Recombinant Human 4-1BB Ligand/TNFSF9 protein (hFc Tag)
种属
Human
纯度
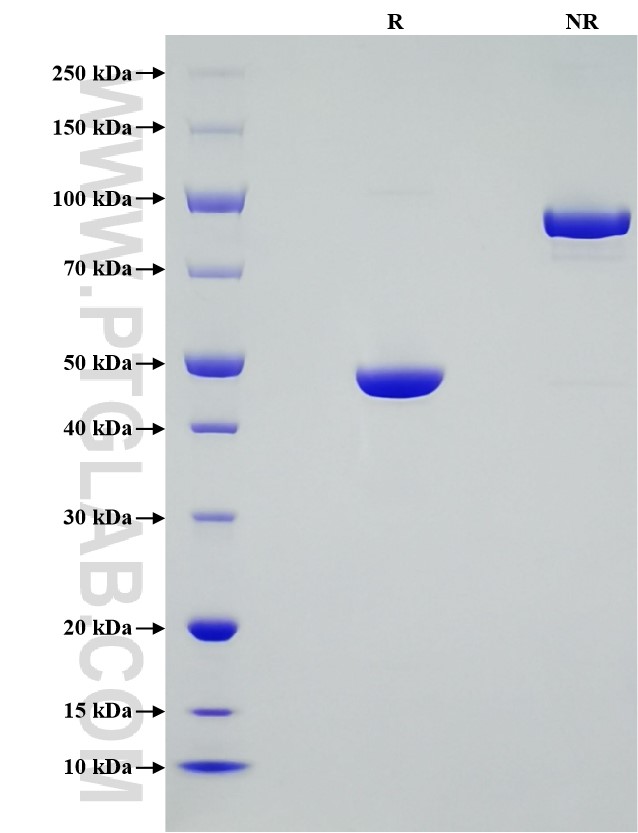
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
标签
hFc Tag
生物活性
EC50: 6-24 ng/mL
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 | Immobilized Human 4-1BB (Myc tag, His tag) at 0.5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human 4-1BB Ligand (hFc tag) with a linear range of 6-24 ng/mL. |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Human 4-1BB Ligand protein Arg71-Glu254 (Accession# P41273) with a human IgG1 Fc tag at the N-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 8744 |
| 蛋白编号 | P41273 |
| 预测分子量 | 45.4 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 45-50 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
TNFSF9 (Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 9) is also known as 4-1BBL (4-1BB ligand) or CD137L. TNFSF9 is a type 2 transmembrane glycoprotein receptor that is found on APCs (antigen presenting cells). TNFSF9 is expressed on activated T Lymphocytes. The TNFSF9/4-1BB complex with the help of T-cell receptor signals can trigger the increase in CD28− T cells and inhibit tumor growth. The interaction between 4-1BB and TNFSF9 provides costimulatory signals to T cells, which can be used to cancer immunotherapy.
参考文献:
1.Jacob Bukczynski. et al. (2003). Eur J Immunol. 33(2): 446-54. 2.Adam T C Cheuk. et al. (2004). Cancer Gene Ther. 11(3): 215-26. 3.Chao Wang. et al. (2009). Immunol Rev. 229(1): 192-215. 4.Dass S Vinay. et al. (2012). Mol Cancer Ther. 11(5): 1062-1070. 5.Cariad Chester. et al. (2018). Blood. 131(1): 49-57.