Re-ChIP-IT®
Re-ChIP-IT-AM524
Synonyms
| Name | Format | Cat No. | Price | Delivery |
|---|
Overview
When performing chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP, chromatin IP) experiments, it is often useful to prove that two different proteins or histone modifications are present at the same site in the genome. Or, you may want to determine if a protein coincides with a specific histone modification at the same regulatory element. Re-ChIP (aka Sequential ChIP, Chromatin Re-IP and ChIP Re-ChIP) is a relatively new technique that enables sequential chromatin immunoprecipitations to be performed using two different antibodies so that you can assay for the simultaneous presence of two proteins or distinct histone modifications at the same genomic region of interest. The Active Motif Re-ChIP-IT® Kit utilizes the efficient magnetic bead-based protocol used to develop our ChIP-IT® Express Kits to provide a convenient kit for Re-ChIP that works with chromatin prepared using either sonication or enzymatic shearing, is compatible with multi-channel pipetting and requires fewer cells than other methods.
To help you improve your results, Active Motif offers a number of ChIP Accessory Products that were designed to make it even easier for you to perform successful sequential ChIP when working with Re-ChIP-IT:
Documents (6)
Description
Identify protein co-localization in vivo with Re-ChIP-IT
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is extremely useful for studying chromatin biology and transcriptional regulation because it enables the localization of chromatin proteins, modified histones and transcription factors that are bound to specific DNA regions in specific cells. Furthermore, because protein/DNA interactions are fixed while in an endogenous, chromosomal context, ChIP results reflect the influence of chromosomal topology and the effects of cellular regulatory proteins.
The Re-ChIP-IT® Kit makes it possible to identify the simultaneous binding of two transcription factors or two histone modifications on a DNA fragment of interest. Chromatin that has been immunoprecipitated is removed from the magnetic beads with a special buffer that prevents the majority of the first antibody from participating in the second IP reaction. The chromatin is then desalted and a second ChIP is performed using a different antibody from the first. The cross-links of these sequentially immunoprecipitated protein-DNA complexes are then reversed and the DNA is analyzed by PCR, similar to conventional ChIP samples.
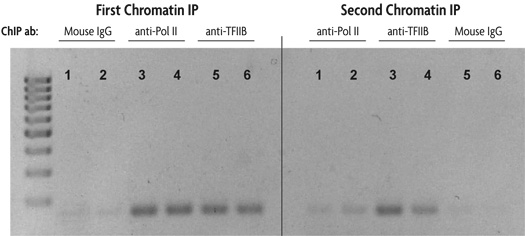
Figure 1: Sequential chromatin immunoprecipitation using Re-ChIP-IT.
HeLa cells were fixed for 10 minutes with 1% formaldehyde and then chromatin was prepared by sonication shearing (5 pulses). ChIP was performed in duplicate on chromatin isolated from 750,000 cells. DNA was analyzed by PCR using GAPDH positive control primers (36 cycles, Tm = 59˚C). This figure was selected to demonstrate the successful sequential chromatin IP with two different antibodies using the Re-ChIP-IT Kit. The antibodies used are listed above the duplicate lanes.
The lane numbers are the same in each panel to indicate that the DNA is from the same chromatin sample. The left panel shows the results of PCR performed on an aliquot of DNA removed from the experiment after the first ChIP step, the right panel represents PCR results on DNA from chromatin samples after both ChIP steps. For example, chromatin samples subjected to first ChIP using Mouse IgG as a negative control (lanes 1 and 2 in the left panel) were then subjected to a second ChIP with an RNA Pol II antibody (lanes 1 and 2 in the right panel). Chromatin samples in which Mouse IgG was used as either the first antibody (lanes 1 and 2) or second antibody (lanes 5 and 6) show little amplification of GAPDH DNA in either the left (first ChIP) or right panel (first and second ChIP). Chromatin samples in which the first antibody used was anti-RNA Pol II and the second antibody was anti-TFIIB (lanes 3 and 4) show good amplification of GAPDH DNA after the second ChIP (right panel) indicating the co-localization of RNA Pol II and TFIIB at the same region of the GAPDH promoter.
Overview
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) involves the immunoprecipitation of protein/DNA complexes that have been stabilized via cross-linking. It offers a versatile solution by combining the specificity of immunoprecipitation, the sensitivity of PCR and the screening power of array profiling. However, ChIP can be technically challenging and difficult to validate without well-proven reagents. By providing proven antibodies, reagents and controls, ChIP-IT Kits guarantee the best results possible.
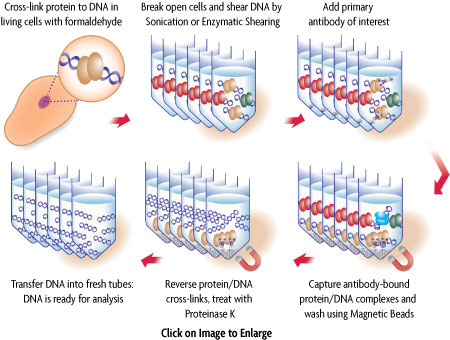
Figure 1: Schematic of chromatin immunoprecipitation using ChIP-IT Express.
