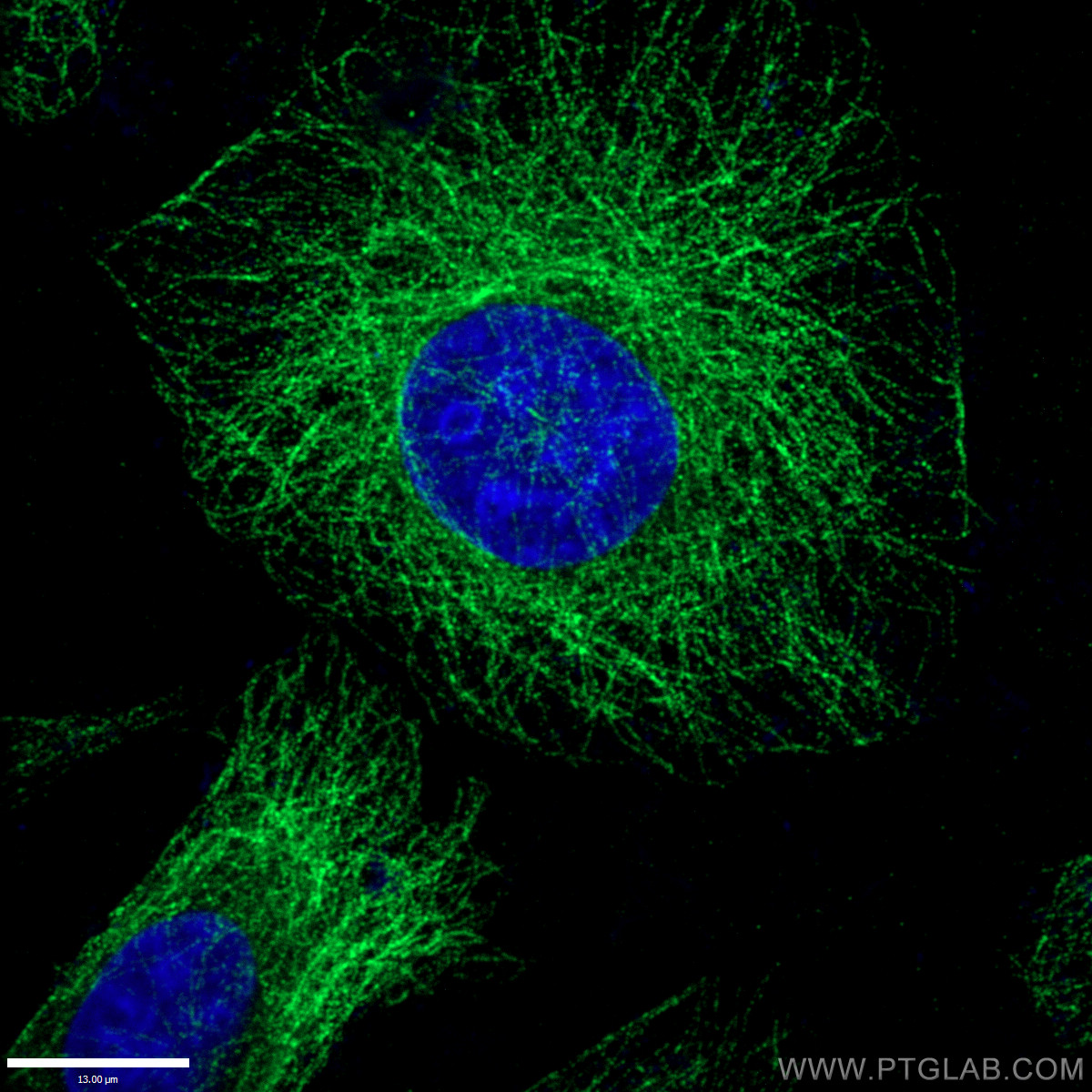
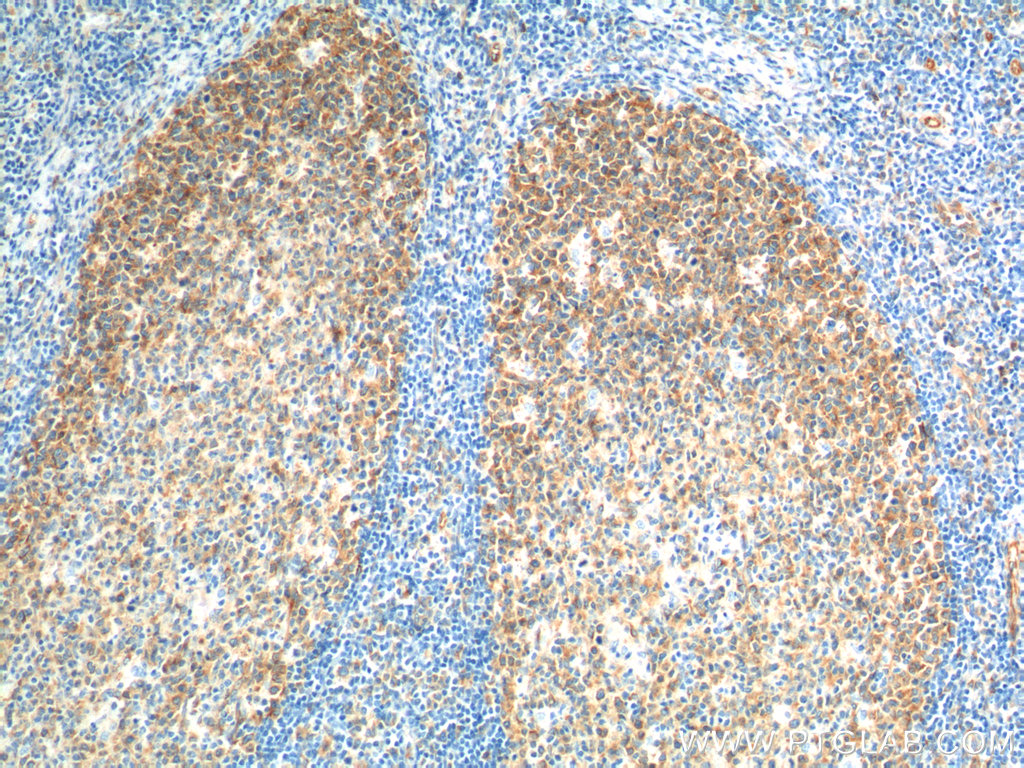
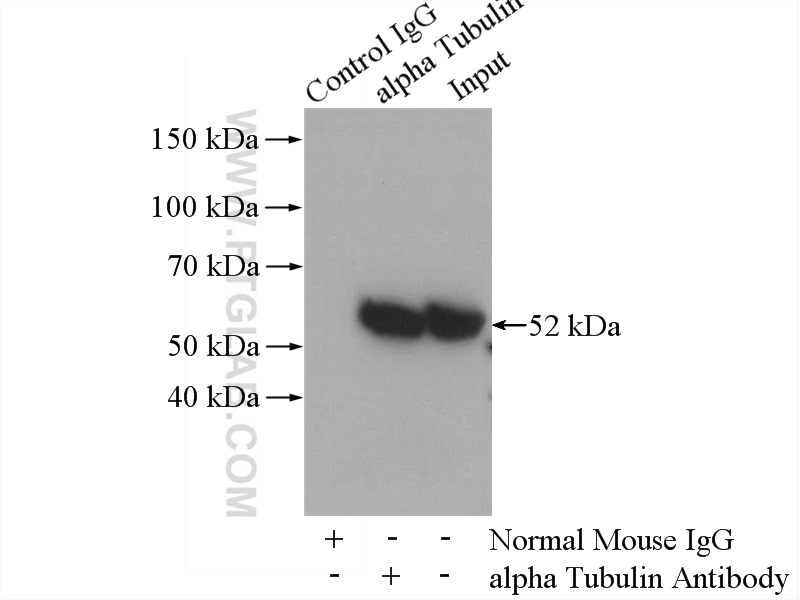
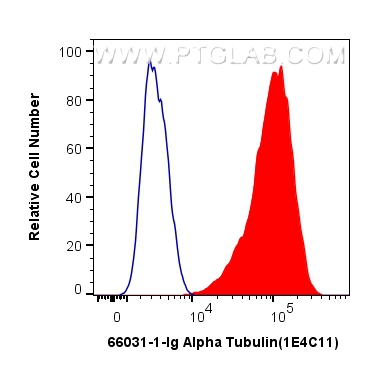
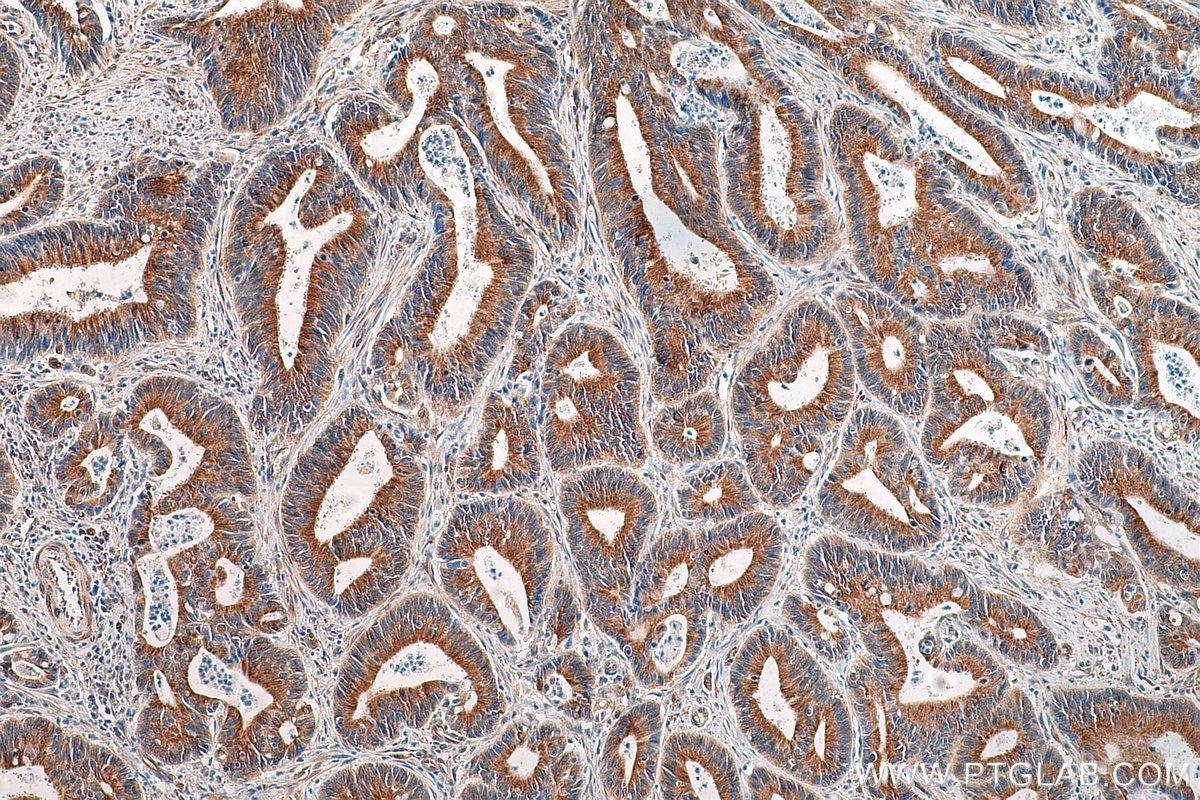
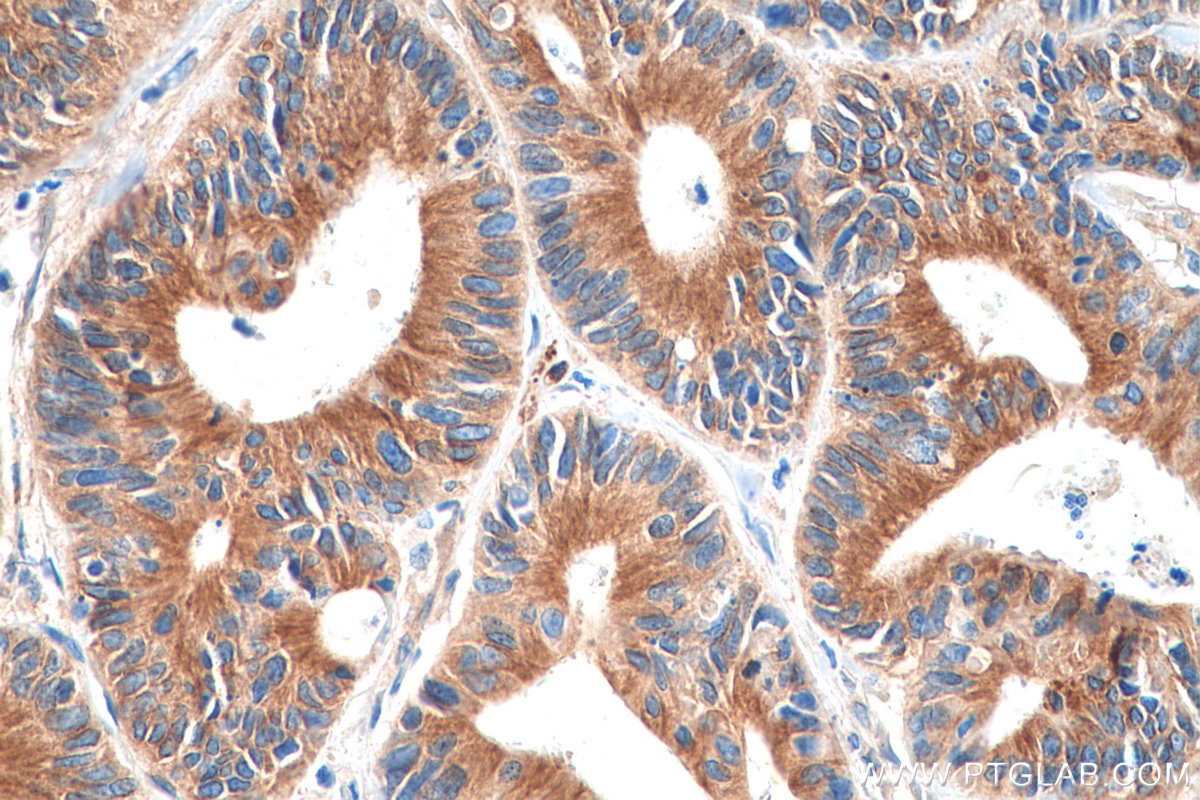
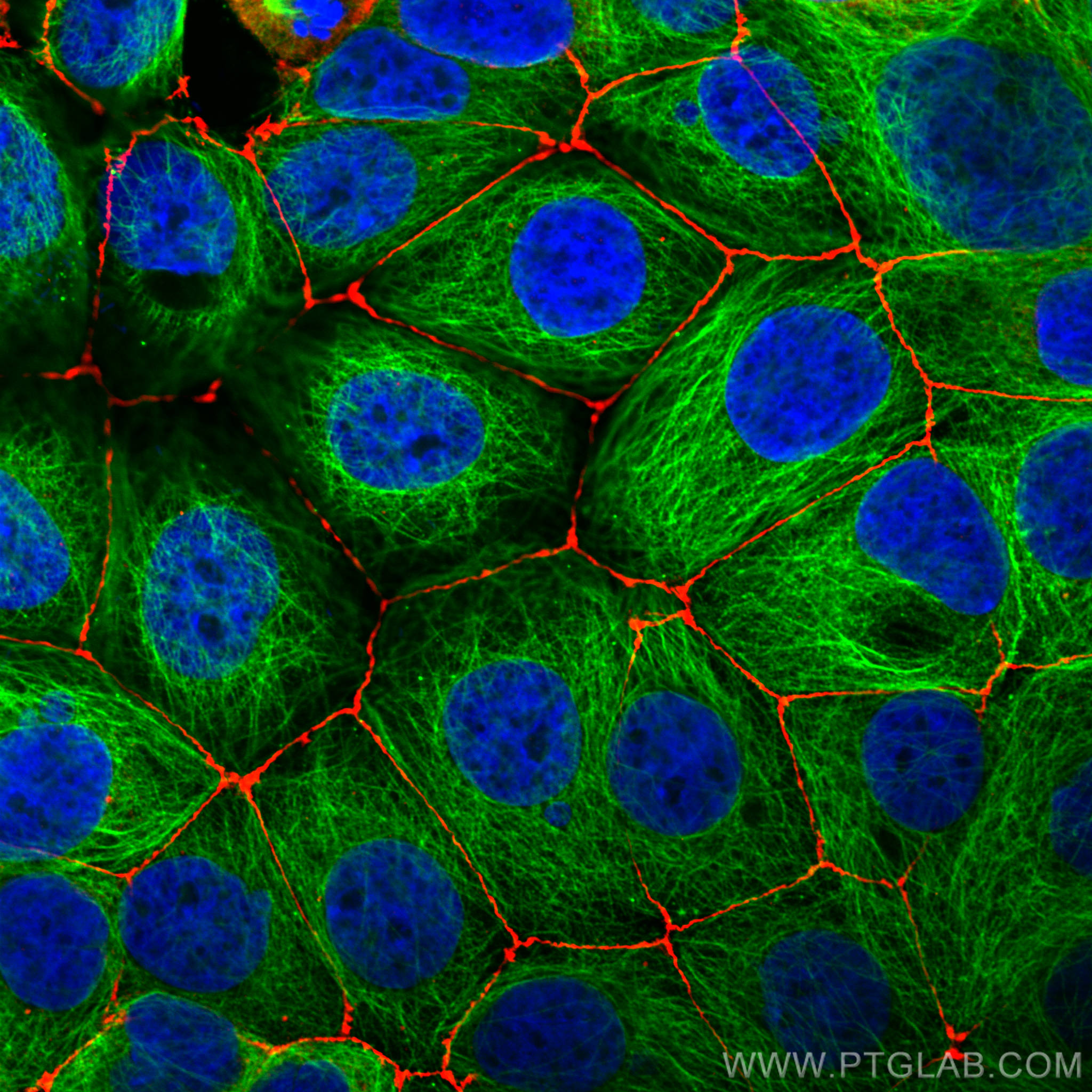
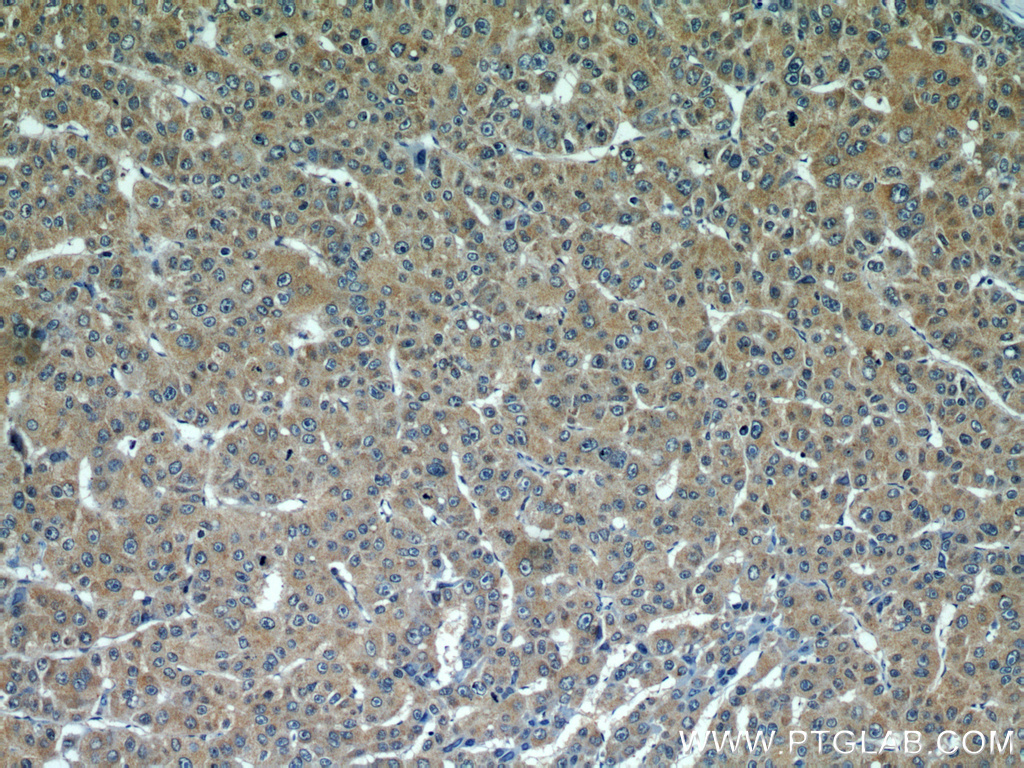
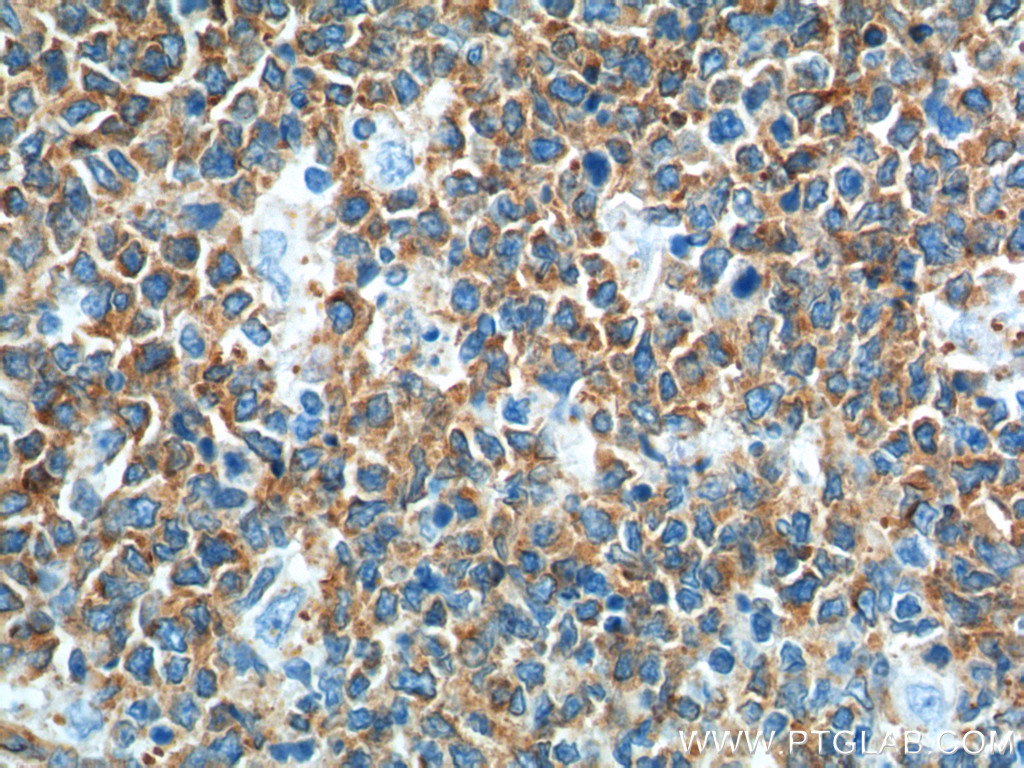
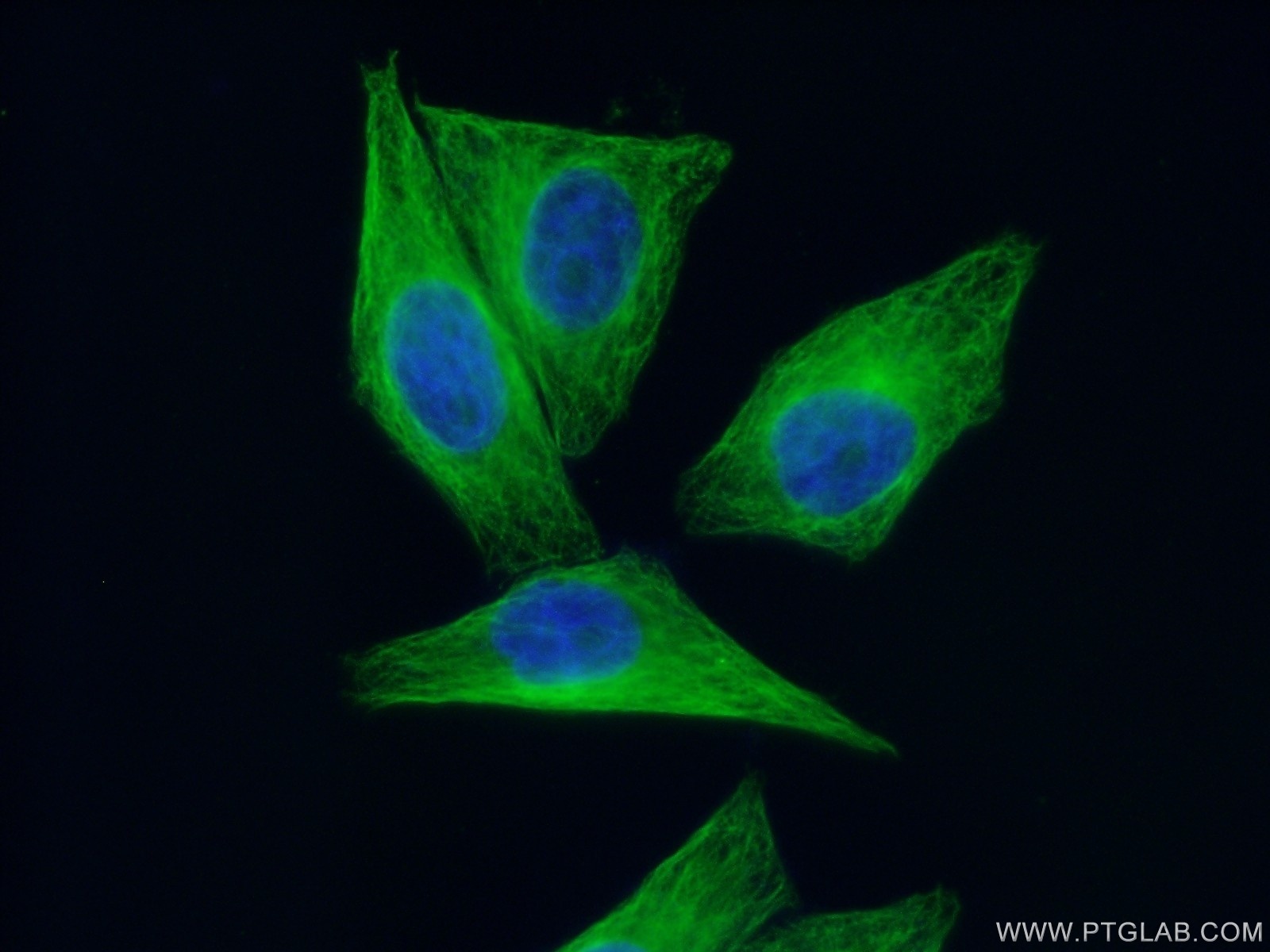
验证数据展示
产品信息
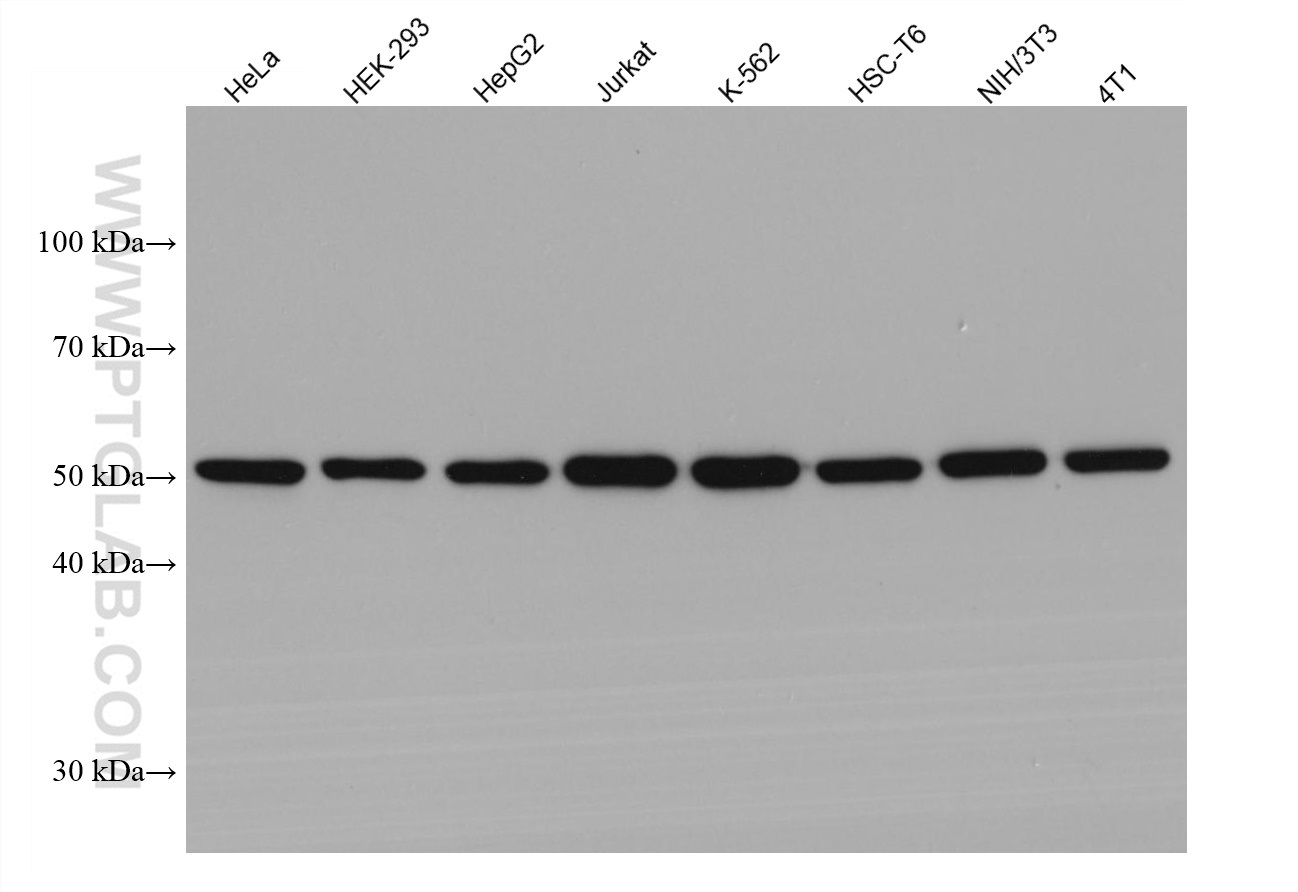
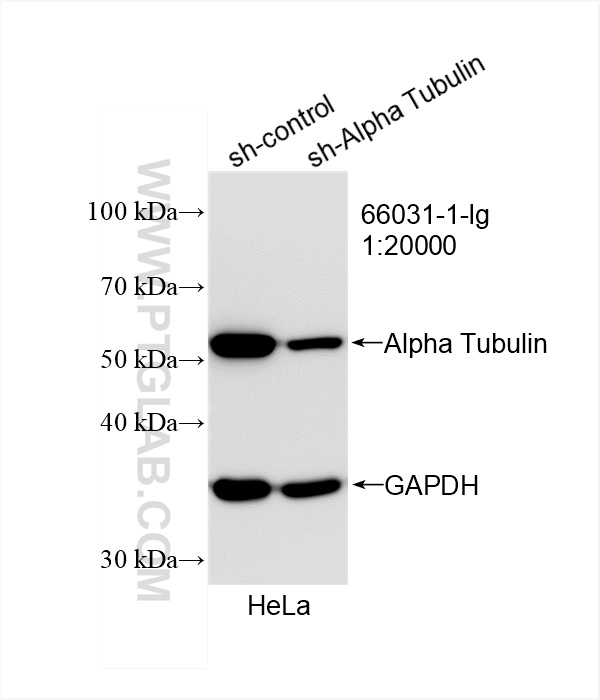
