验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
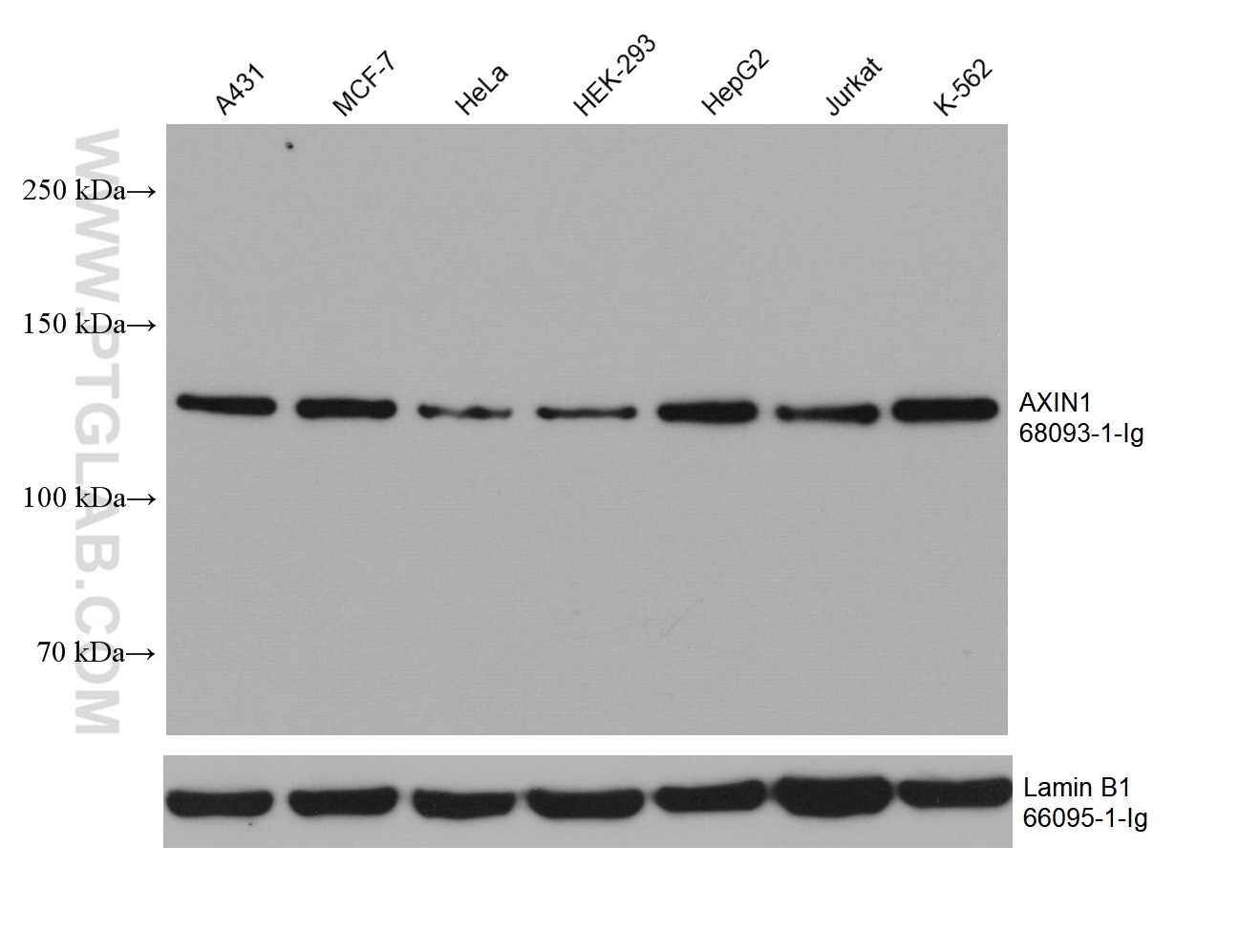
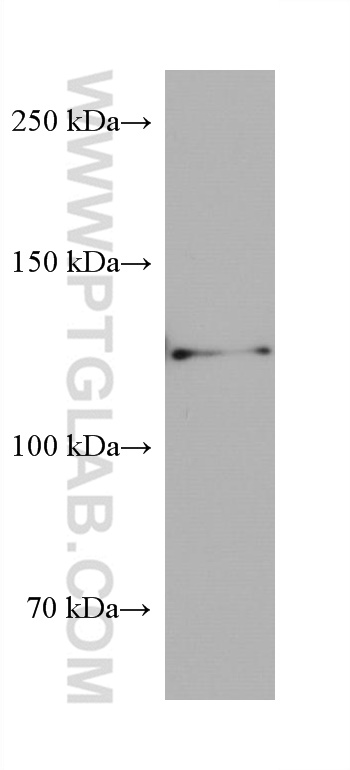
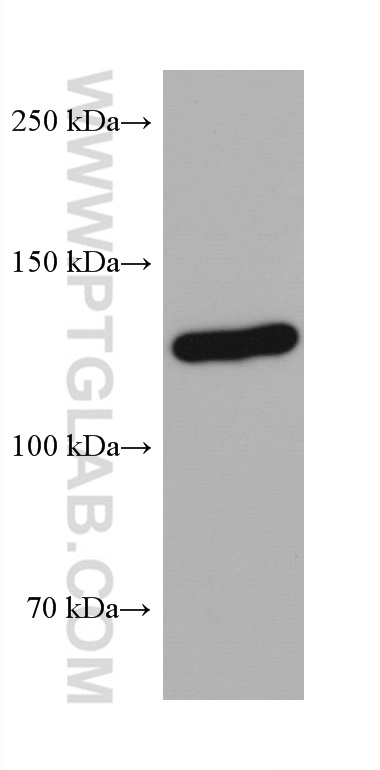
| Positive WB detected in | A431 cells, HSC-T6 cells, NIH/3T3 cells, MCF-7 cells, HeLa cells, HEK-293 cells, HepG2 cells, Jurkat cells, K-562 cells |
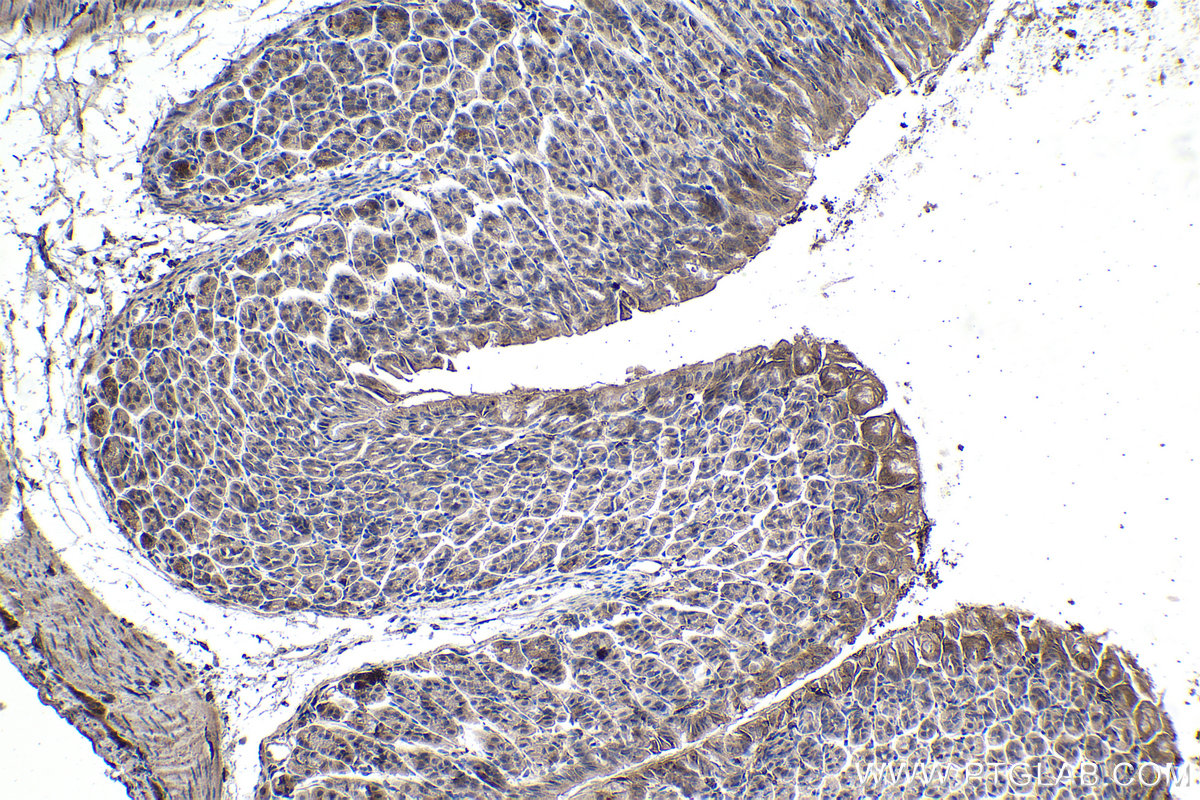
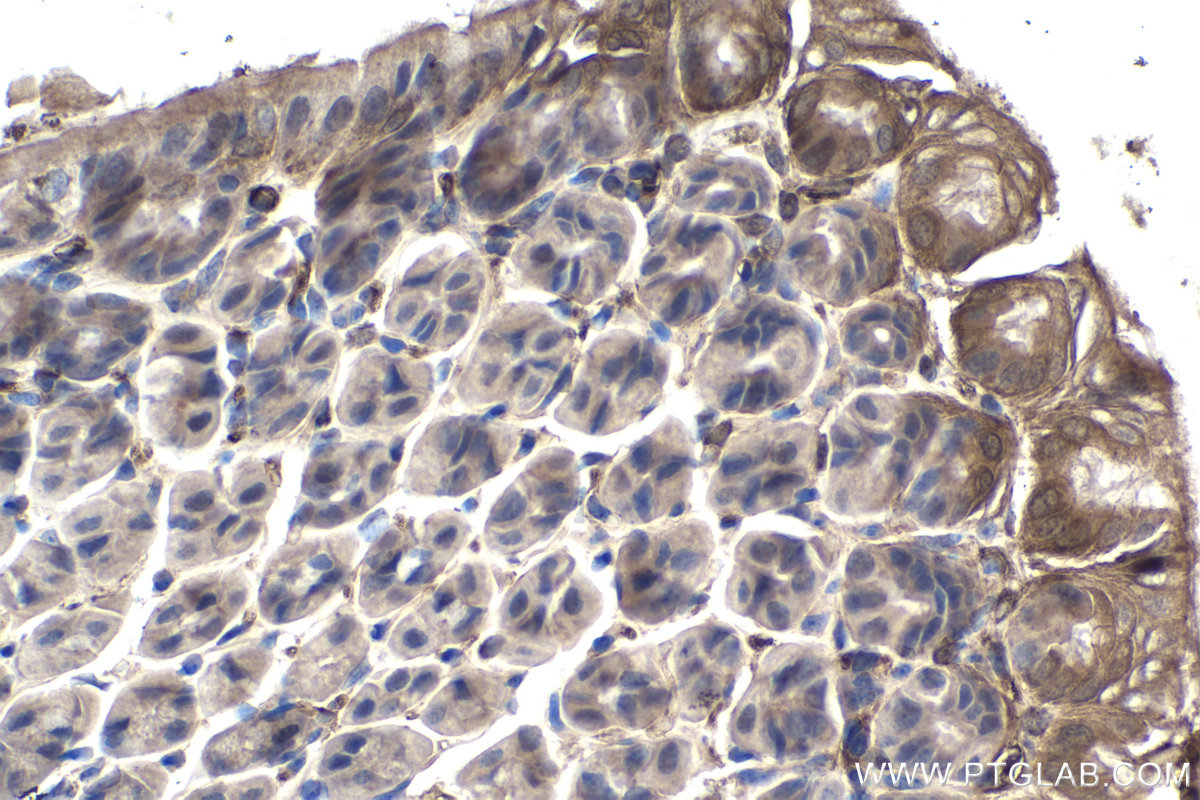
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse stomach tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
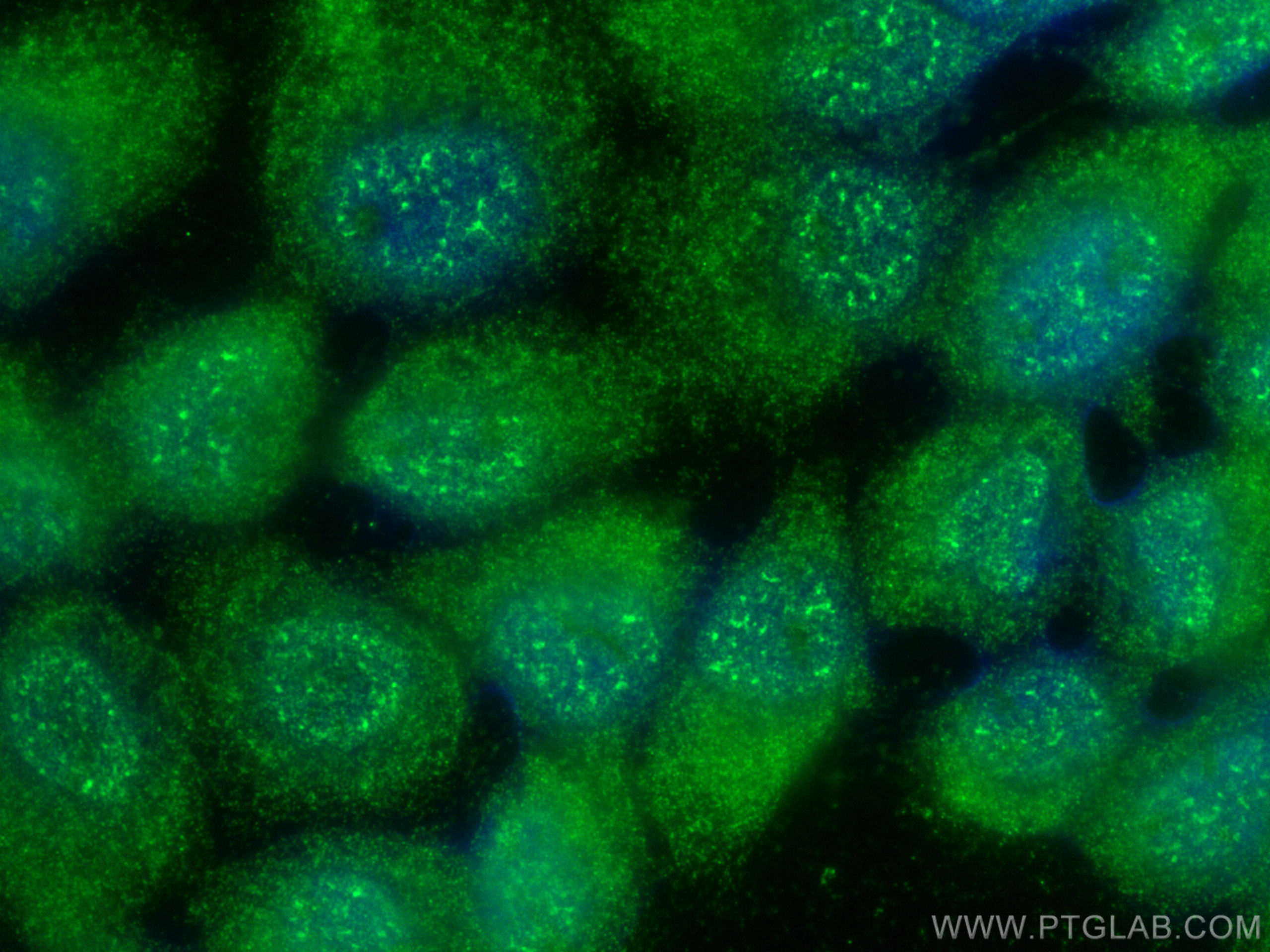
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | A431 cells |
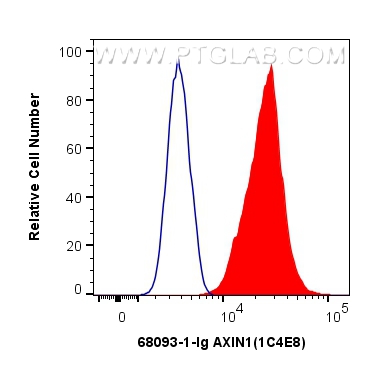
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | A431 cells |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
发表文章中的应用
| WB | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
产品信息
68093-1-Ig targets AXIN1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), ELISA Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | WB, IF |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat |
| 文献引用反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 | AXIN1 fusion protein Ag10079 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG1 |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | axin 1 |
| 别名 | hAxin, Axis inhibition protein 1, Axin-1, AXIN 1, AXIN |
| 计算分子量 | 826aa,92 kDa; 862aa,95 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 110-120 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC044648 |
| 基因名称 | AXIN1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8312 |
| RRID | AB_2918830 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O15169 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
Axis inhibition protein1 (AXIN1), also called AXIN, together with AXIN2 are multidomain scaffold proteins that negatively regulate Wnt signaling. AXIN1 is likely to function as a tumor suppressor. Under UV irradiation, AXIN1-HIPK2-TP53 complex forms. The complex also controls cell growth, apoptosis and development. Like AXIN2, AXIN1 undergoes poly(ADP-ribosy)lation by tankyrase TNKS and TNKS2 followed by unbiquitination by RNF146 which leads to its degradation and subsequent activation of Wnt signaling. Its deubiquitination by USP34 is important for nuclear accumulation during Wnt signaling. Recent researches find that CircAXIN1 encodes a novel protein, AXIN1-295aa, which shows at around 40-55 kDa by Western Blot. AXIN1-295aa functions as an oncogenic protein, activating the Wnt signaling pathway to promote GC tumorigenesis and progression, suggesting a potential therapeutic target for GC.
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for AXIN1 antibody 68093-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for AXIN1 antibody 68093-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for AXIN1 antibody 68093-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| FC protocol for AXIN1 antibody 68093-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Int Immunopharmacol Preliminary investigation on the mechanism of baicalein regulating the effects of Nischarin on invasion and apoptosis of human breast cancer cells MCF-7 through Wnt3α/β-catenin pathway | ||
Biochem Pharmacol SMURF1 leads to the β-catenin signaling-mediated progression of esophageal squamous carcinoma by losing PATZ1-induced CCNG2 transcription | ||
Int J Biol Macromol Xylooligosaccharides alleviate the carbohydrate-enriched diet-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction in carp Megalobrama amblycephala by promoting intestinal development, immunity and gut microbiota |