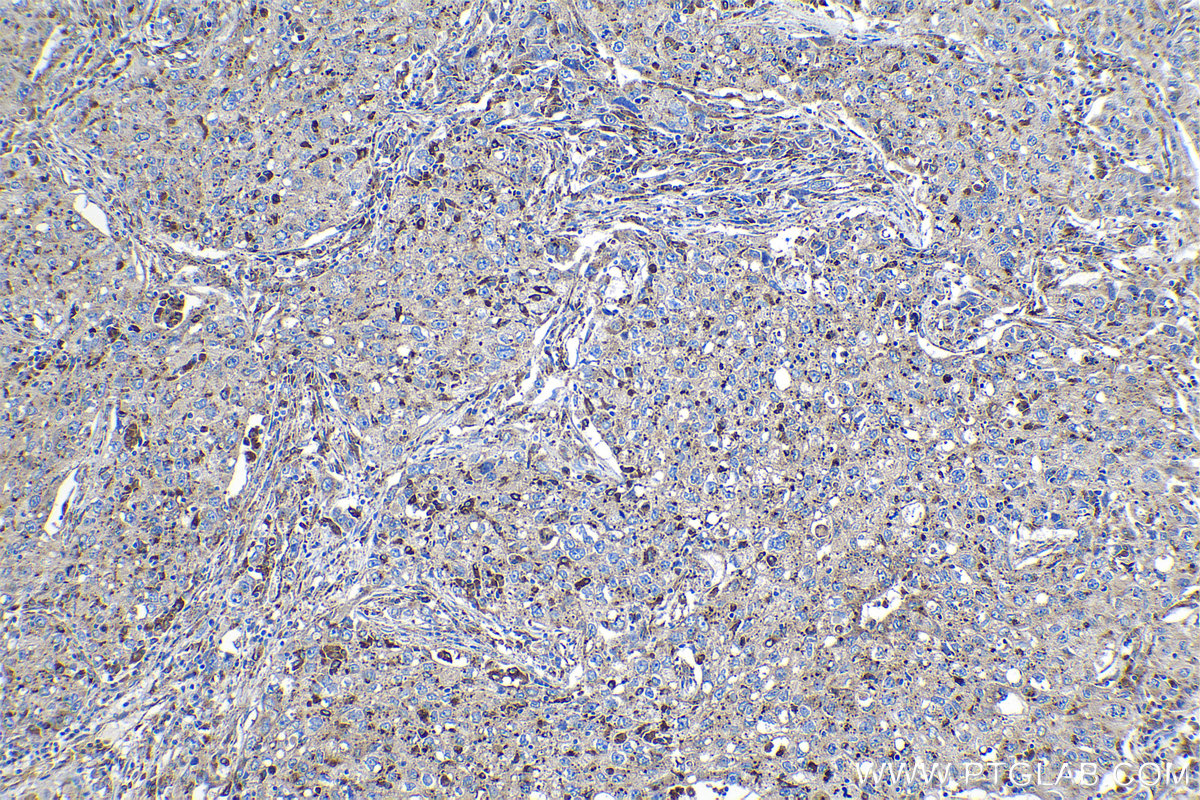
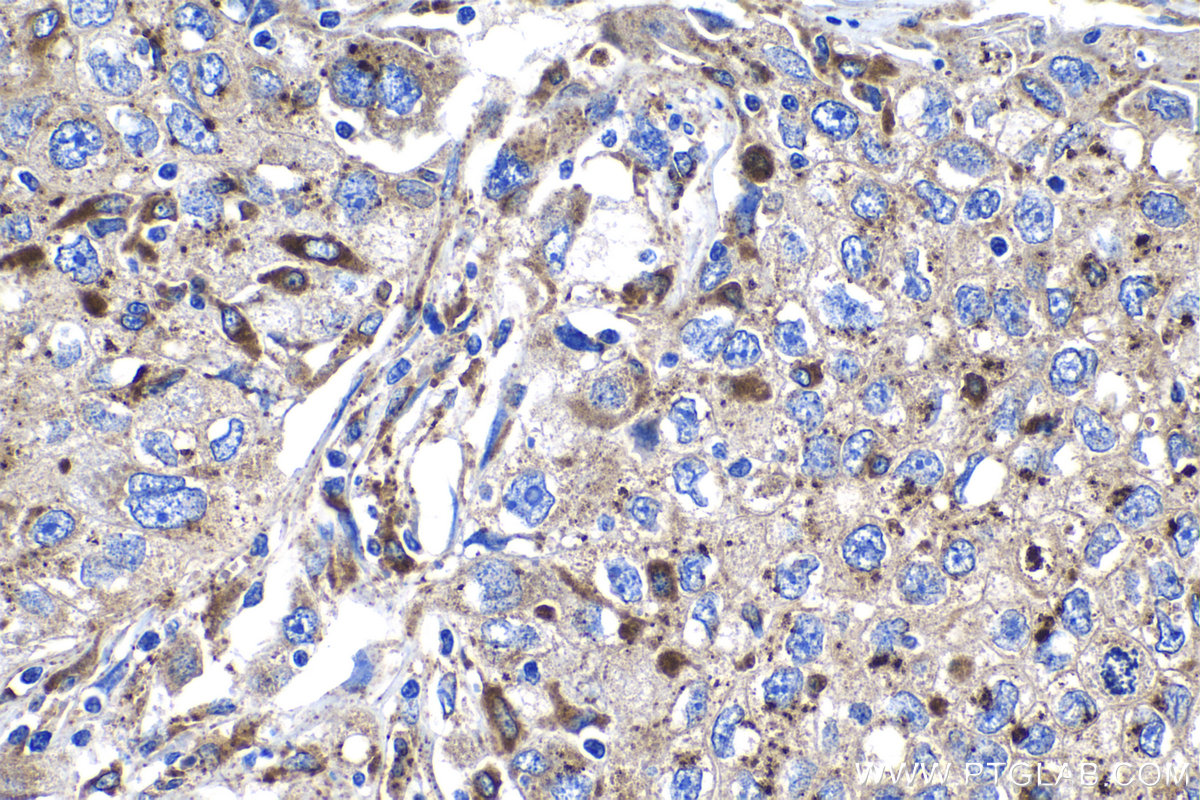
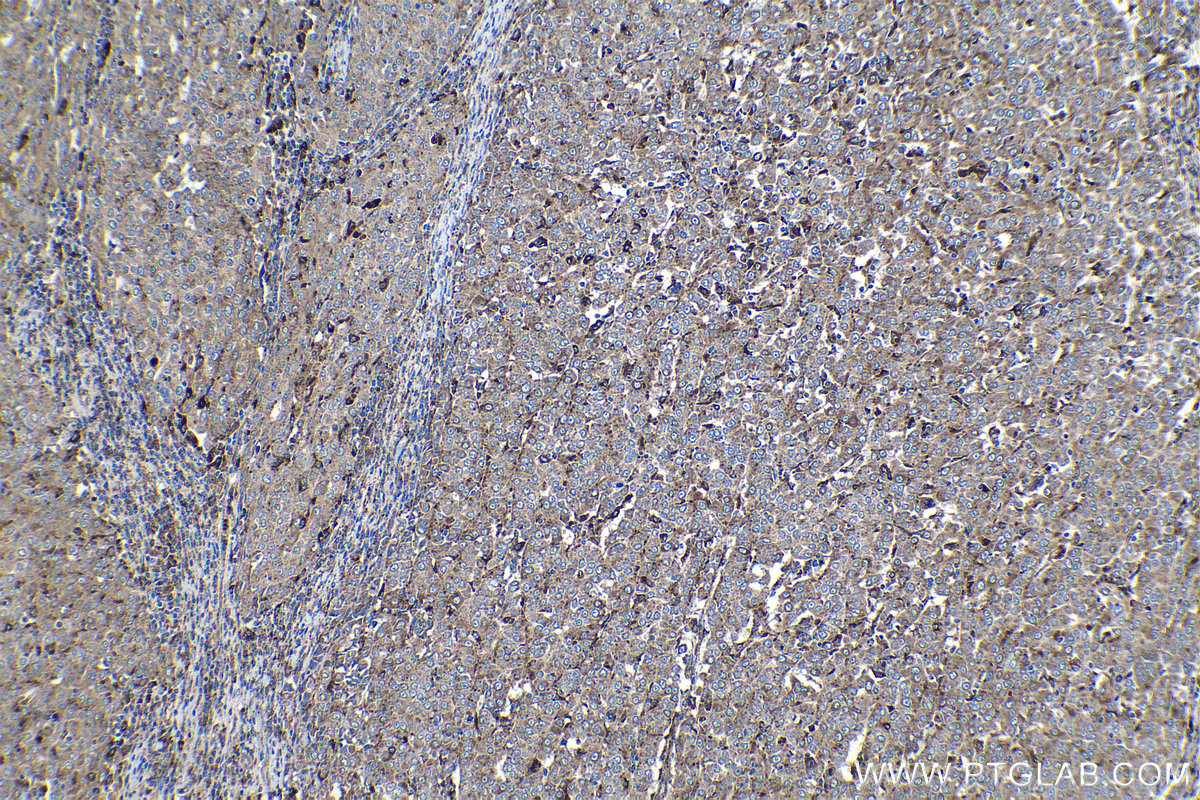
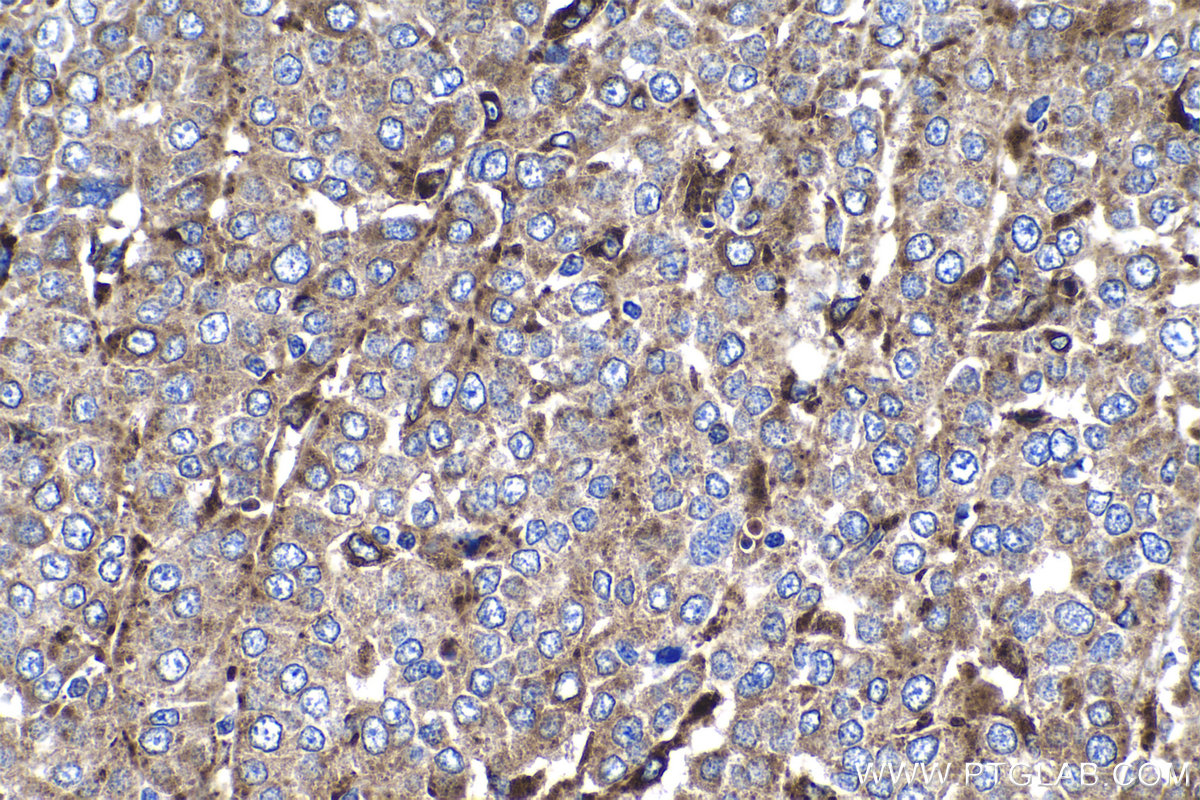
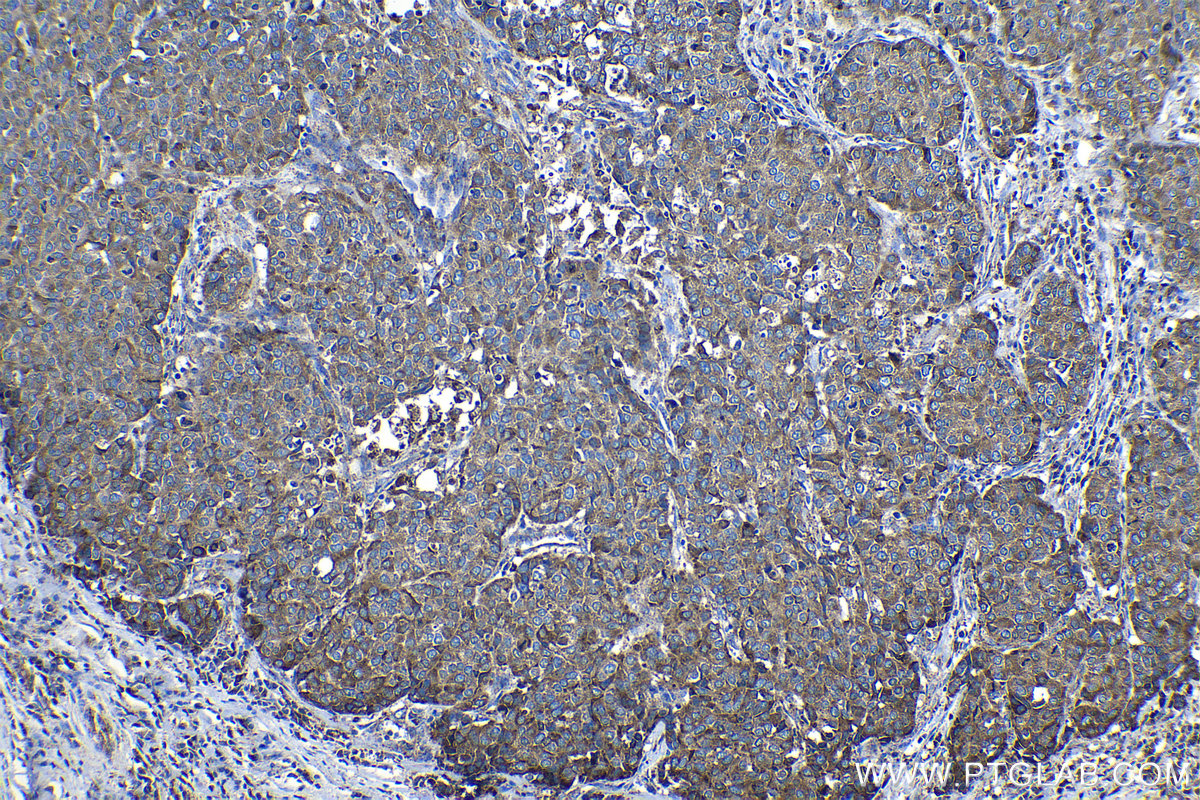
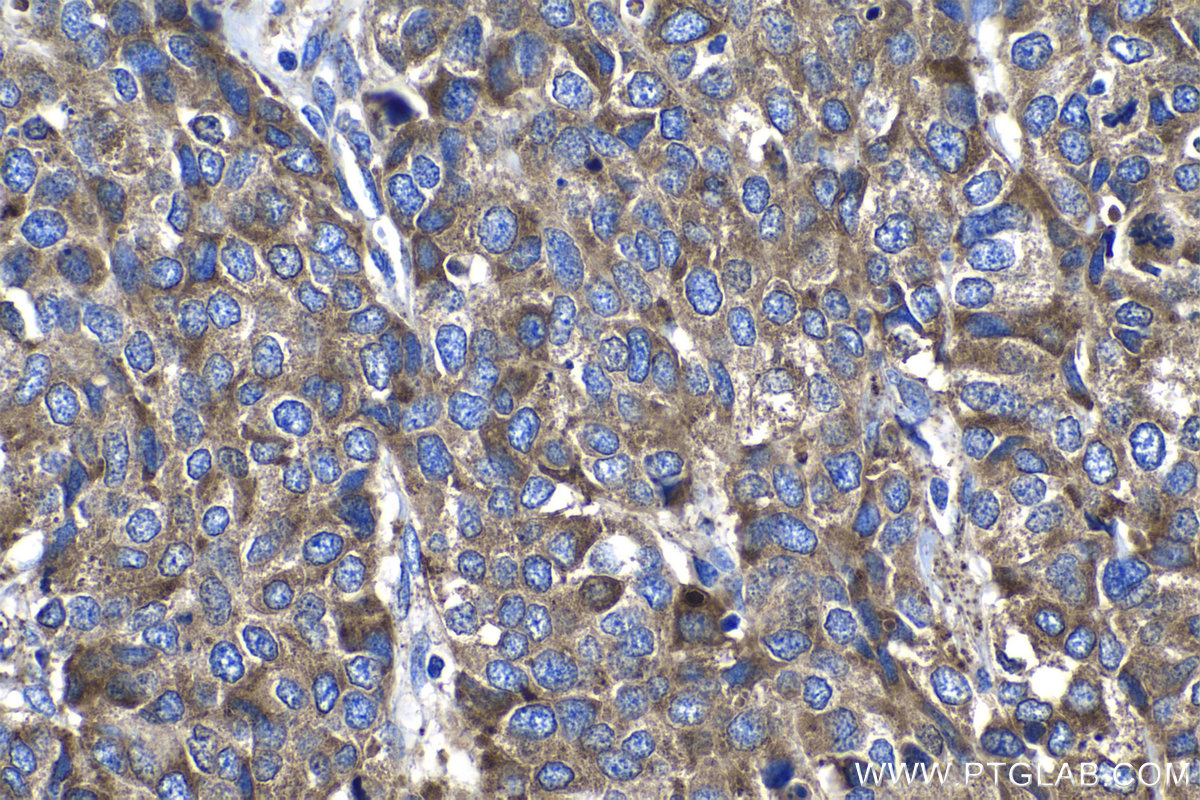
验证数据展示
产品信息
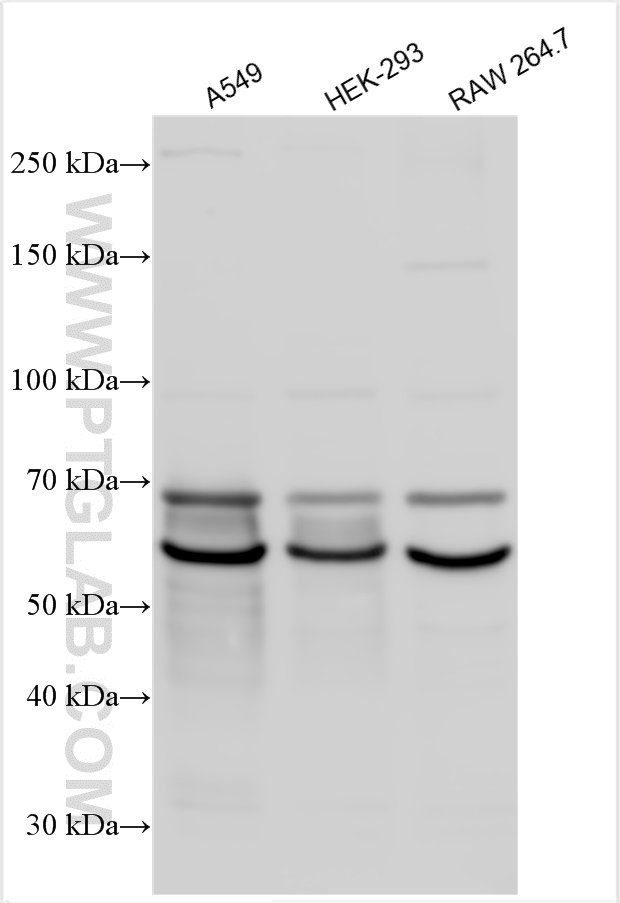
