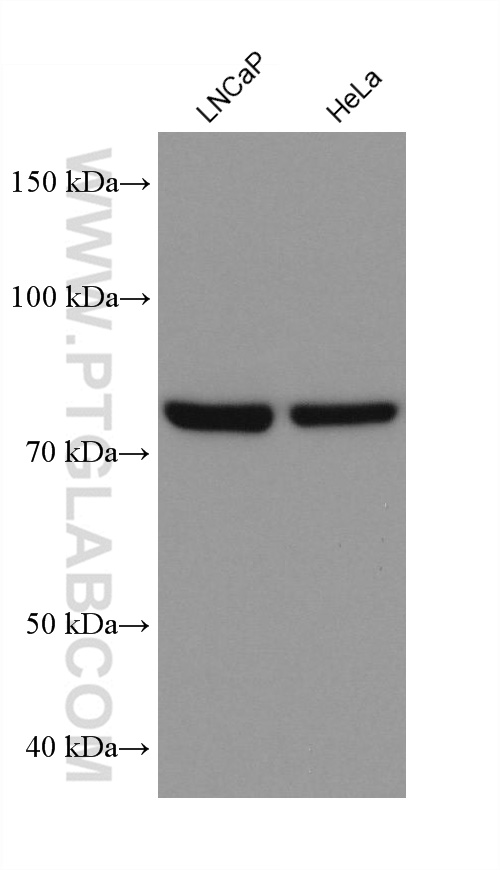
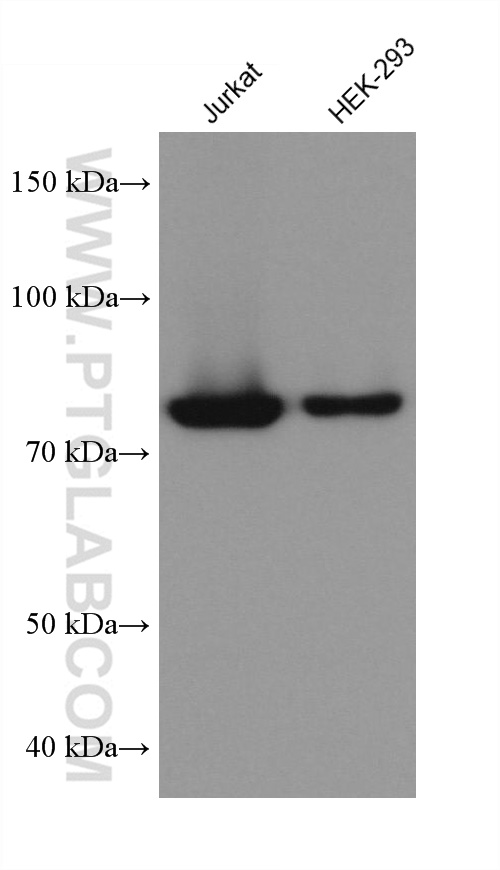
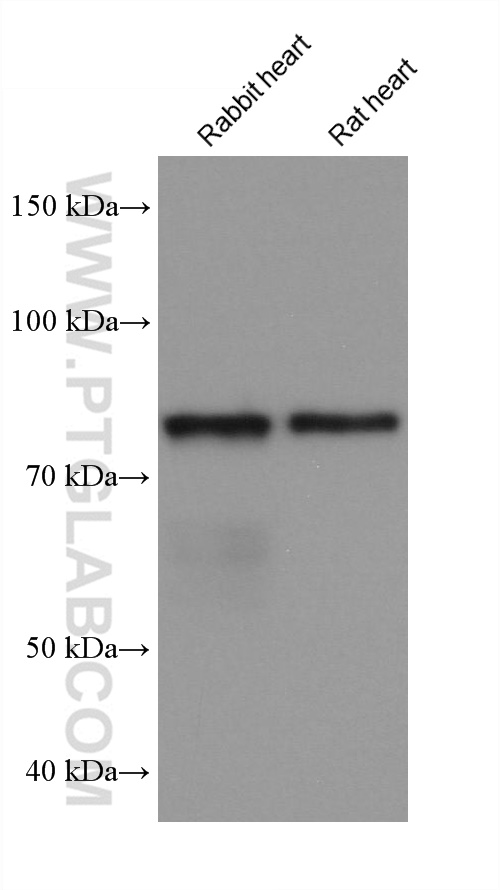
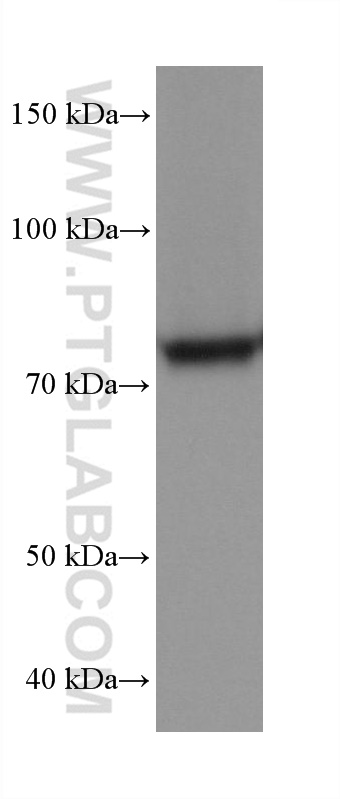
验证数据展示
产品信息
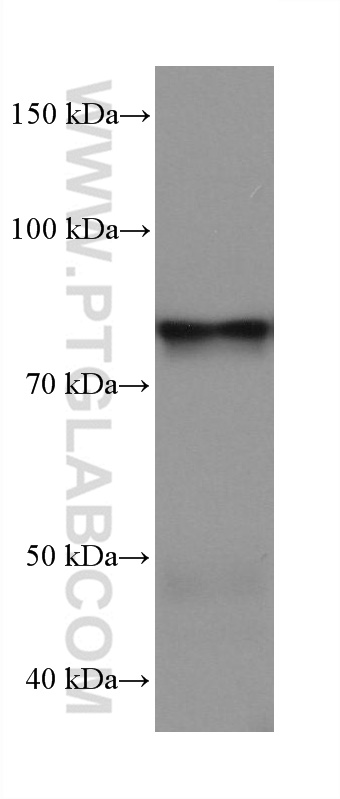
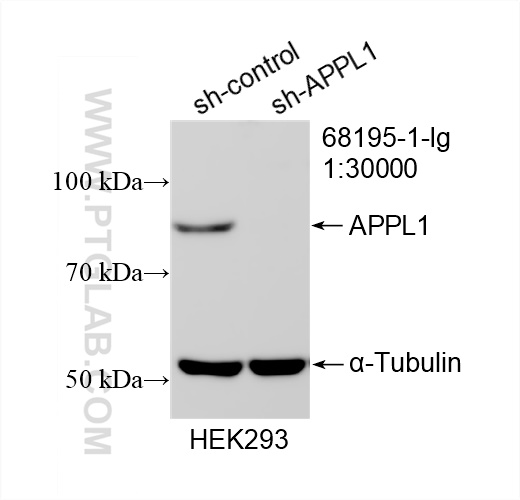
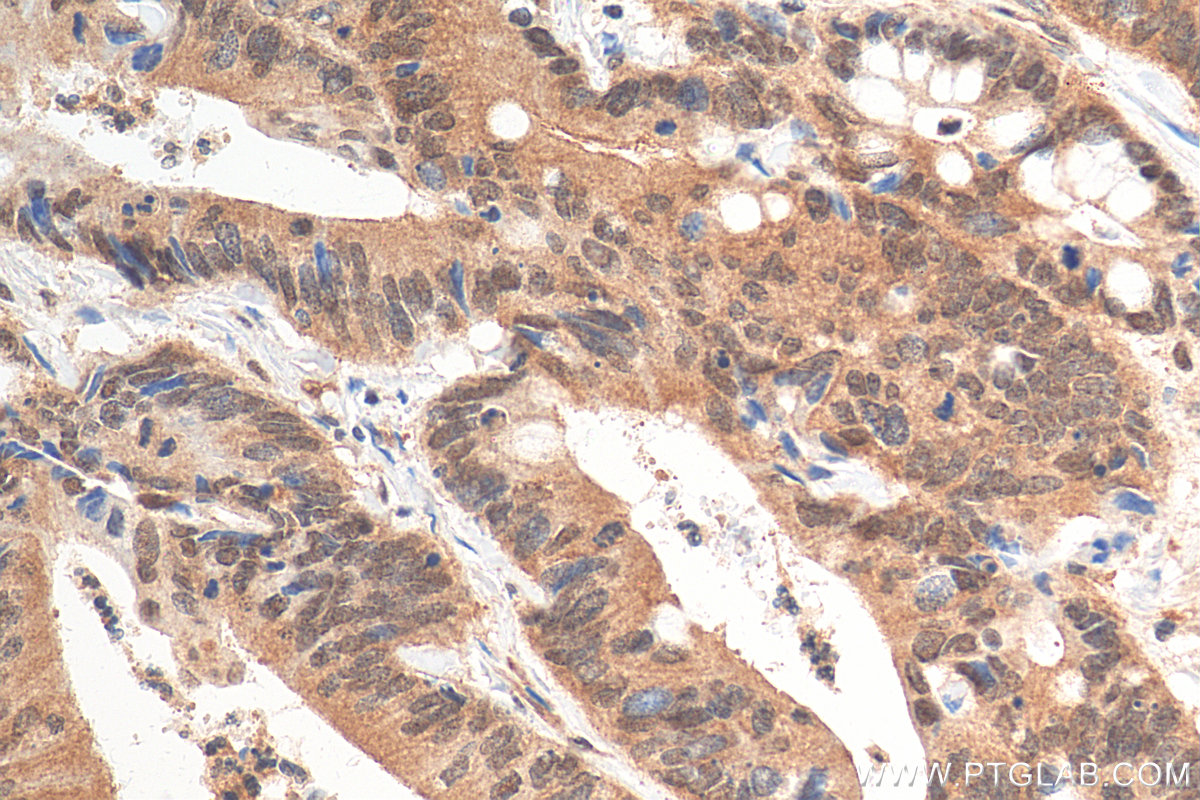
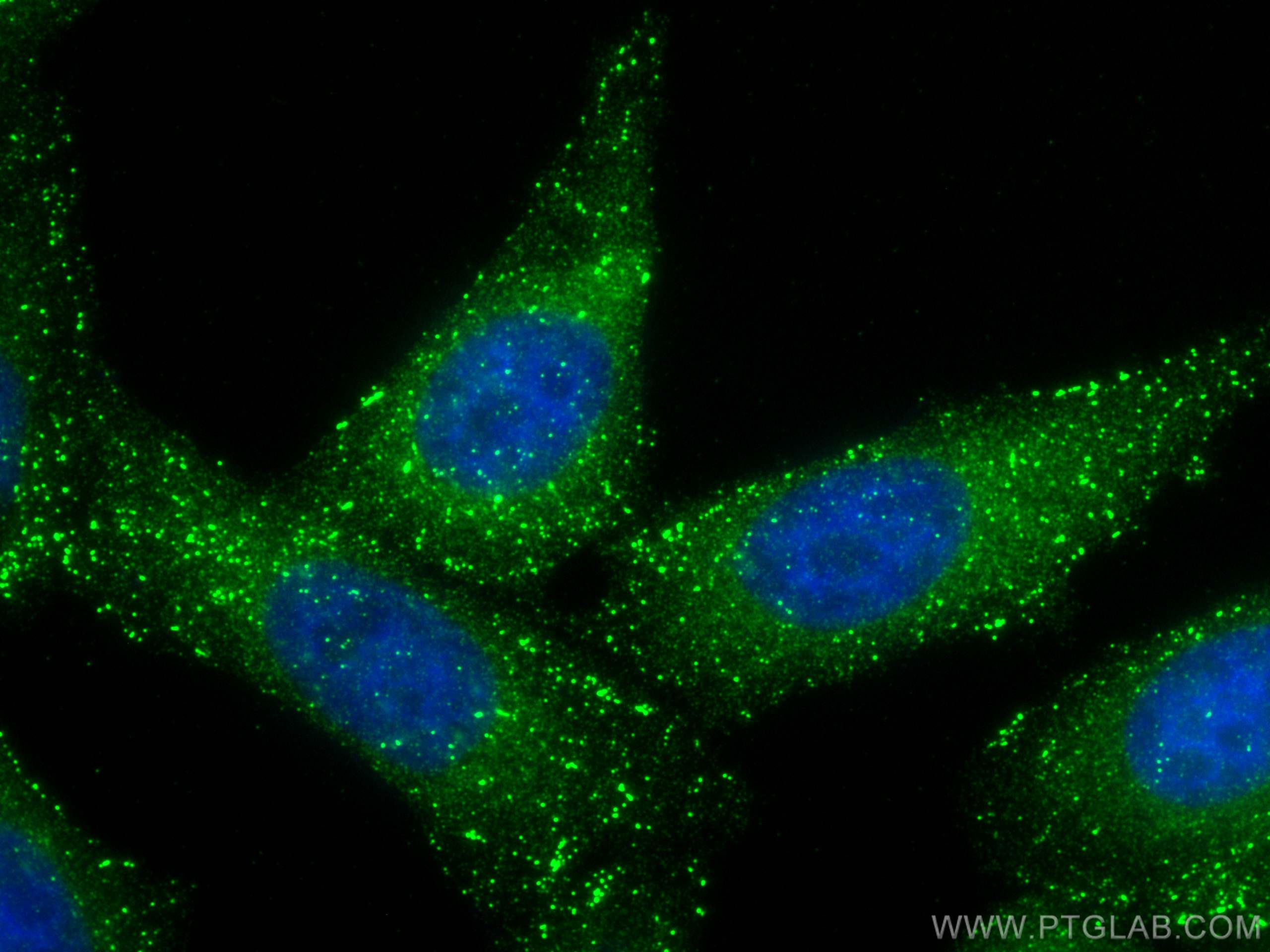
68195-1-PBS targets APPL1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, pig, rabbit samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat, pig, rabbit |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag3334 Product name: Recombinant human