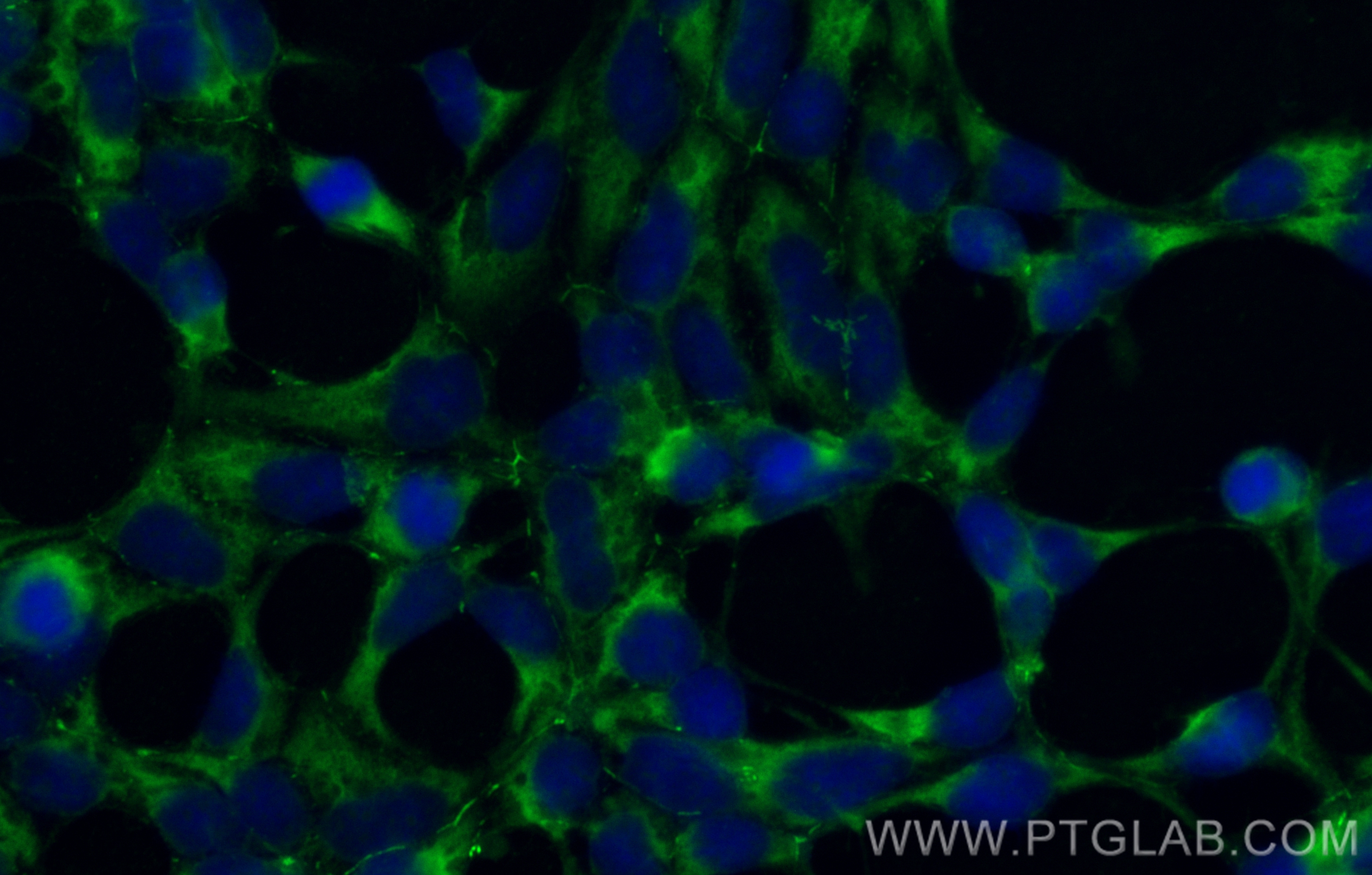
验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HEK-293 cells |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
产品信息
CL488-24550 targets AMOT in IF/ICC applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | IF/ICC Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 | AMOT fusion protein Ag19784 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | angiomotin |
| 别名 | KIAA1071, Angiomotin |
| 计算分子量 | 1084 aa, 118 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 80 kDa, 130 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC130294 |
| 基因名称 | AMOT |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 154796 |
| RRID | AB_3672768 |
| 偶联类型 | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| 最大激发/发射波长 | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q4VCS5 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
Angiomotin belongs to the motin family of angiostatin binding protein. The encoded protein is expressed predominantly in endothelial cells of capillaries as well as larger vessels of the placenta where it may mediate the inhibitory effect of angiostatin on tube formation and the migration of endothelial cells during the formation of new blood vessels. Most abundant expression was found in placenta and skeletal muscle. AMOT has two isoforms with MW 130 kDa (p130) and 80 kDa (p80). The p130 isoform can interact with F-actin.This antibody recognizes both p130 and p80.
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 AMOT antibody CL488-24550 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |