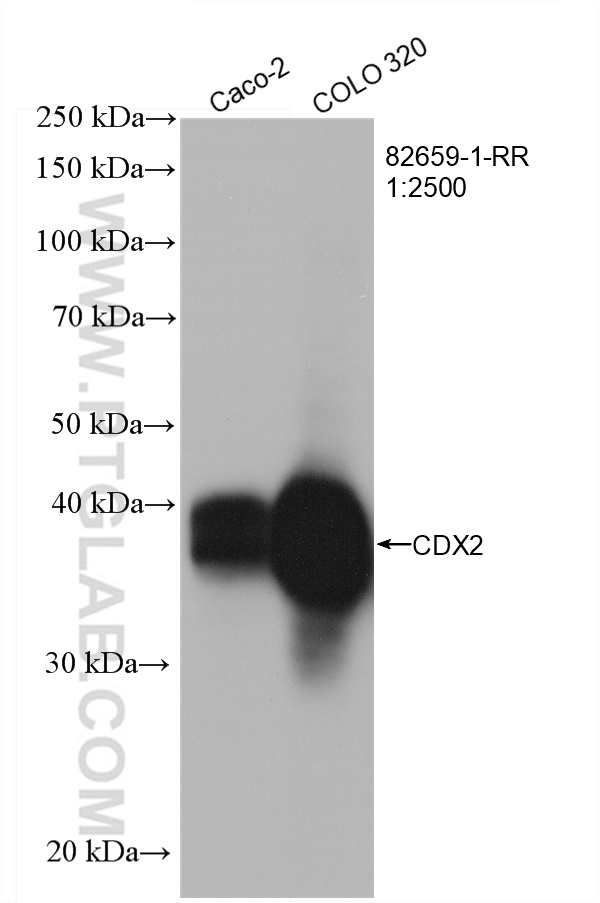
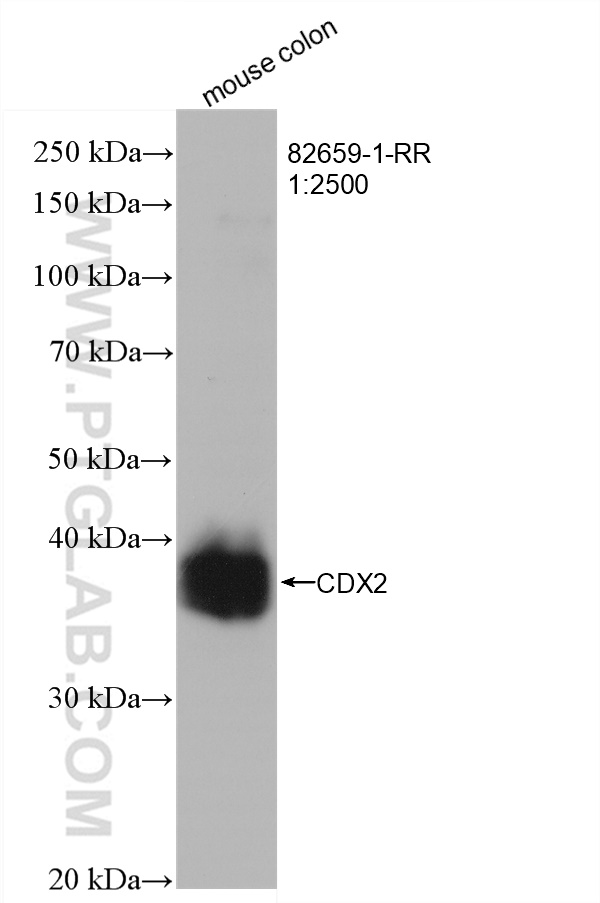
