验证数据展示
产品信息
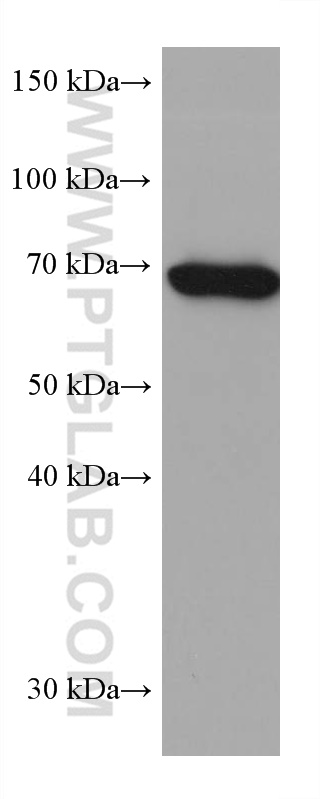
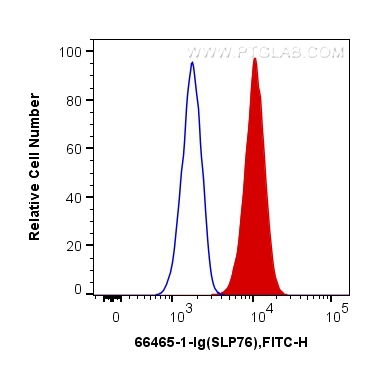
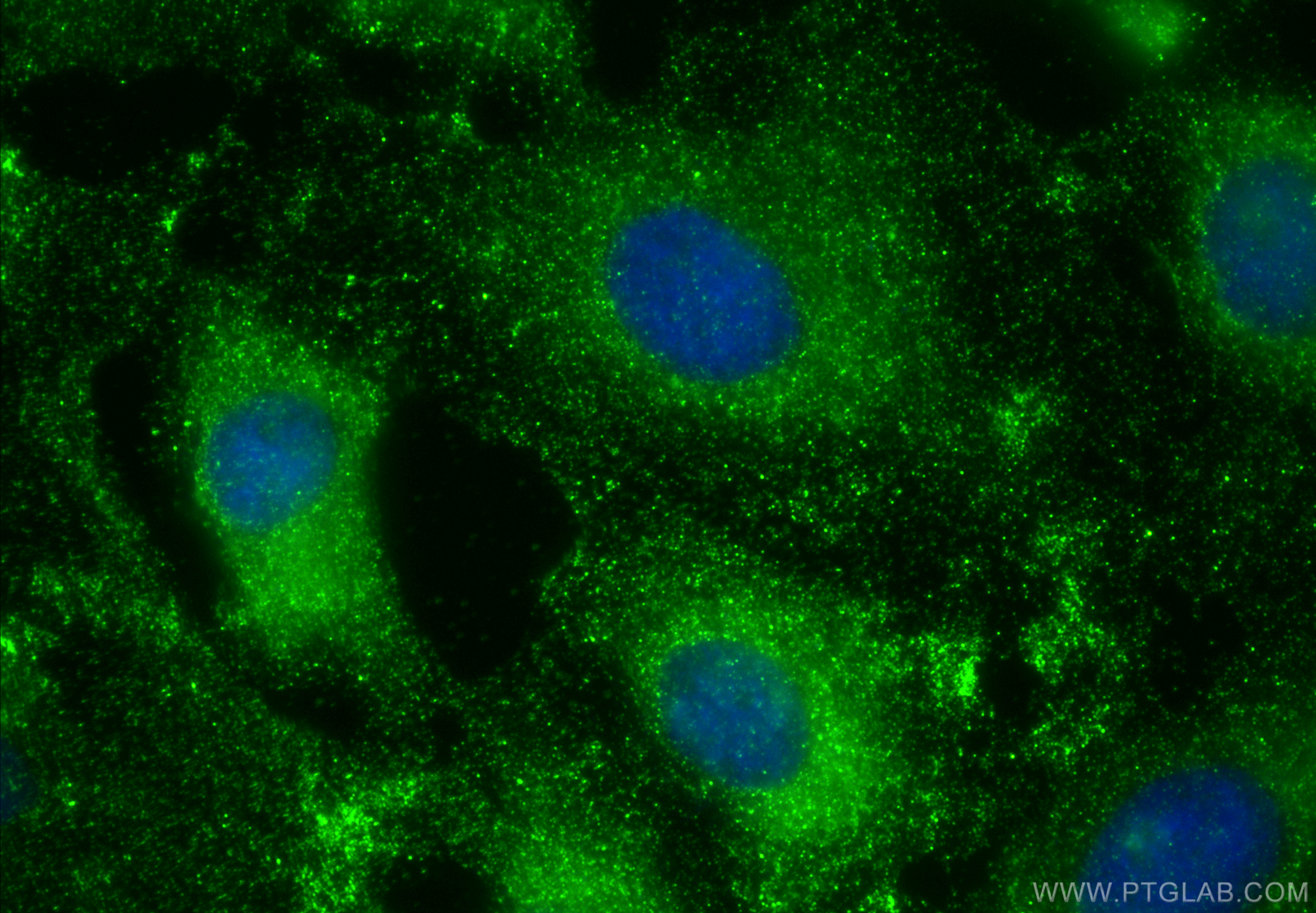
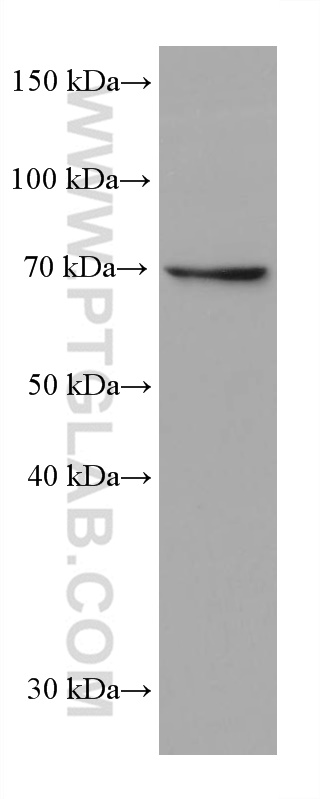
66465-1-PBS targets SLP76 in WB, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 | SLP76 fusion protein Ag3432 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG1 |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2 (SH2 domain containing leukocyte protein of 76kDa) |
| 别名 | LCP2, 4H10B1, SLP 76 tyrosine phosphoprotein, SLP 76, SH2 domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa |
| 计算分子量 | 533 aa, 60 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 76 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC016618 |
| 基因名称 | SLP76 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3937 |
| RRID | AB_2881833 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q13094 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
LCP2, also named as SLP76, is an adapter protein that acts as a substrate of the T cell antigen receptor (TCR)-activated protein tyrosine kinase pathway. It contains an N-terminal leucine Zip motif, a tyrosine-rich domain, a proline-rich domain and a C-terminal SH2 domain. It is constitutively associated with the growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (Grb2)-related adapter protein 2 (Grap2, a.k.a. GADS) through the interaction of its proline residues with one of the SH3 domains of Grap2. SLP76 associates with growth factor receptor bound protein 2 (Grap2), and is thought to play a role TCR-mediated intracellular signal transduction. SLP76 is also expressed by mast cells, and mast cell activation was markedly impaired in SLP76-deficient mice.