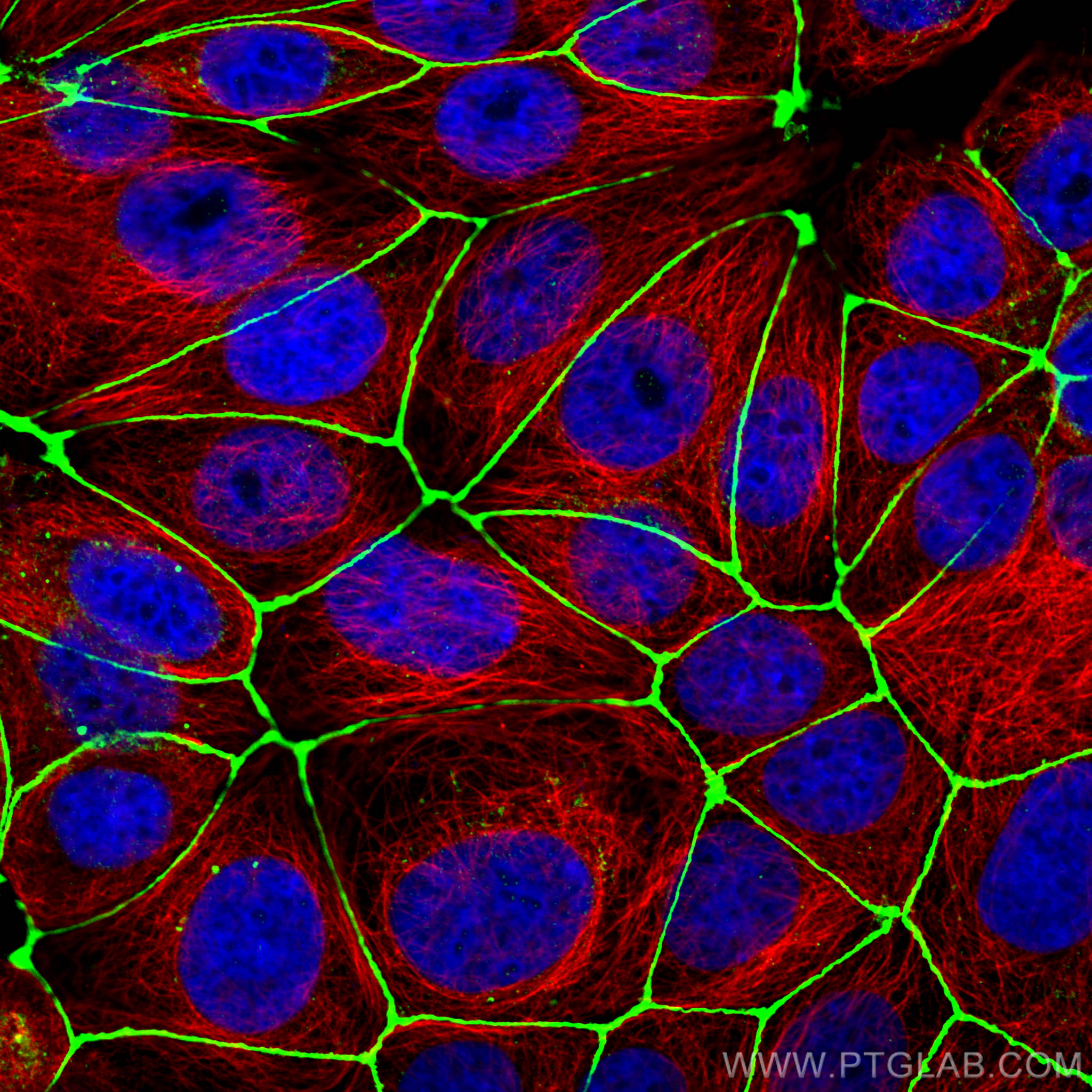
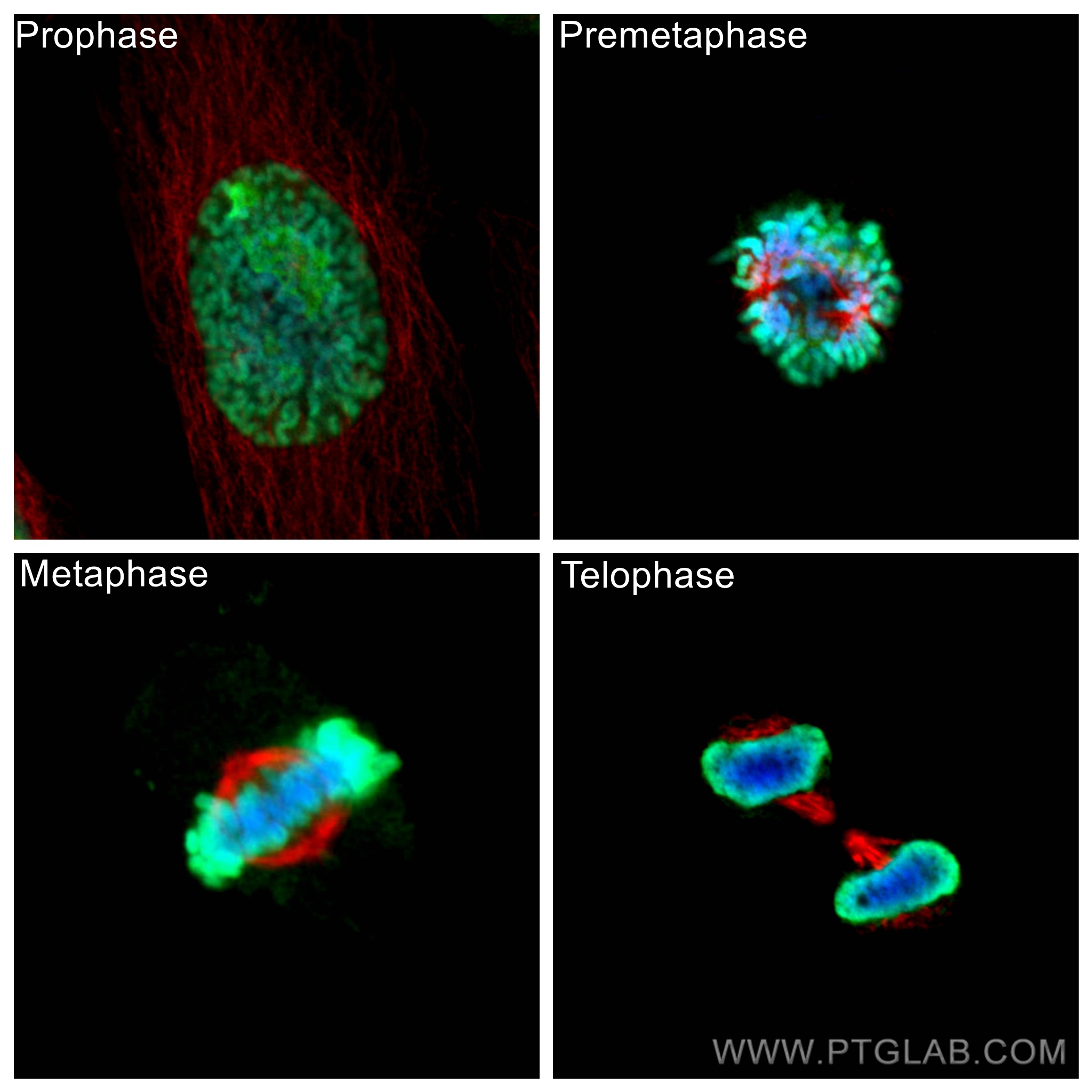
66031-1-PBS targets Alpha Tubulin in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, canine samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat, canine |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag18034 Product name: Recombinant human Tubulin-Alpha protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-451 aa of BC009314 Sequence: MRECISIHVGQAGVQIGNACWELYCLEHGIQPDGQMPSDKTIGGGDDSFNTFFSETGAGKHVPRAVFVDLEPTVIDEVRTGTYRQLFHPEQLITGKEDAANNYARGHYTIGKEIIDLVLDRIRKLADQCTGLQGFLVFHSFGGGTGSGFTSLLMERLSVDYGKKSKLEFSIYPAPQVSTAVVEPYNSILTTHTTLEHSDCAFMVDNEAIYDICRRNLDIERPTYTNLNRLISQIVSSITASLRFDGALNVDLTEFQTNLVPYPRIHFPLATYAPVISAEKAYHEQLSVAEITNACFEPANQMVKCDPRHGKYMACCLLYRGDVVPKDVNAAIATIKTKRSIQFVDWCPTGFKVGINYQPPTVVPGGDLAKVQRAVCMLSNTTAIAEAWARLDHKFDLMYAKRAFVHWYVGEGMEEGEFSEAREDMAALEKDYEEVGVDSVEGEGEEEGEEY 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG2b |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | tubulin, alpha 1b |
| 别名 | TUBA1B, Tubulin alpha 1B chain, 1E4C11, Alpha-tubulin ubiquitous, EC:3.6.5.- |
| 计算分子量 | 50 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 50-55 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC009314 |
| 基因名称 | Alpha Tubulin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10376 |
| RRID | AB_11042766 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P68363 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
What is the function of alpha tubulin?