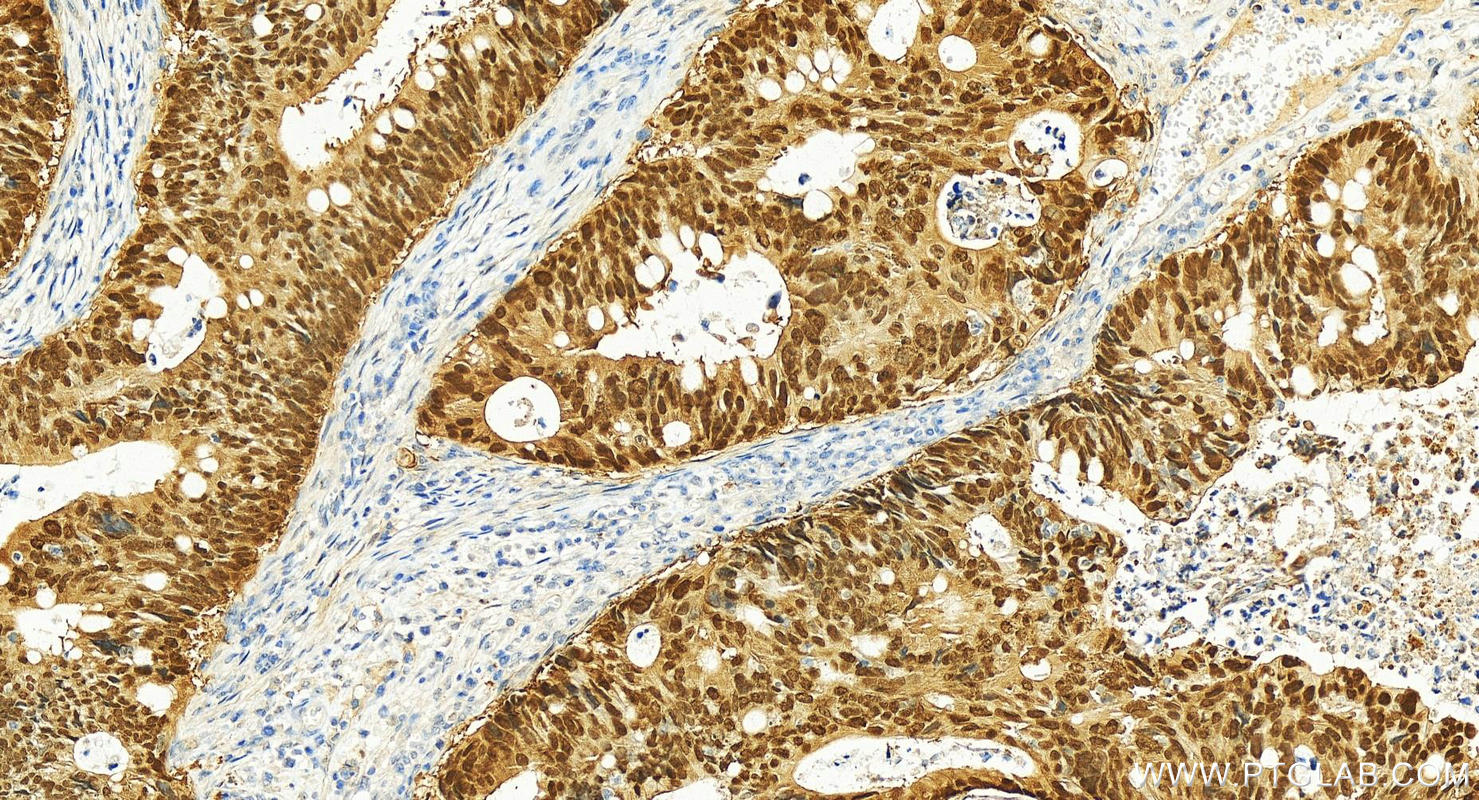
