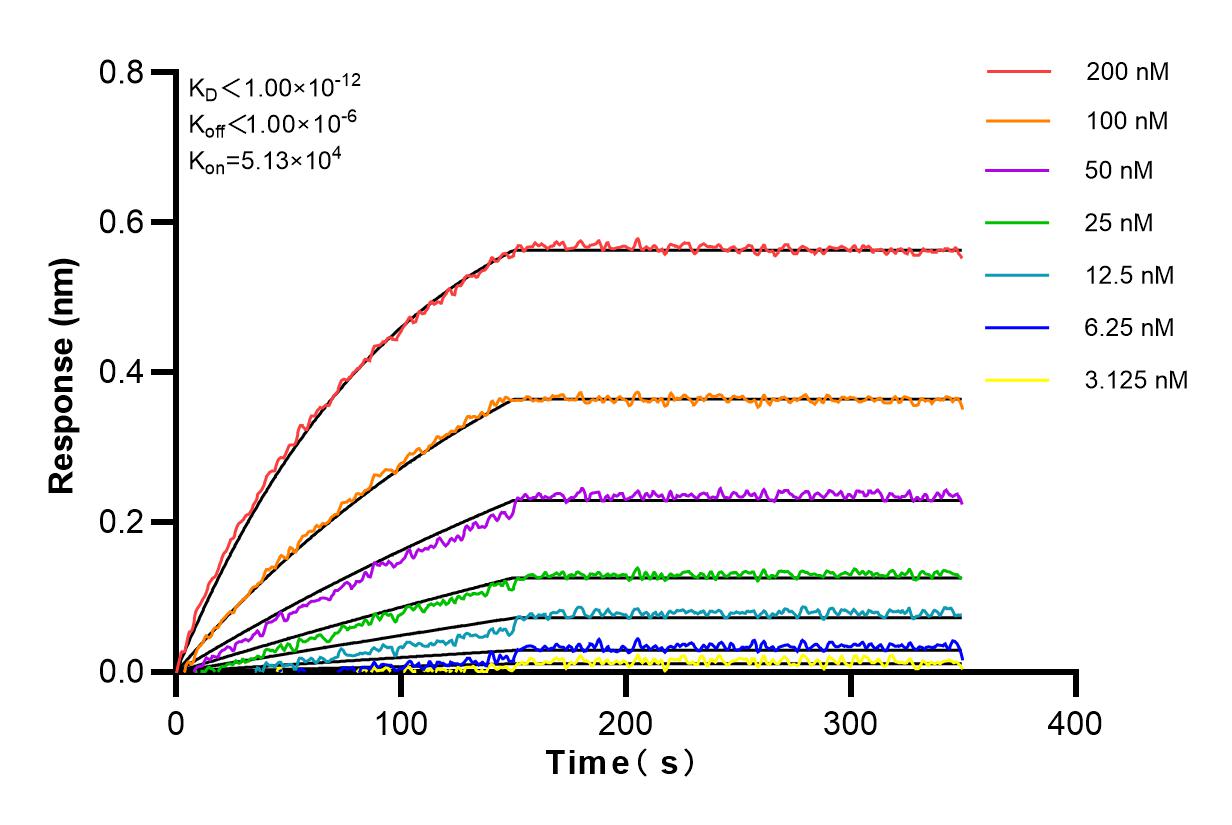
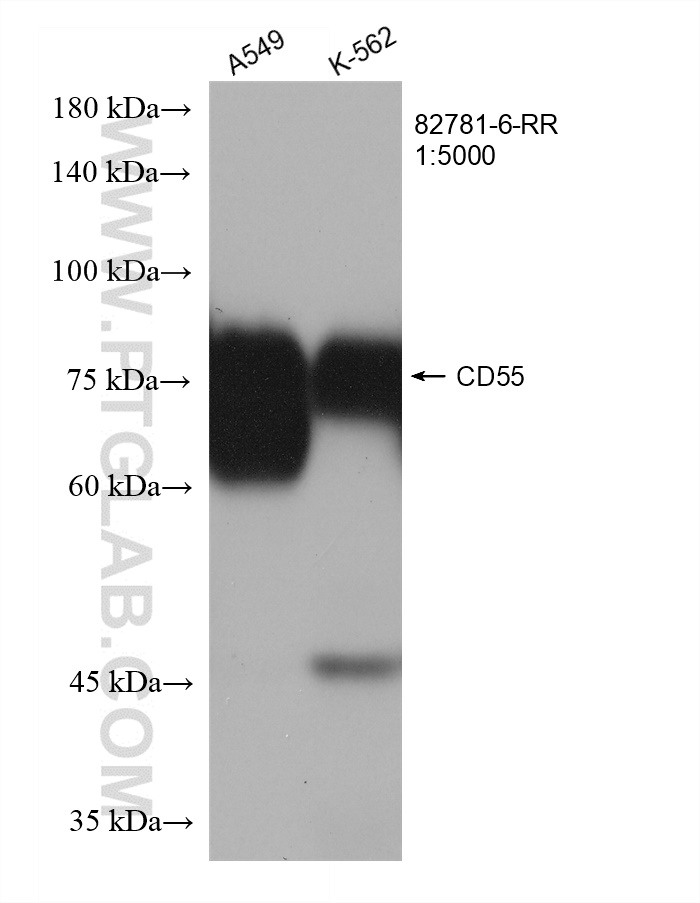
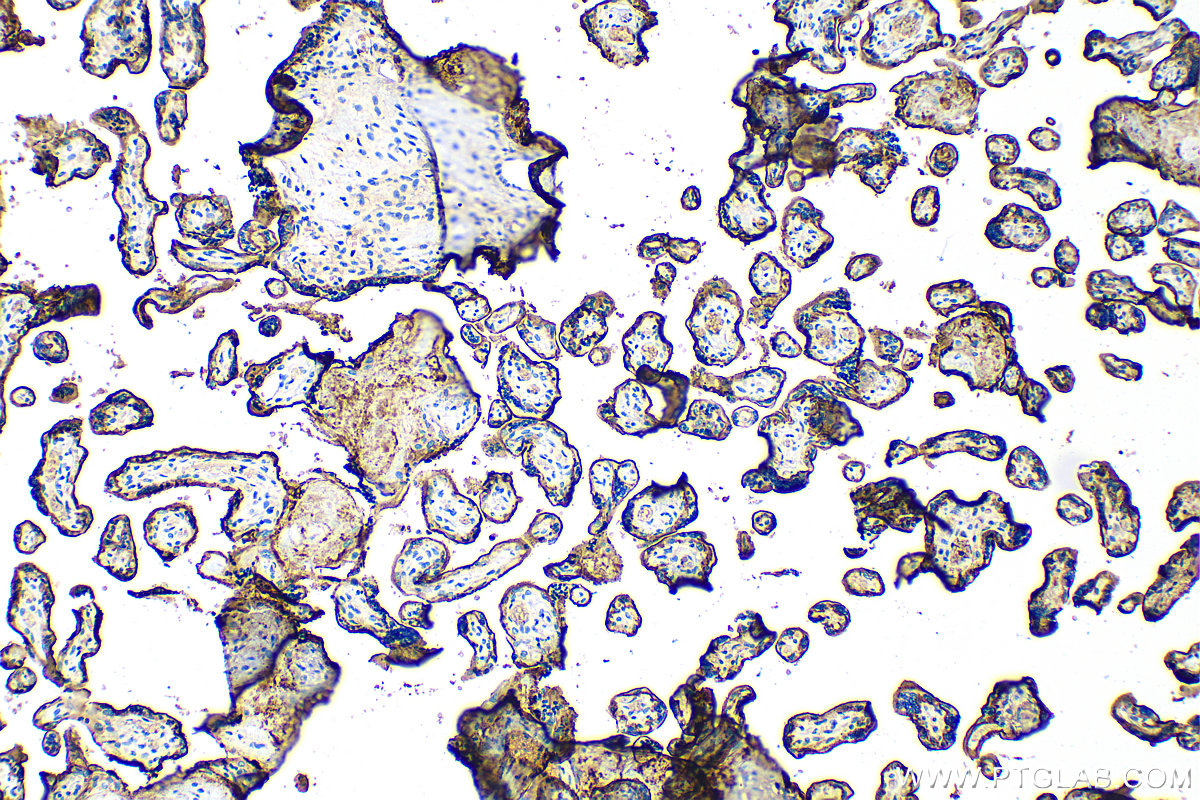
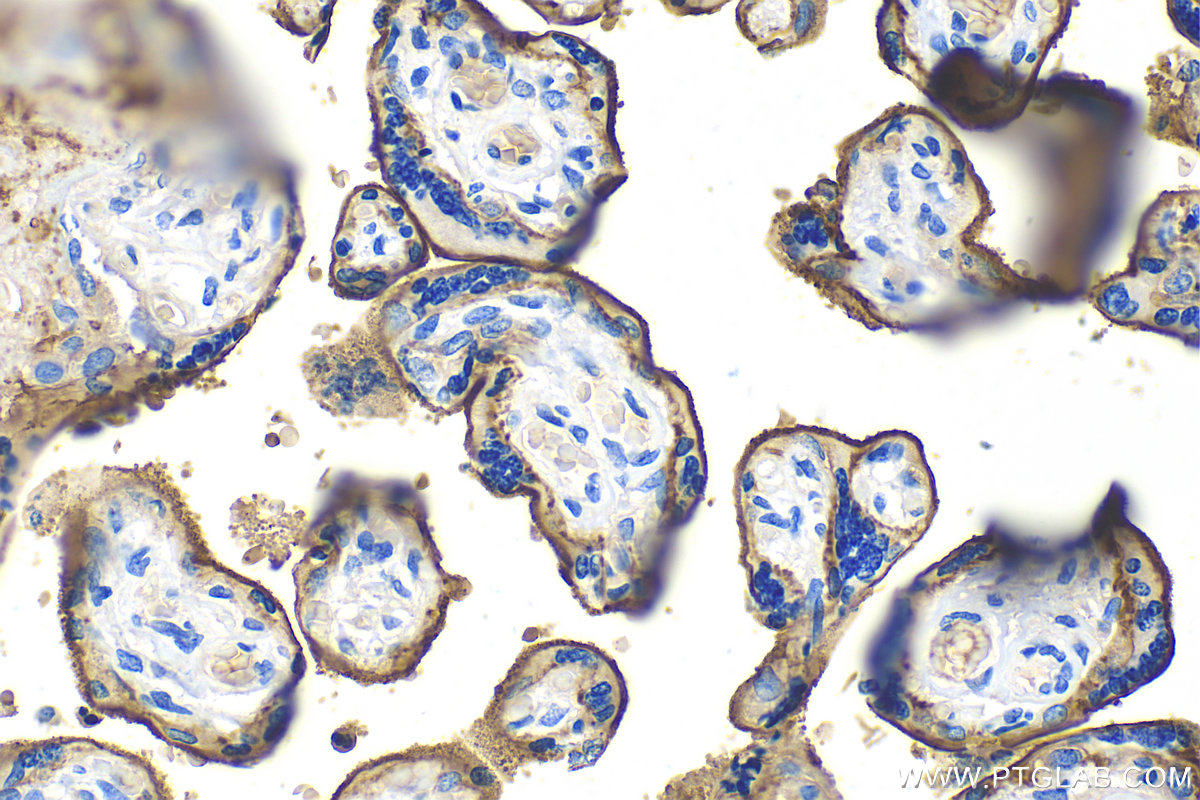
验证数据展示
产品信息
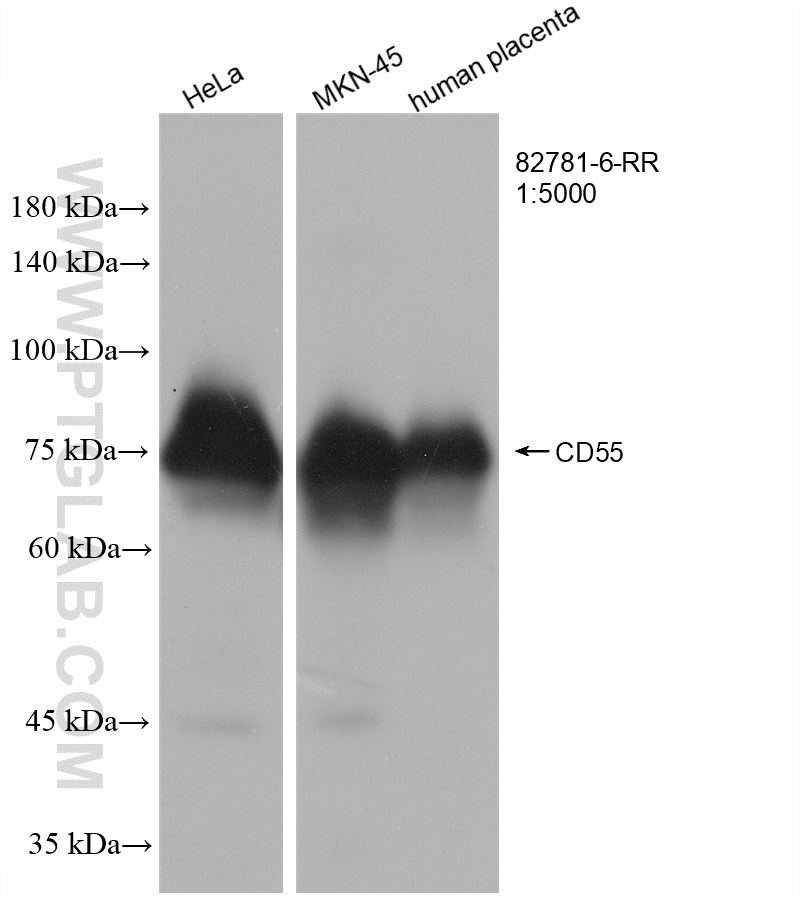
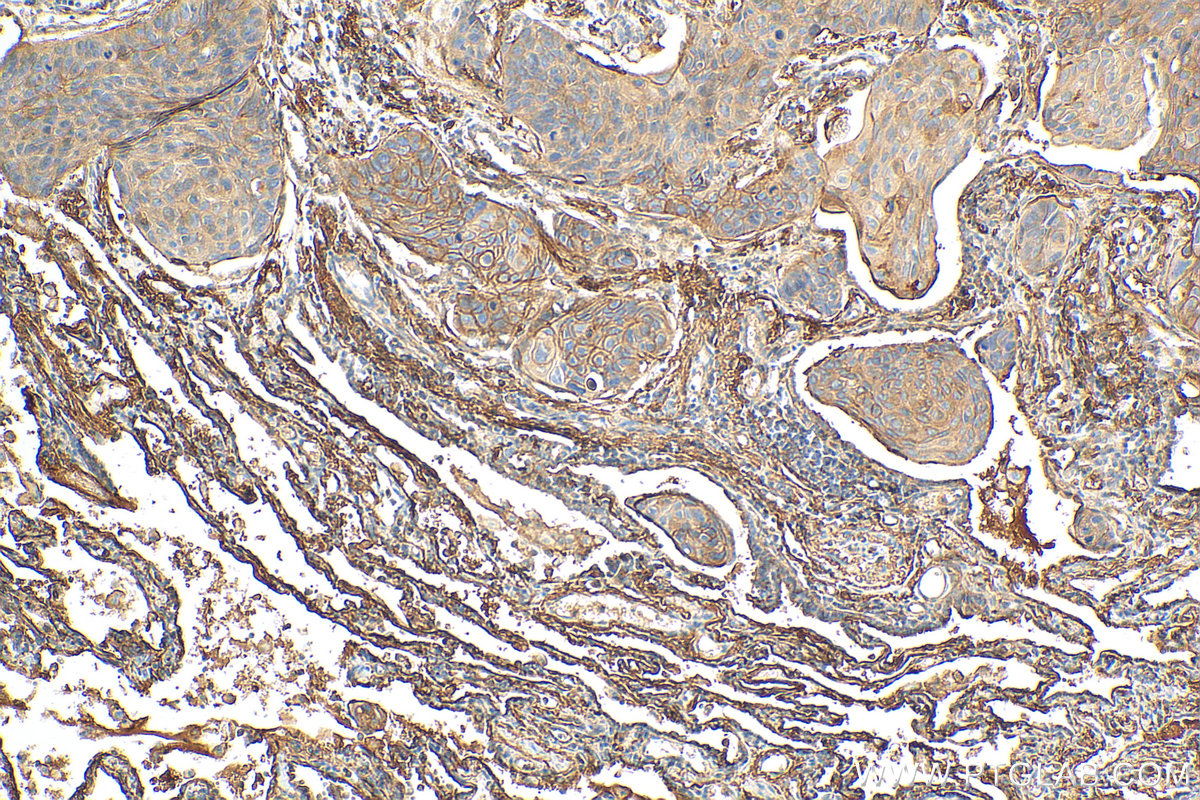
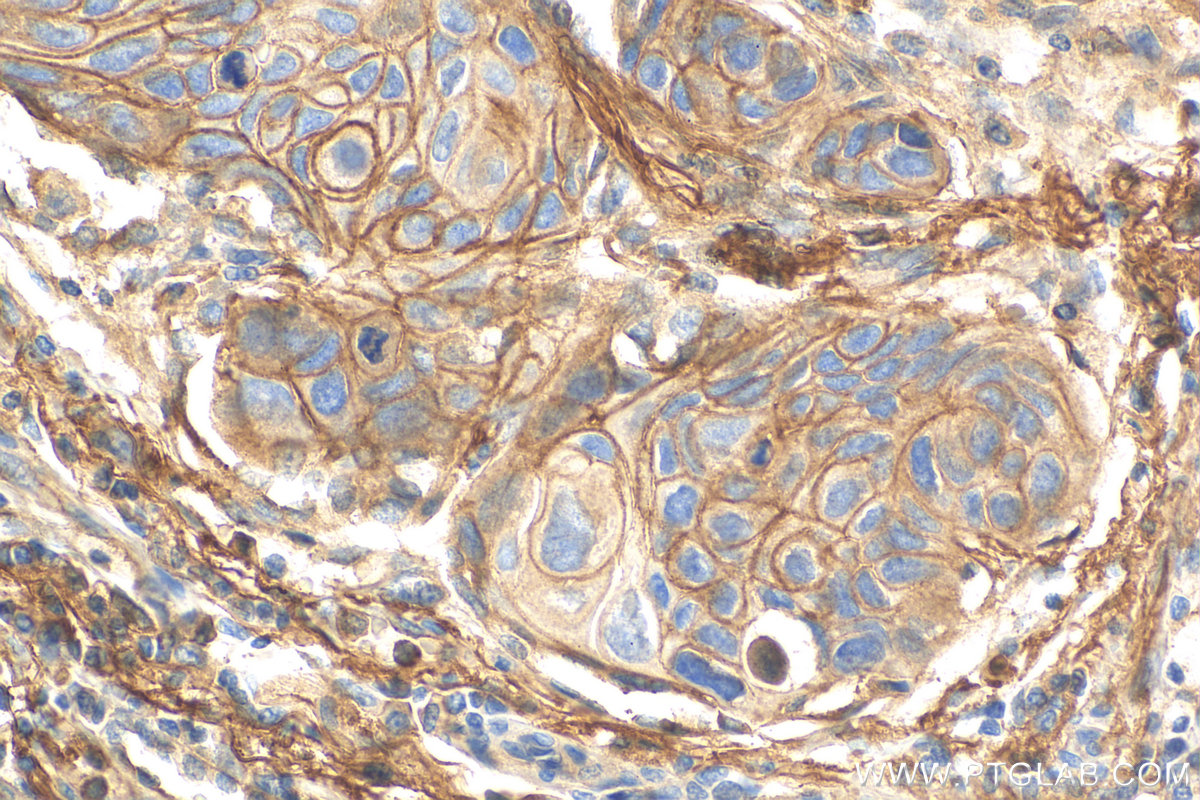
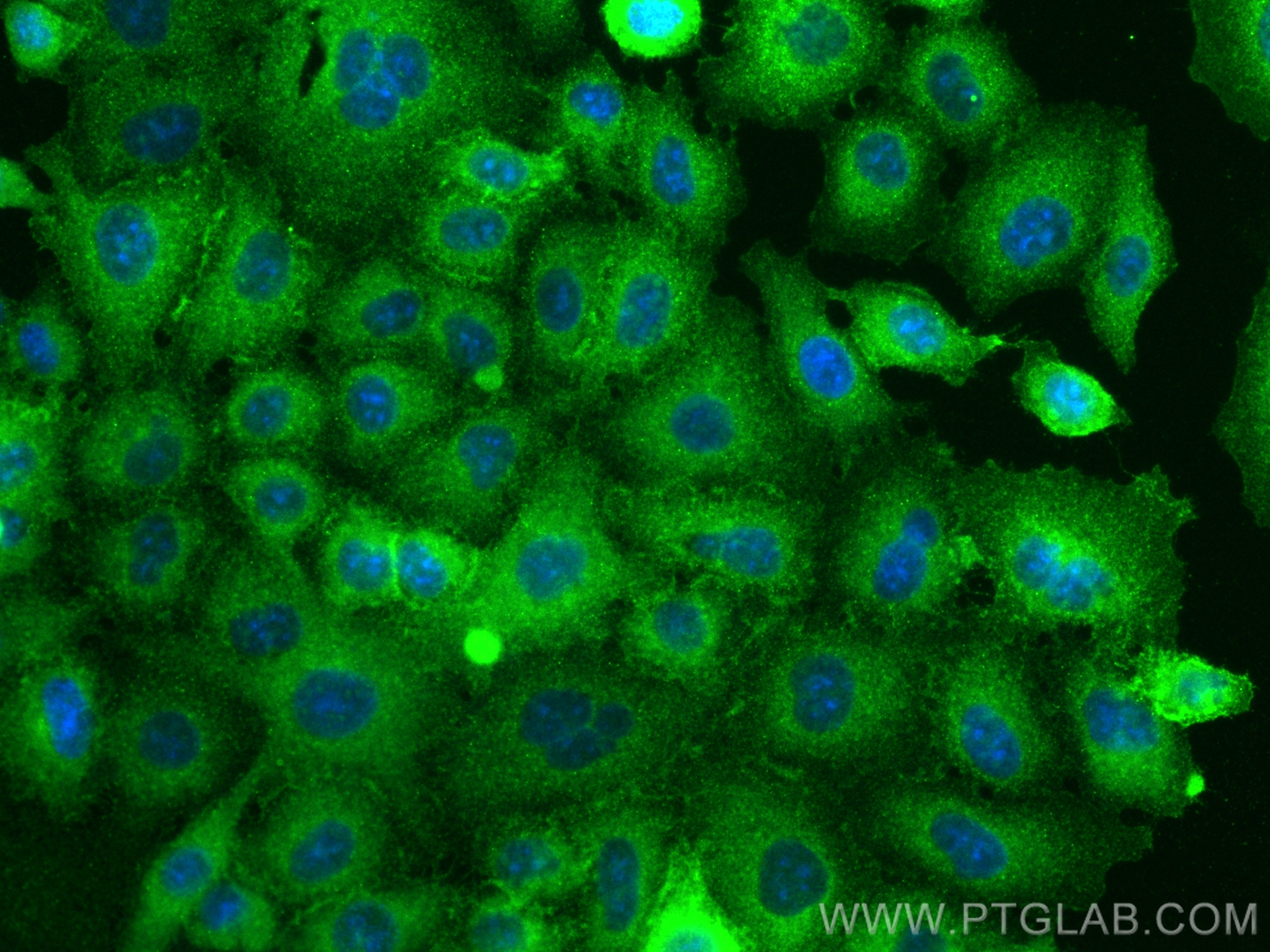
82781-6-PBS targets CD55 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 | CD55 fusion protein Ag25026 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Recombinant |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | CD55 molecule, decay accelerating factor for complement (Cromer blood group) |
| 别名 | TC, DAF, CROM, CR, Complement decay-accelerating factor |
| 计算分子量 | 41 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 75 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC001288 |
| 基因名称 | CD55 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1604 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P08174 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS Only |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
CD55, also known as DAF, is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored surface glycoprotein that is widely distributed on blood, stroma, epithelial, and endothelial cells (PMID: 7517044; 29503741). It can also exist as a soluble form in plasma, urine, saliva, tears, and synovial fluids (PMID: 29503741). CD55 is a complement regulatory protein (PMID: 2469439; 7517044). It inhibits formation of the C3 convertases through binding to C3b and C4b. It also binds the alternate pathway convertase C3bBb, the classical pathway convertase and C4b2a to accelerate their decay (PMID: 17289551). CD55 also serves as a receptor for coxsackieviruses B1, B3, and B5 and several enteroviruses (PMID: 7538177; 7517044). The observed molecular weight of mature CD55 varies between 50 to 100 kDa depending on the cell type. Different sizes of CD55 might be caused by alternative splicing or different glycosylation patterns (PMID: 29503741).