Alpha-tubulin belongs to a large superfamily of tubulin proteins. There are a number of different subtypes that have a molecular weight of ~50kDa and are able to bind to beta-tubulin, forming a heterodimer that polymerises to microtubules as part of the cytoskeleton. These maintain cell structure, provide platforms for intracellular transport and are also involved in cell division.
Where is alpha-tubulin expressed?
Alpha tubulin is highly conserved and is present in nearly all eukaryotic cells as one of the building blocks of microtubules. The ubiquitous nature of this protein has led to its common use as a control protein for many tissue types as well as highlighting the structure of the cytoskeleton.
What are the post-translational modifications of alpha tubulin?
The function and properties of microtubules are drastically affected by the post-translational modifications undergone by tubulin, which may occur to the tubulin dimer directly or to the polymerised mictotubule. For example, the first modification to be identified was detyrosination1, as most alpha-tubulins have a tyrosine at their terminus. This process affects microtubules more than dimers and leads to patches of detyronisation along the structure, regulating protein interactions and allowing subcellular compartments to be defined.2,3 Polyglutamylation also occurs on several sites within the carboxy-terminal tails. However, to date, the most-studied alpha tubulin modification is related to acetylation of lysine 40 (K40).
1. Gundersen, G. G., Khawaja, S. & Bulinski, J. C. Postpolymerization detyrosination of alpha-tubulin: a mechanism for subcellular differentiation of microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 105, 251-64 (1987).
2. Galjart, N. Plus-End-Tracking Proteins and Their Interactions at Microtubule Ends. Curr. Biol. 20, R528-R537 (2010).
3. Jiang, K. & Akhmanova, A. Microtubule tip-interacting proteins: a view from both ends. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 23, 94-101 (2011).