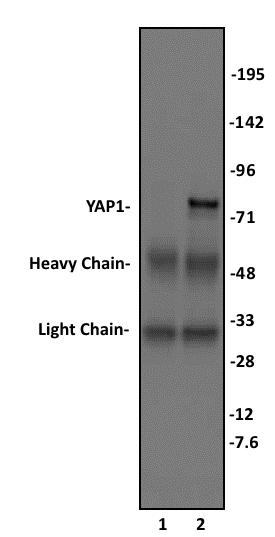
YAP1 antibody (pAb)
Host / Isotype
Rabbit / IgG
Reactivity
Human
Applications
IP, WB
Cat No : 61293,61294 61293
Synonyms
验证数据展示
产品信息
| Tested Applications |
IP, WB
Applications Validated by Active Motif: IP: 10 ul per IP WB: 1:500 - 1:1,000 dilution |
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | This YAP1 antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to the C-terminal region of human YAP1. |
| Full Name | YAP1 antibody (pAb) |
| Synonyms | YAP1, Yes-associated protein 1, YAP, YKI, YAP2, YAP65, antibody, polyclonal, pAb, sample, western blotting, hippo, taz/wwtr1, taz, wwtr1, pax8, nkx2-1, ttft, smad, stem cell, stem, stem cells, immunoprecipitation, ip |
| Molecular weight | 75 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NP_001123617 | RRID | AB_2614990 | Purification Method | Affinity Purified |
| Buffer | Purified IgG in PBS with 30% glycerol and 0.035% sodium azide. Sodium azide is highly toxic. |
| Storage | Some products may be shipped at room temperature. This will not affect their stability or performance. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles by aliquoting items into single-use fractions for storage at -20°C for up to 2 years. Keep all reagents on ice when not in storage. |
背景介绍
YAP1 (Yes-associated protein 1, YAP, YKI, YAP2, YAP65) is a transcriptional regulator which can act both as a coactivator and a corepressor and is the critical downstream regulatory target in the Hippo signaling pathway that plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. Is a critical modulator of epidermal stem cell proliferation. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein MST1/MST2, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP1 oncoprotein and WWTR1/TAZ. Plays a key role to control cell proliferation in response to cell contact. Phosphorylation of YAP1 by LATS1/2 inhibits its translocation into the nucleus to regulate cellular genes important for cell proliferation, cell death, and cell migration. The presence of TEAD transcription factors are required for it to stimulate gene expression, cell growth, anchorage-independent growth, and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) induction.