ChromoTek anti-IL6 recombinant VHH, for 1x Cys conjugation
IL6Cys1 is an unconjugated recombinant anti IL6 Nanobody (VHH). Suitable for for dual cysteine conjugation with thiol-reactive reagents, e.g. maleimides. Note: unconjugated VHHs are not suited for usage without prior labeling, since they contain reactive Cysteines. Shipment and storage buffers contain TCEP to keep Cysteines reduced.
Host/Type
Alpaca VHH
Reactivity
Human
Applications
Conjugation
Conjugate
Unconjugated
Cat No : IL6Cys1
Synonyms
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
IL6Cys1 is an unconjugated recombinant anti IL6 Nanobody (VHH). Suitable for for dual cysteine conjugation with thiol-reactive reagents, e.g. maleimides. Note: unconjugated VHHs are not suited for usage without prior labeling, since they contain reactive Cysteines. Shipment and storage buffers contain TCEP to keep Cysteines reduced.
| Applications | Conjugation |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Type | Nanobody |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Host | Alpaca |
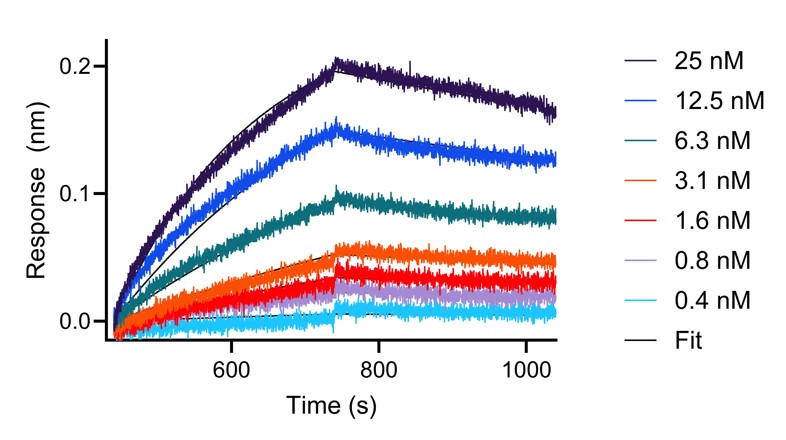
| Affinity | 3 nM |
| Molecular Weight | 13.7 kDa |
| Form | Liquid |
| RRID | AB_3665393 |
| Storage Buffer | 10 mM HEPES pH 7.0, 500 mM NaCl, 0.09% sodium azide |
| Storage Condition | Store at -20°C |
| Shipping | dry ice |
| Background | Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine. IL-6 protein is secreted by a variety of cell types including T cells and macrophages as phosphorylated and variably glycosylated molecule. IL-6 plays an essential role in the final differentiation of B-cells into Ig-secreting cells involved in lymphocyte and monocyte differentiation. It induces myeloma and plasmacytoma growth and induces nerve cells differentiation acts on B-cells, T-cells, hepatocytes, hematopoietic progenitor cells and cells of the CNS. IL-6 is also considered a myokine, a cytokine produced from muscle, and is elevated in response to muscle contraction. IL-6 has been shown to interact with interleukin-6 receptor and glycoprotein 130. Additionally, IL-6 is involved in hematopoiesis, bone metabolism, and cancer progression, and has been defined an essential role in directing transition from innate to acquired immunity. |
Documentation
| SDS |
|---|
| SDS_Immuno-Oncology VHHs (grouped) |