APPL1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 405-709 aa of BC028599 Sequence: QQRHESLRPAAGQSRPPTARTSSSGSLGSESTNLAALSLDSLVAPDTPIQFDIISPVCEDQPGQAKAFGQGGRRTNPFGESGGSTKSETEDSILHQLFIVRFLGSMEVKSDDHPDVVYETMRQILAARAIHNIFRMTESHLLVTCDCLKLIDPQTQVTRLTFPLPCVVLYATHQENKRLFGFVLRTSSGRSESNLSSVCYIFESNNEGEKICDSVGLAKQIALHAELDRRASEKQKEIERVKEKQQKELNKQKQIEKDLEEQSRLIAASSRPNQASSEGQFVVLSSSQSEESDLGEGGKKRESEA 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG2b |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interaction, PH domain and leucine zipper containing 1 |
| 别名 | 1B7B11, Adapter protein containing PH domain, PTB domain and leucine zipper motif 1, APPL, DCC-interacting protein 13-alpha, Dip13 alpha |
| 计算分子量 | 709 aa, 80 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 80 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC028599 |
| 基因名称 | APPL1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 26060 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9UKG1 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
Adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interaction, PH domain and leucine zipper containing 1 (APPL1), a binding partner of Akt2 and an important regulator of INS signaling, plays a key role in the regulation of INS secretion [PMID:22615370]. APPL1 interacts with adiponectin receptors and mediates the INS-sensitizing effects of adiponectin in muscle and endothelial cells. It also participates in nuclear signaling and transcriptional regulation, mostly by modulating the activity of various nuclear factors [PMID:22685329]. Apart from its role in endocytosis and endosomal transport, APPL1 was reported to undergo nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and participate in transcriptional regulation, e.g. by interactions with histone deacetylases (HDACs) [PMID:19686092].