SAAL1 Polyclonal antibody
SAAL1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, ELISA
Host / Isotype
Rabbit / IgG
Reactivity
human and More (1)
Applications
WB, ELISA
Conjugate
Unconjugated
验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
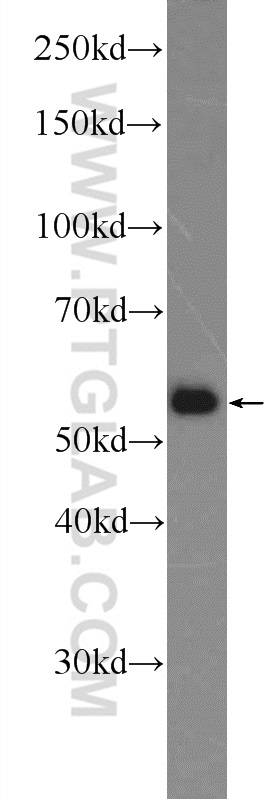
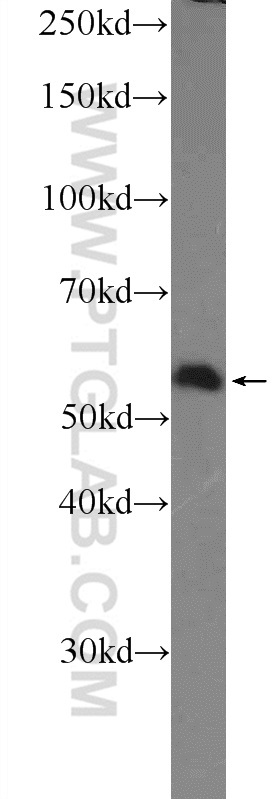
| Positive WB detected in | HepG2 cells, HEK-293 cells |
推荐稀释比
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
发表文章中的应用
| WB | See 2 publications below |
产品信息
25467-1-AP targets SAAL1 in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Applications | WB, ELISA Application Description |
| Cited Applications | WB |
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Immunogen | SAAL1 fusion protein Ag22186 种属同源性预测 |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Full Name | serum amyloid A-like 1 |
| Synonyms | Synoviocyte proliferation-associated in collagen-induced arthritis protein 1, SPACIA1, serum amyloid A like 1, Protein SAAL1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 475 aa, 54 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 54-55 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC012010 |
| Gene Symbol | SAAL1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 113174 |
| RRID | AB_2880094 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q96ER3 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for SAAL1 antibody 25467-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
BMC Cancer The effects of the prognostic biomarker SAAL1 on cancer growth and its association with the immune microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma | ||
Front Pharmacol Bicyclol attenuates high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis through modulating multiple pathways in mice |