Cytoskeleton Markers
The cytoskeleton is a three-dimensional network supporting and stabilizing the cell.
Introduction
The cytoskeleton is a three-dimensional network supporting and stabilizing the cell. All cells, even bacteria, have a type of cytoskeleton. It is responsible for the shape of the cell and its mechanical properties. Many dynamic cellular processes cooperate with the cytoskeleton, such as cell motion, cell division, intracellular transport, and cell signaling. Therefore, the cytoskeleton interacts with several cytoplasmic proteins or organelles.
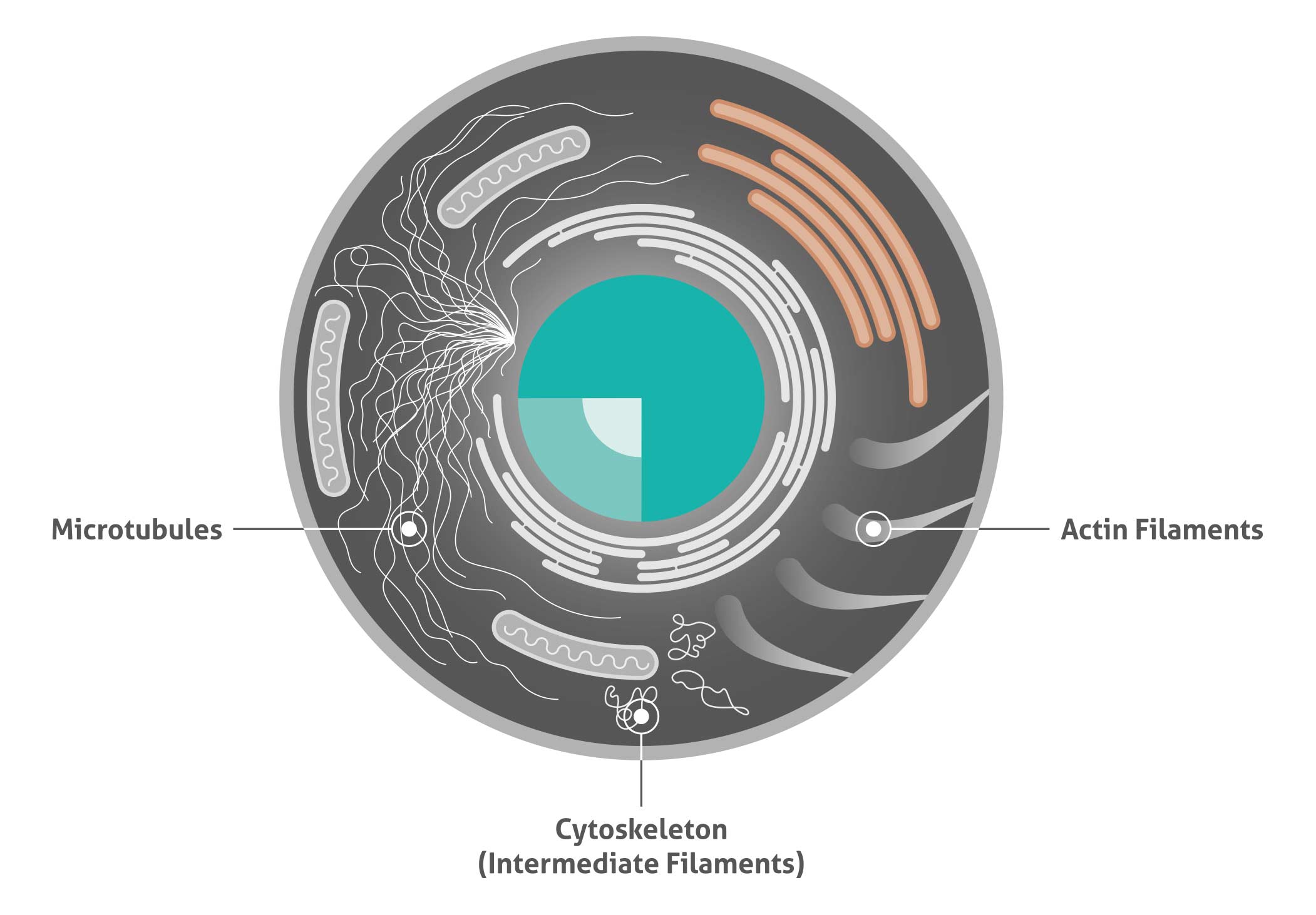
The cytoskeletal network is composed of three different protein structures named filaments: microtubules, microfilaments (actin), and intermediate filaments. These proteins form their own unique networks within the cell that have different interdependent functions.