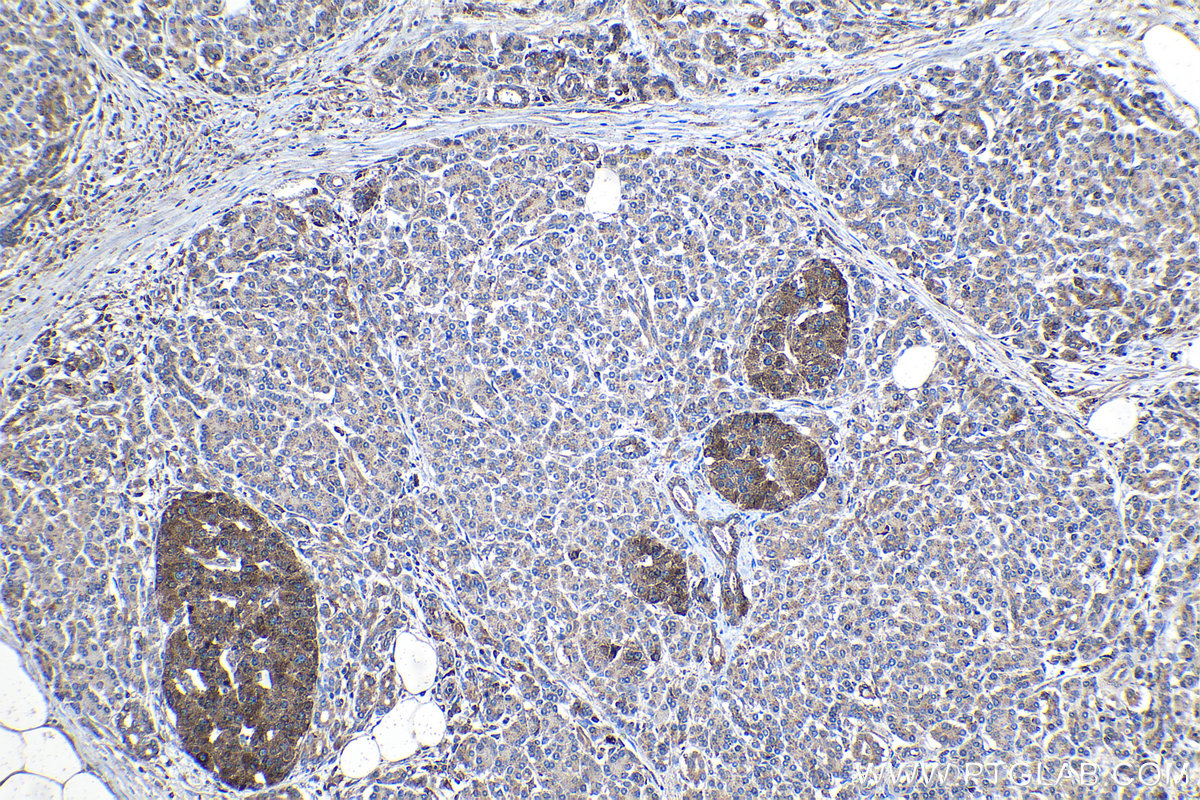
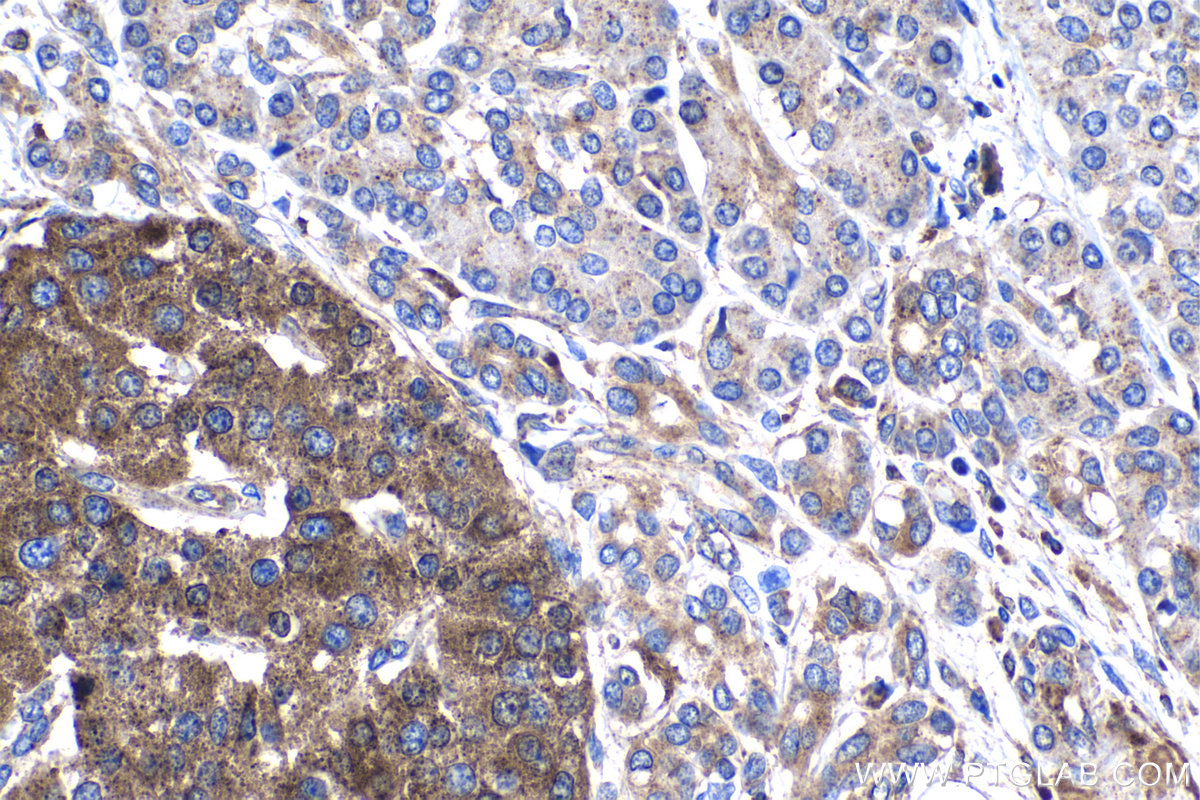
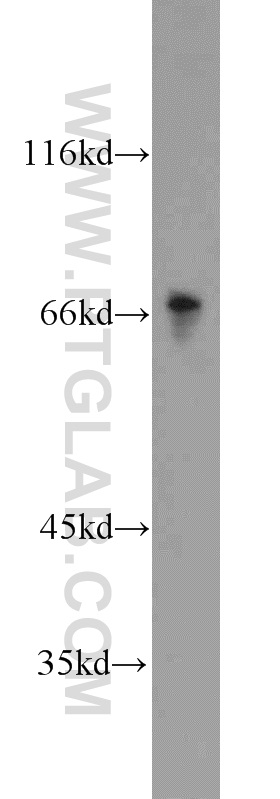
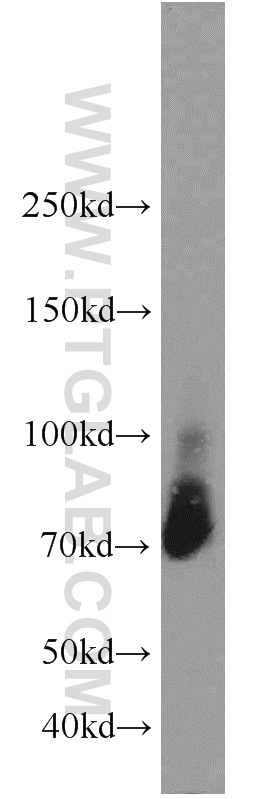
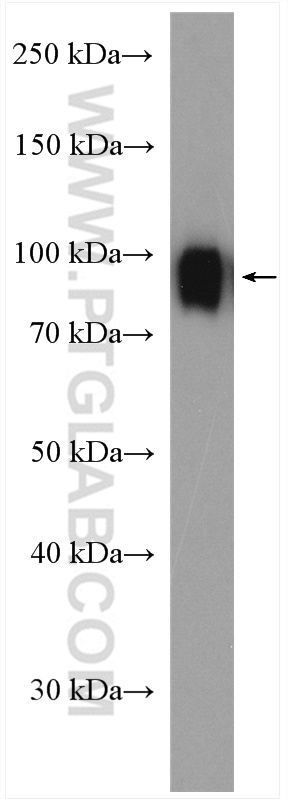
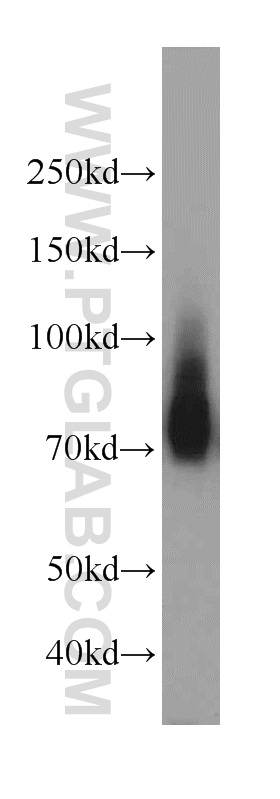
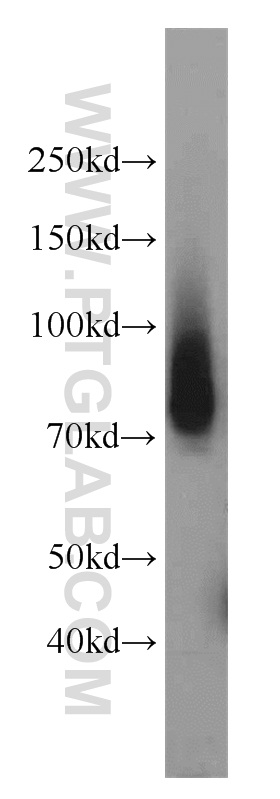
