STT3A Recombinant antibody
STT3A Uni-rAbTM Recombinant Antibody for ELISA
Host / Isotype
Rabbit / IgG
Reactivity
human
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate
Unconjugated
CloneNo.
230426B10
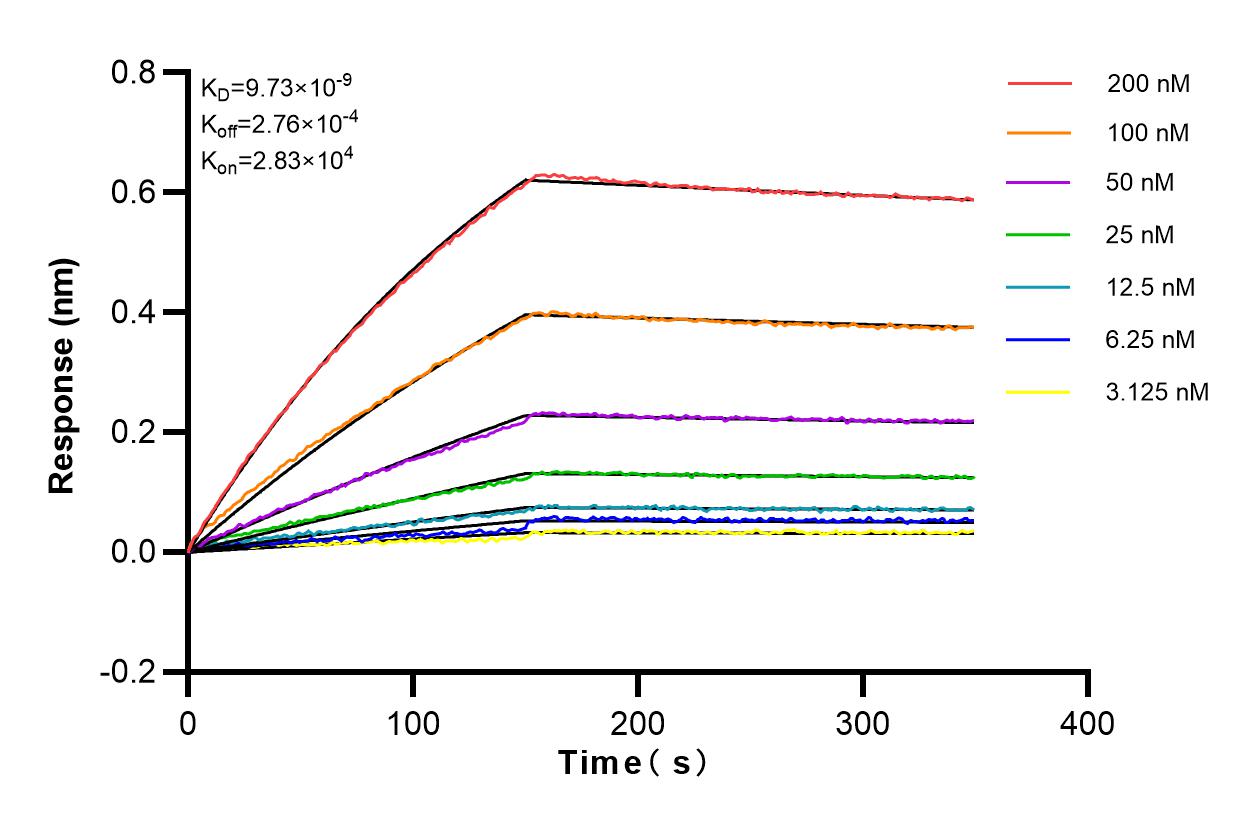
验证数据展示
产品信息
83077-4-RR targets STT3A in ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Applications | ELISA Application Description |
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Immunogen | STT3A fusion protein Ag31994 种属同源性预测 |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Full Name | STT3, subunit of the oligosaccharyltransferase complex, homolog A (S. cerevisiae) |
| Synonyms | ITM1, Integral membrane protein 1, EC:2.4.99.18, Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide--protein glycosyltransferase subunit STT3A, B5 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 705 aa, 81 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC020965 |
| Gene Symbol | STT3A |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3703 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | P46977 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
STT3A, also named as Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide--protein glycosyltransferase subunit STT3A, is a 705 amino acid prtein, which belongs to the STT3 family. STT3A is expressed at high levels in placenta, liver, muscle and pancreas, and at very low levels in brain, lung and kidney. STT3A is a catalytic subunit of the N-oligosaccharyl transferase (OST) complex which catalyzes the transfer of a high mannose oligosaccharide from a lipid-linked oligosaccharide donor to an asparagine residue within an Asn-X-Ser/Thr consensus motif in nascent polypeptide chains. N-glycosylation occurs cotranslationally and the complex associates with the Sec61 complex at the channel-forming translocon complex that mediates protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). SST3A seems to be involved in complex substrate specificity. STT3A is present in the majority of OST complexes and mediates cotranslational N-glycosylation of most sites on target proteins, while STT3B-containing complexes are required for efficient post-translational glycosylation and mediate glycosylation of sites that have been skipped by STT3A.