| Main functions of the cytoskeleton |
| Structural support |
| Cell trafficking |
| Transducer of mechanical signals |
| Associated with several diseases |
| Cellular signaling |
Cell illustrating the three different cytoskeleton structure proteins
Most popular cytoskeleton markers from Proteintech
| Antibody name | Catalog number | Type |
| ACTA2/alpha smooth muscle actin | 23081-1-AP | Rabbit poly |
| alpha Tubulin | 11224-1-AP | Rabbit poly |
| beta Actin | 20536-1-AP | Rabbit poly |
| beta Actin | 60008-1-IG | Mouse Mono |
| beta Tubulin | 10068-1-AP | Rabbit poly |
| Cofilin | 10960-1-AP | Rabbit poly |
| Cytokeratin 17 specific | 17516-1-AP | Rabbit poly |
| Desmin | 60226-1-IG | Mouse Mono |
| GFAP | 60190-1-IG | Mouse Mono |
| Palladin | 10853-1-AP | Rabbit poly |
| Vimentin | 10366-1-AP | Rabbit poly |
Actin filament markers
Actin is an abundant protein in all eukaryotic cells. Monomers of the globular actin (G-actin) polymerize to form actin filaments (F-actin), long and thin fibers. These fibers have a diameter of ca. 5–9 nm and form the thinnest of all cytoskeleton fibers. Therefore, they are also named microfilaments. Actin filaments are very flexible and show a helical structure.
Actin filaments form bands close to the plasma membrane. They can form their own network, shaped by several actin-binding proteins. Many different cellular processes related to cell shape or cell motion depend on actin filaments. They are responsible for the mechanical strength of the cell and connect cytoplasmic and transmembrane proteins.
Related antibodies
| Antibody name | Catalog number | Type |
| ACTN4 | 10996-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| ACTR10 | 20101-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| ARP2 |
10922-1-AP
|
Rabbit Poly |
| ARP3 | 13822-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| ARP5 | 21505-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| CAPG-Specific | 19535-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| CAPZA1 | 11806-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| CORO1A | 17760-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| CORO1C | 14749-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| DBNL | 13025-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| Fascin | 14384-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
Intermediate filament markers
Intermediate filaments are polymers of different proteins, depending on the cellular context. Thus, intermediate filaments do not have as rigidly defined a structure as actin filaments or microtubules.Regardless of the composition, intermediate filaments have a diameter of around 10 nm. These filaments are less dynamic and flexible than microtubules and actin filaments.
Related antibodies
| Antibody name | Catalog number | Type |
| NF-H | 21471-1-AP | Rabbit poly |
| NF-L | 60189-1-IG | Mouse mono |
| NF-M-Specific | 20664-1-AP | Rabbit poly |
The neurofilament proteins belong to the intermediate filament family. Neurofilaments are the 10 nm intermediate filaments found specifically in neurons. They are a major component of the cell’s cytoskeleton, and provide support for normal axonal radial growth. Neurofilaments usually contain three intermediate filament proteins: L, M, and H that are involved in the maintenance of neuronal caliber.
Microtubules markers
Microtubules form the most rigid part of the cytoskeleton and are responsible for the intracellular movement of organelles or proteins. Microtubules are 20 nm in diameter and are composed of alpha and beta tubulin subunits. The formation of microtubules depends on the temperature and available tubulins. Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) regulate the dynamics of microtubules within a cell.
Related antibodies
| Antibody name | Catalog number | Type |
| 66200-1-IG | Mouse Mono | |
| TBCB | 15782-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| TUBGCP3 | 15719-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| TUBGCP4 | 17088-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |
| TUBGCP5 | 14620-1-AP | Rabbit Poly |





