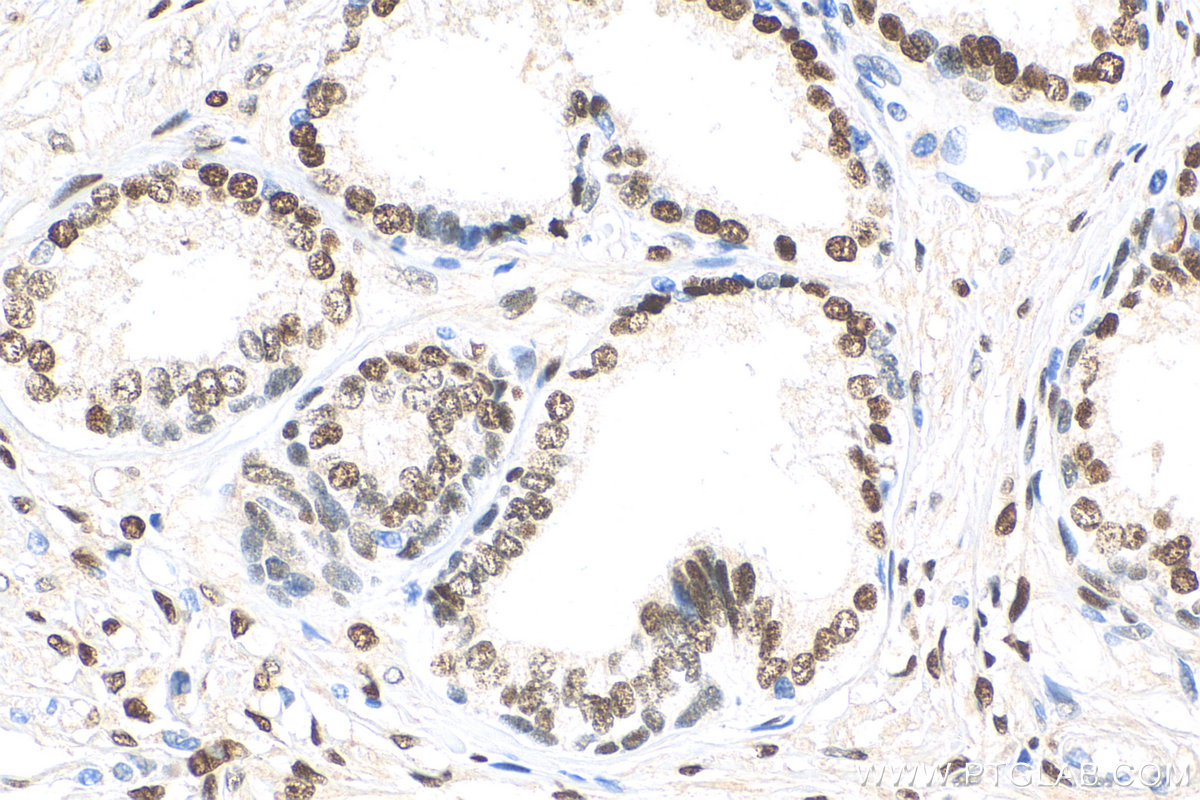
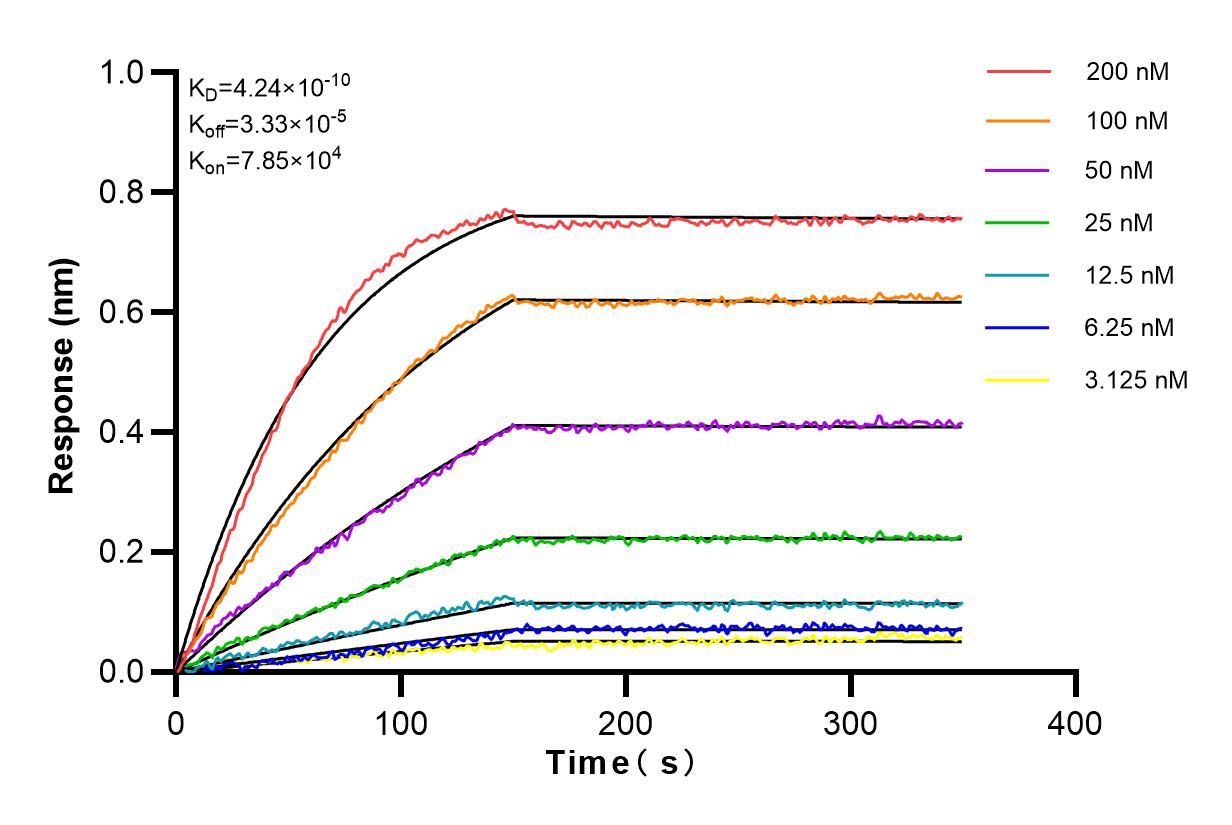
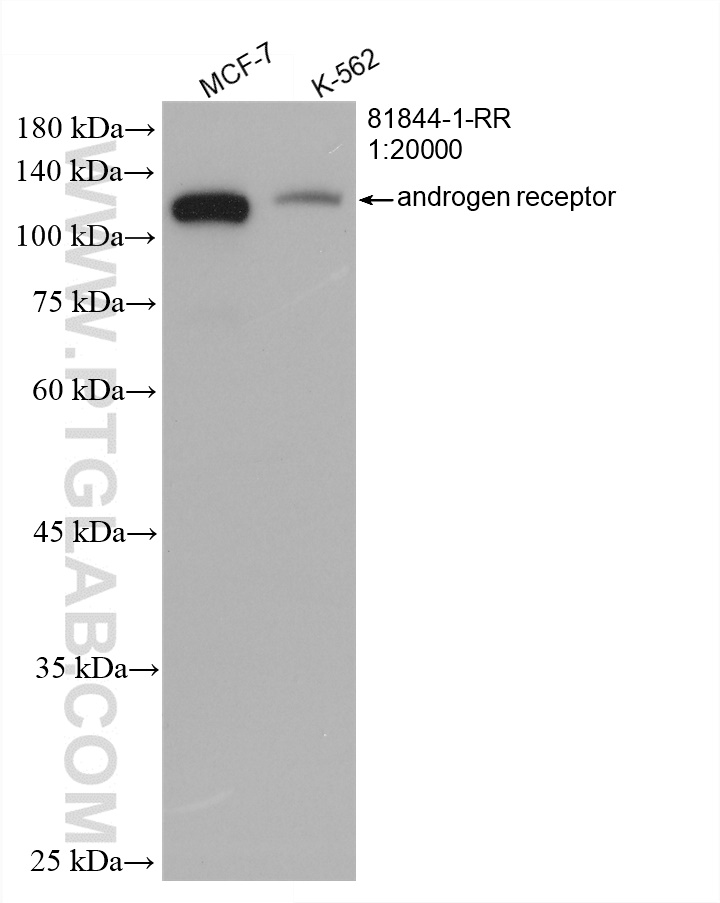
验证数据展示
产品信息
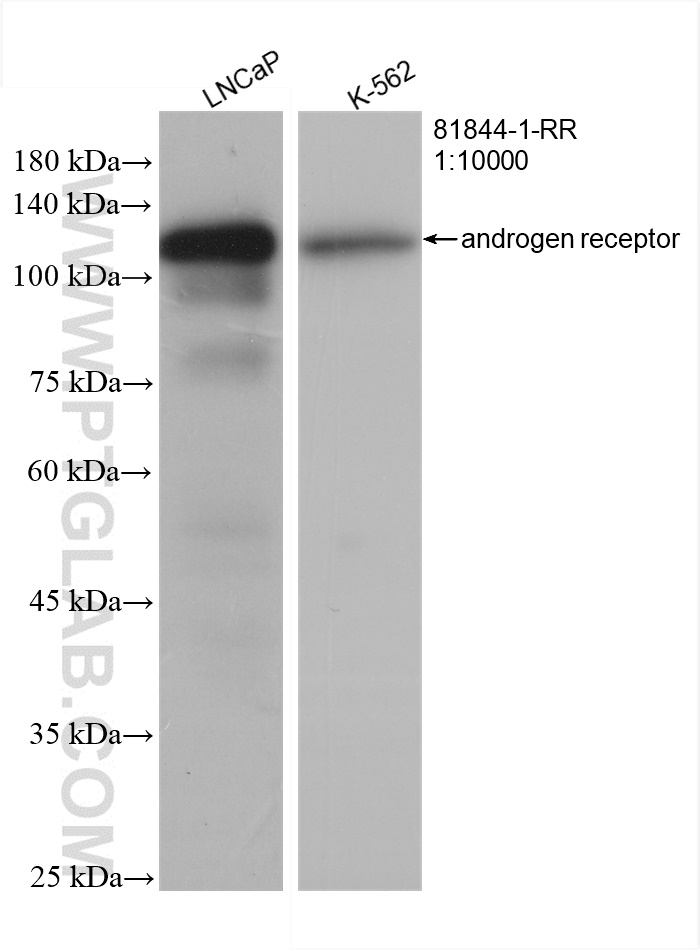
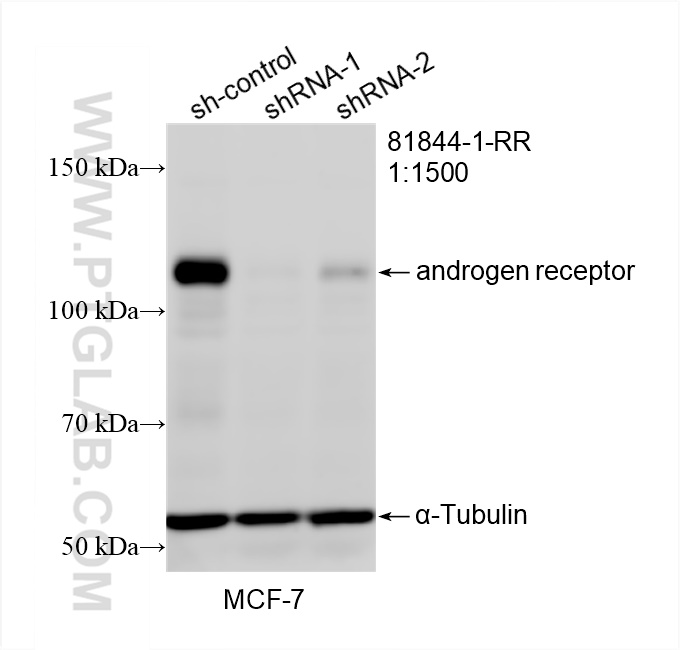
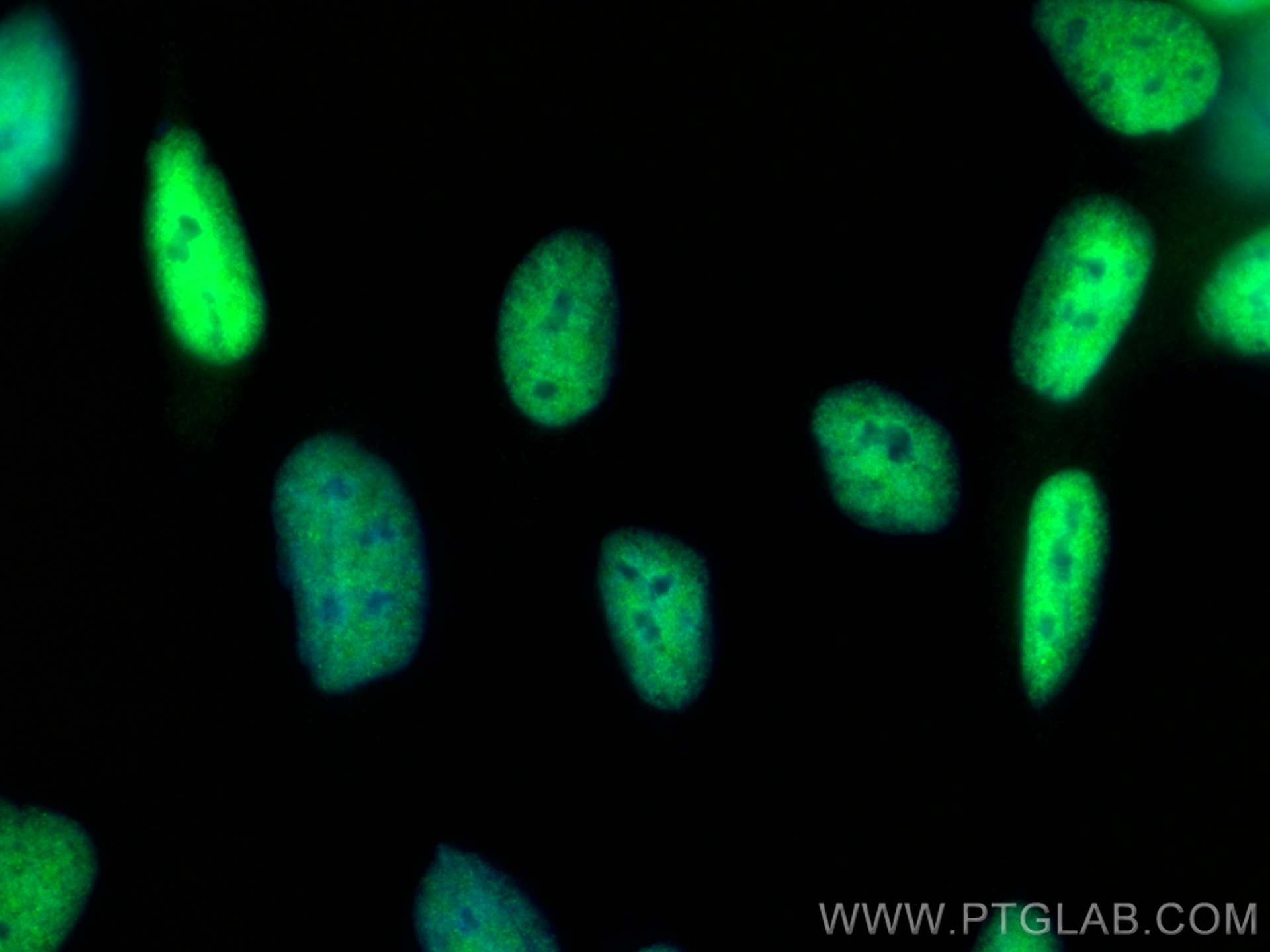
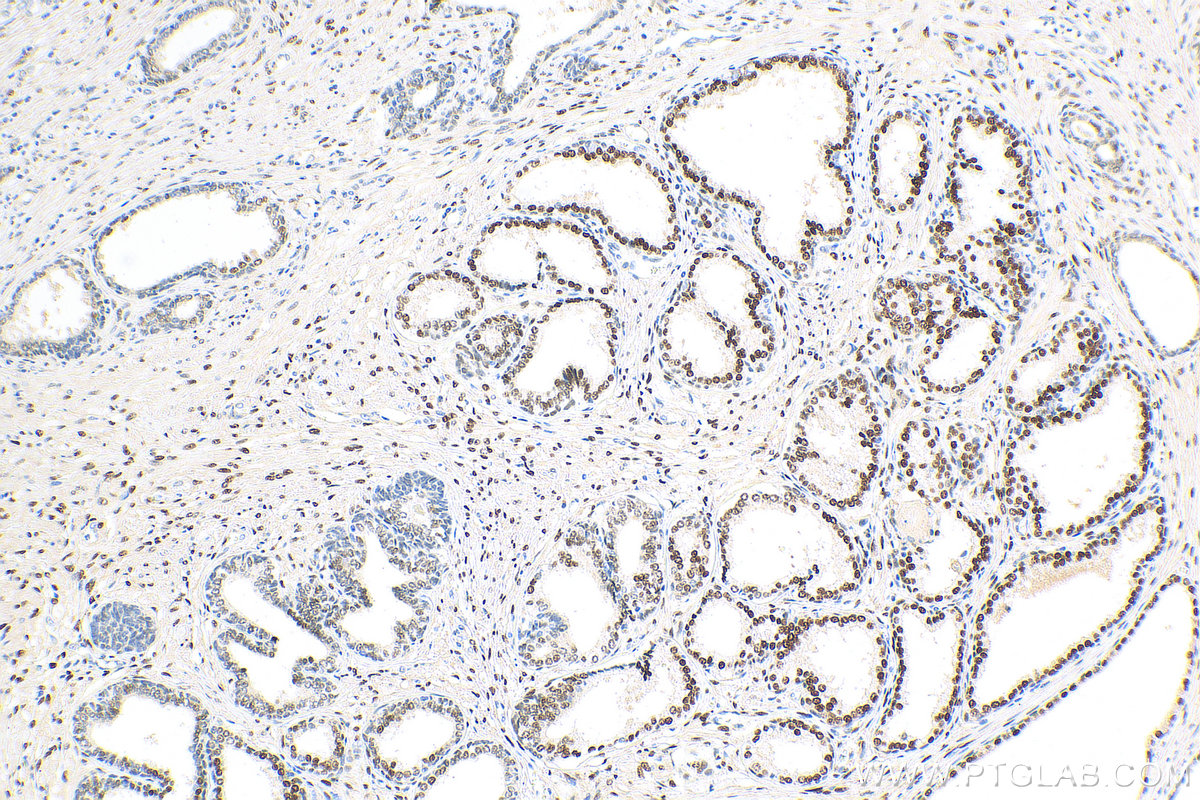
81844-1-PBS targets androgen receptor in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 | androgen receptor fusion protein Ag17291 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Recombinant |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | androgen receptor |
| 别名 | AR, androgen receptor,AR, NR3C4, DHTR, 4O18 |
| 计算分子量 | 914 aa, 99 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 110-120 kD |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC132975 |