In ChIP, intact cells are fixed using formaldehyde, which cross-links and therefore preserves protein/DNA interactions. DNA is then sheared into small uniform fragments and the DNA/protein complexes are immunoprecipitated using an antibody directed against the DNA-binding protein of interest. Following immunoprecipitation, the DNA is washed, cross-linking is reversed, and the proteins are removed by Proteinase K treatment. In standard ChIP methods, the DNA is then cleaned up using DNA purification columns. However, this DNA purification step in not necessary when using ChIP-IT Express (Figure 1). The DNA is then screened to determine which genes were bound by the protein of interest.
In Re-ChIP-IT, following formaldehyde fixation of the cells, chromatin is sheared and incubated with the first antibody, and antibody-bound protein/DNA complexes are precipitated through use of magnetic Protein G-coated beads. The captured “First ChIP” chromatin is then eluted with a specialized buffer that prevents the first antibody from participating in the second ChIP reaction. After the second ChIP reaction is completed with a different antibody, the cross-links are reversed and the released DNA is analyzed by PCR to examine the co-localization of the two proteins at a specific region of interest.
Why use ChIP-IT® Kits?
- Complete solution – all critical reagents needed are supplied
- Direct measurement of protein/DNA interactions, not just histone modifications
- Compatible with genome-wide profiling or selective PCR-based approaches
- No need to optimize reagents and protocol
- No phenol/chloroform extractions required – DNA purification step eliminated in ChIP-IT Express
Classically, ChIP has been performed with antibodies directed against abundant chromatin components, such as acetylated histones. While this yields information about transcriptional activity of promoters, it does not reveal which transcription factor is bound to the promoter(s) of interest. In contrast, ChIP using transcription factor-specific antibodies enables direct monitoring of transcription factor/DNA interactions. Unfortunately, this is technically more challenging than classical ChIP, and requires the preparation of several complicated buffers, inhibitor cocktails and blocking reagents. In addition, result validation is difficult without antibodies, controls and a protocol proven to work in ChIP (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Improved chromatin immunoprecipitation using ChIP-IT Express.
A PCR analysis of immunoprecipitated DNA is shown. This figure was selected to demonstrate the efficiency of the ChIP-IT Express Kit. Typically ChIP requires 2 million cells per reaction. However, we have been able to reduce the amount of starting material and observed positive ChIP data from 100,000 cells or less.
HeLa cells were fixed for 10 minutes with 1% formaldehyde and then chromatin was prepared by sonication shearing (5 pulses). ChIP was performed in duplicate on chromatin isolated from 100,000 and 750,000 cells using a Negative Control IgG and an RNA pol II antibody. The DNA isolated through these ChIP reactions was then analyzed by 36 cycles of PCR using GAPDH positive control primers. (These antibodies and primers are available as the ChIP-IT Control Kit – Human. Kits for mouse and rat are also available.) Ten µl of each PCR was separated on a 1% agarose gel and visualized by UV-illumination following ethidium bromide staining. PCR using the GAPDH primers on DNA isolated with the RNA pol II antibody reproducibly generated more product than similar reactions performed on DNA isolated using the Negative Control IgG.These results demonstrate that ChIP performed with RNA pol II antibody greatly enriched for GAPDH promoter DNA, while ChIP performed with negative IgG did not.
Contents
Flexible ordering options
The Re-ChIP-IT Kit provides sufficient components to perform 25 Re-ChIP reactions. The Re-ChIP-IT Kit does not include the shearing components found in the ChIP-IT Express Kits. For this reason, the ChIP-IT Express Shearing & Enzymatic Shearing Kits are sold separately. We recommend that you also purchase whichever ChIP-IT Control Kit is appropriate for your sample type, as using proven controls helps in troubleshooting, interpreting your results and validating antibodies for use in ChIP.
Contents & Storage
Protein G Magnetic Beads, LSV Protein G Magnetic Beads, Re-ChIP Purification Columns, ChIP Buffer 1, ChIP Buffer 2, Re-ChIP-IT Elution Buffer, Elution Buffer AM2, Reverse Cross-linking Buffer, Buffered NaCl, 5 M NaCl, Proteinase K, Proteinase K Stop Solution, Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, 10X PCR Buffer, 10X PCR Loading Dye, Bar Magnet, 15 ml Conical Tube, Mini Glue Dots, DEPC-treated Water, Siliconized 1.7 ml microfuge tubes, 0.2 ml PCR stripwell tubes
References
Some select publications are listed below.
- “Merkel cell polyomavirus recruits MYCL to the EP400 complex to promote oncogenesis.” by Cheng et al. (2017) PLoS Pathogens 13(10): e1006668.
- “Distinctive patterns of epigenetic marks are associated with promoter regions of mouse LINE-1 and LTR retrotransposons.” by Rangasamy. (2013) Mob DNA 4(1):27.
- “The chromatin modification by SUMO-2/3 but not SUMO-1 prevents the epigenetic activation of key immune-related genes during Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus reactivation.” by Chang et al. (2013) BMC Genomics 14(824).
- “Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) silences genes responsible for neurodegeneration.” by von Schimmelmann et al. (2016) Nat Neurosci 19(10):1321-30.