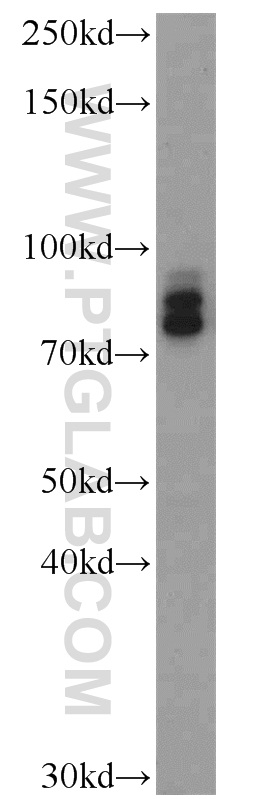
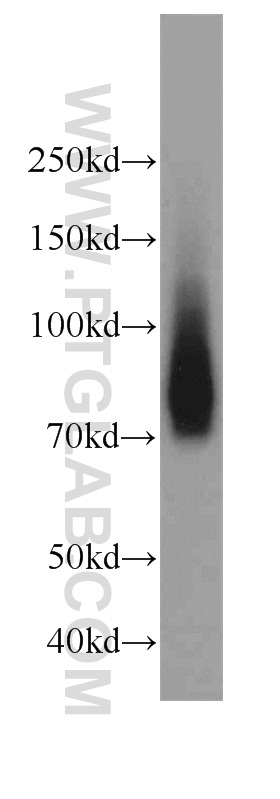
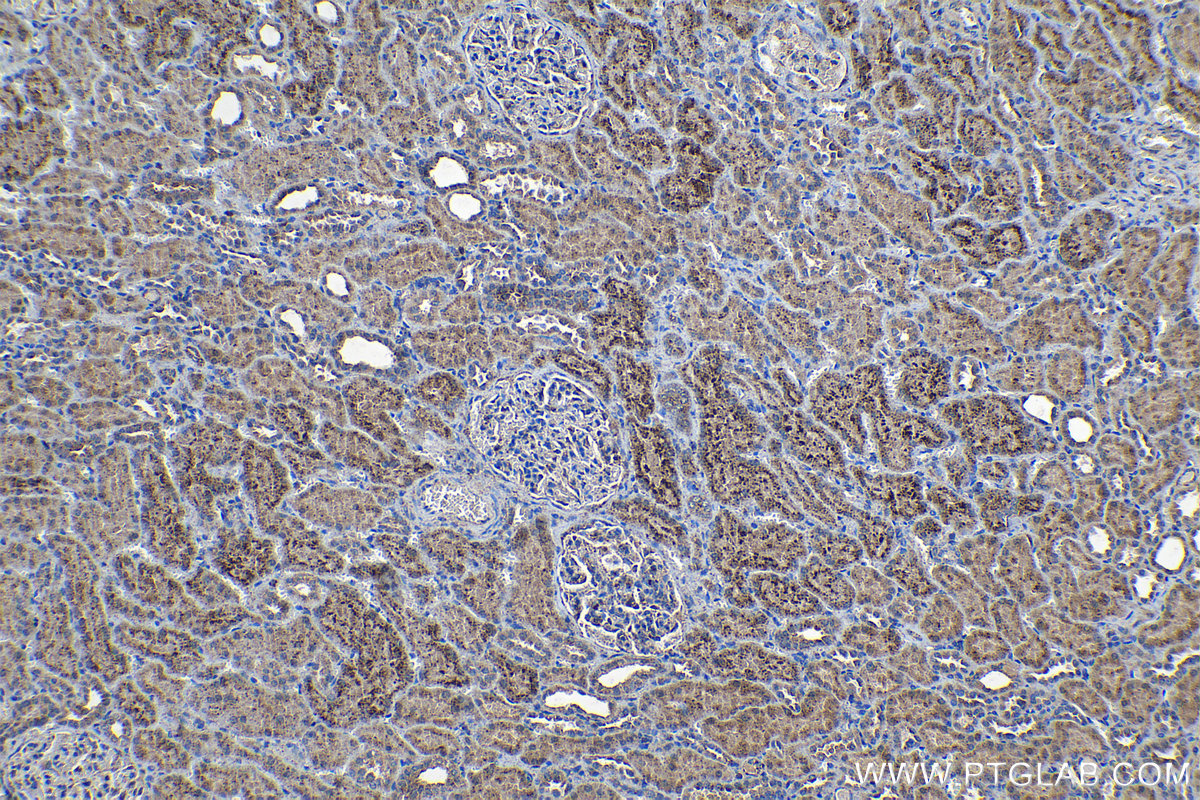
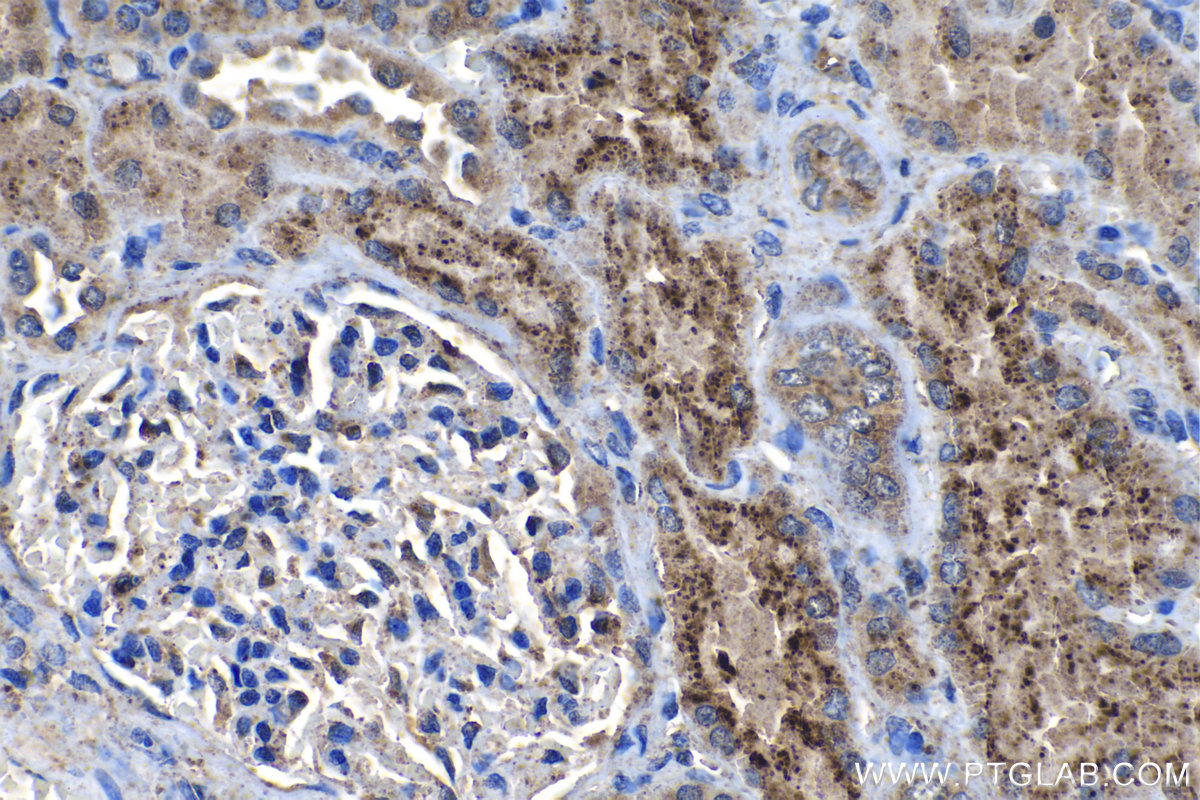
18410-1-PBS targets Progranulin/PGRN in WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat |
| 免疫原 | Progranulin/PGRN fusion protein Ag13178 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | granulin |
| 别名 | granulin, Granulin-1, Granulin precursor, Glycoprotein of 88 Kda, Glycoprotein 88 |
| 计算分子量 | 64 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 60-70 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC000324 |
| 基因名称 | Granulin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2896 |
| RRID | AB_10598161 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P28799 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
GRN, also known as PGRN or PCDGF, is a cysteine-rich protein of 68.5 kDa that is typically secreted into a highly glycosylated 88 kDa form. PGRN is a unique growth factor that plays an important role in cutaneous wound healing. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and promotes cell proliferation. When PCDGF is degraded to several 6-25 kDa fragments, called granulins (GRNs) by neutrophil proteases, a pro-inflammatory reaction occurs. PGRN is widely expressed, particularly in epithelial cells, immune cells, neurons, and chondrocytes. High levels of PGRN expression have been reported in human cancers, and its expression is closely correlated with the development and metastasis of several cancers. The recent discovery that mutations in the gene encoding for pro-granulin (GRN) cause frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), and other neurodegenerative diseases leading to dementia, has brought renewed interest in progranulin and its functions in the central nervous system.