| 基因名称 | AR |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 367 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P10275 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
Androgen receptor (AR) is a steroid hormone receptor for androgenic hormones such as 17β-Hydroxy-3-oxo-4-androstene and DHT. AR plays a vital role in developing and maintaining male sex phenotypes as well as an additional role in regulating bone metabolism.
1. What is the molecular weight of AR? Are there any isoforms of AR?
The molecular weight of full-length androgen receptor (AR-B) is 110 kDa. An additional variant, AR-A, has an 87 kDa size and lacks the N-terminal 187 amino acids of AR-A (PMID: 8108393). Recently, more splice variants of AR have been discovered, raising protein products of around 80 kDa length (PMID: 19244107), as well as an AR45 variant of 45 kDa size (PMID: 15634333). AR splice variants differ in their cell line-specific expression (PMID: 24570075).
2. What is the subcellular localization of AR?
AR can be present in either or both of the cytoplasm and nucleus. In androgen-deprived cells, AR is found predominantly in the cytoplasm, while stimulation by androgens causes enrichment of androgen-bound AR in the nucleus. AR shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus and its phosphorylation state has an impact on subcellular localization (PMID: 16282370).
3. Is AR post-translationally modified?
Post-translational modifications of the AR include phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, SUMOylation, and ubiquitination (PMID: 21820033). These modifications have an impact on receptor stability, activity, and can change the observed molecular weight of the AR.
4. How to study AR signaling in cell culture?
It is important to control levels of cell stimulation while also looking at AR signaling. Fetal bovine serum (FBS) that is typically used in cell culture contains low levels of 17β-Hydroxy-3-oxo-4-androstene that are enough to stimulate the growth of prostate cells (PMID: 19676093), including the LNCaP cell line that is a commonly used human prostatic carcinoma cell model (PMID: 6831420). One possibility for complete 17β-Hydroxy-3-oxo-4-androstene deprivation is to use charcoal stripped FBS that removes lipophilic agents, including androgens. It is also not recommended to use phenol red in your medium because it is a weak estrogen (PMID: 3458212). Cell stimulation is often conducted by DHT.
5. What is the role of AR in prostate cancer?
AR plays a key role in the development and physiology of the prostate gland, and also cancer progression (PMID: 15082523). Mutations in AR altering ligands have been observed. The progression of the prostate cancer depends on AR activity and therefore blocking AR activity or lowering androgen levels is a key step related to androgen deprivation therapy (ADT).