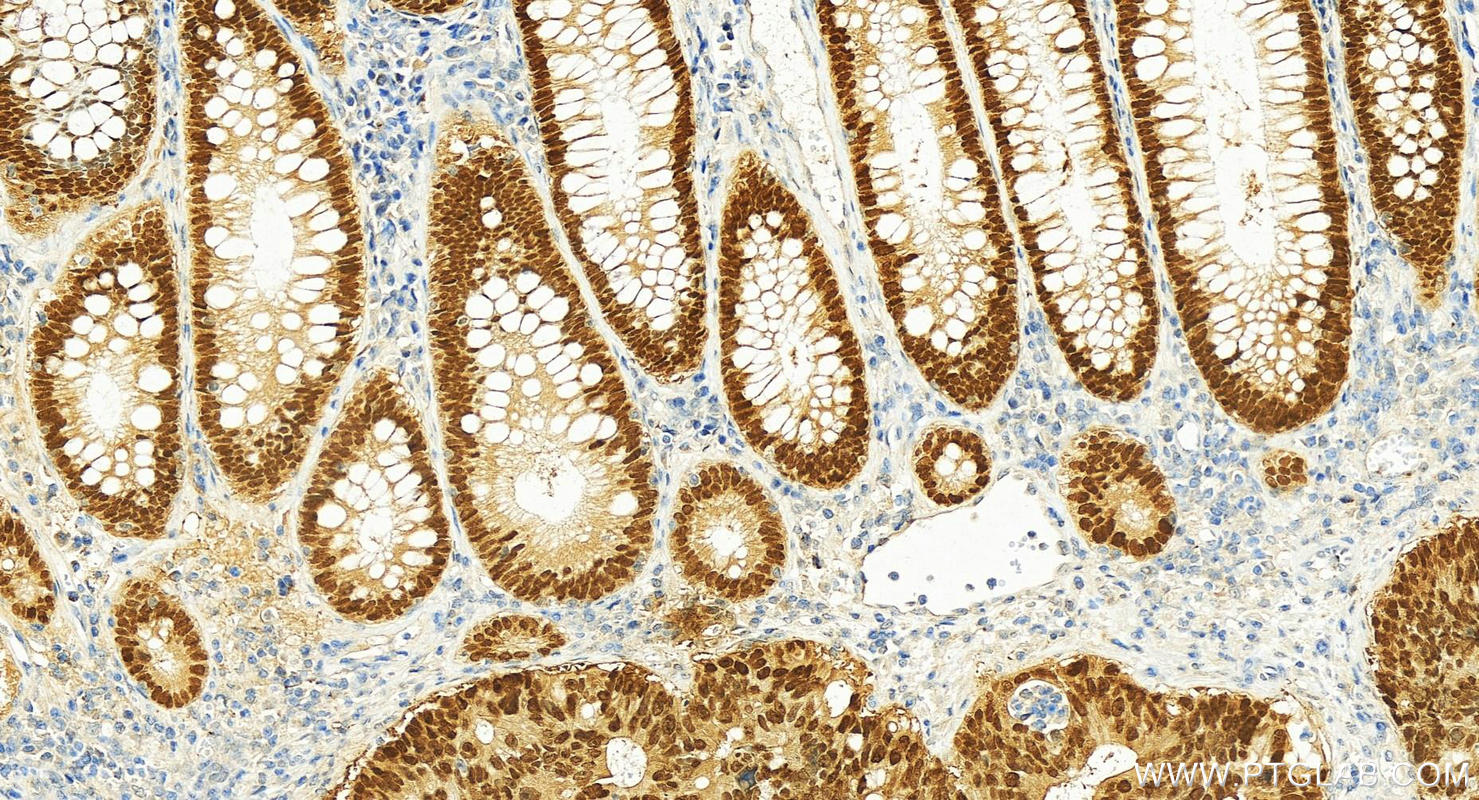
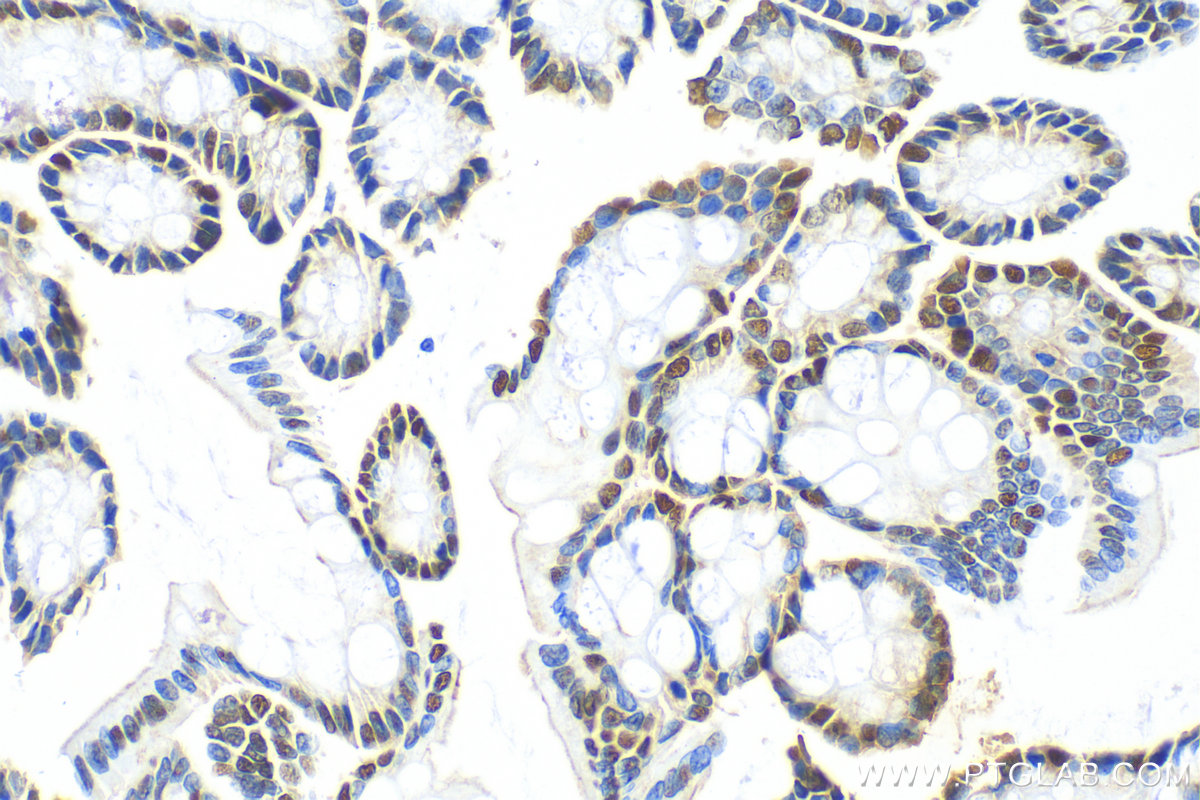
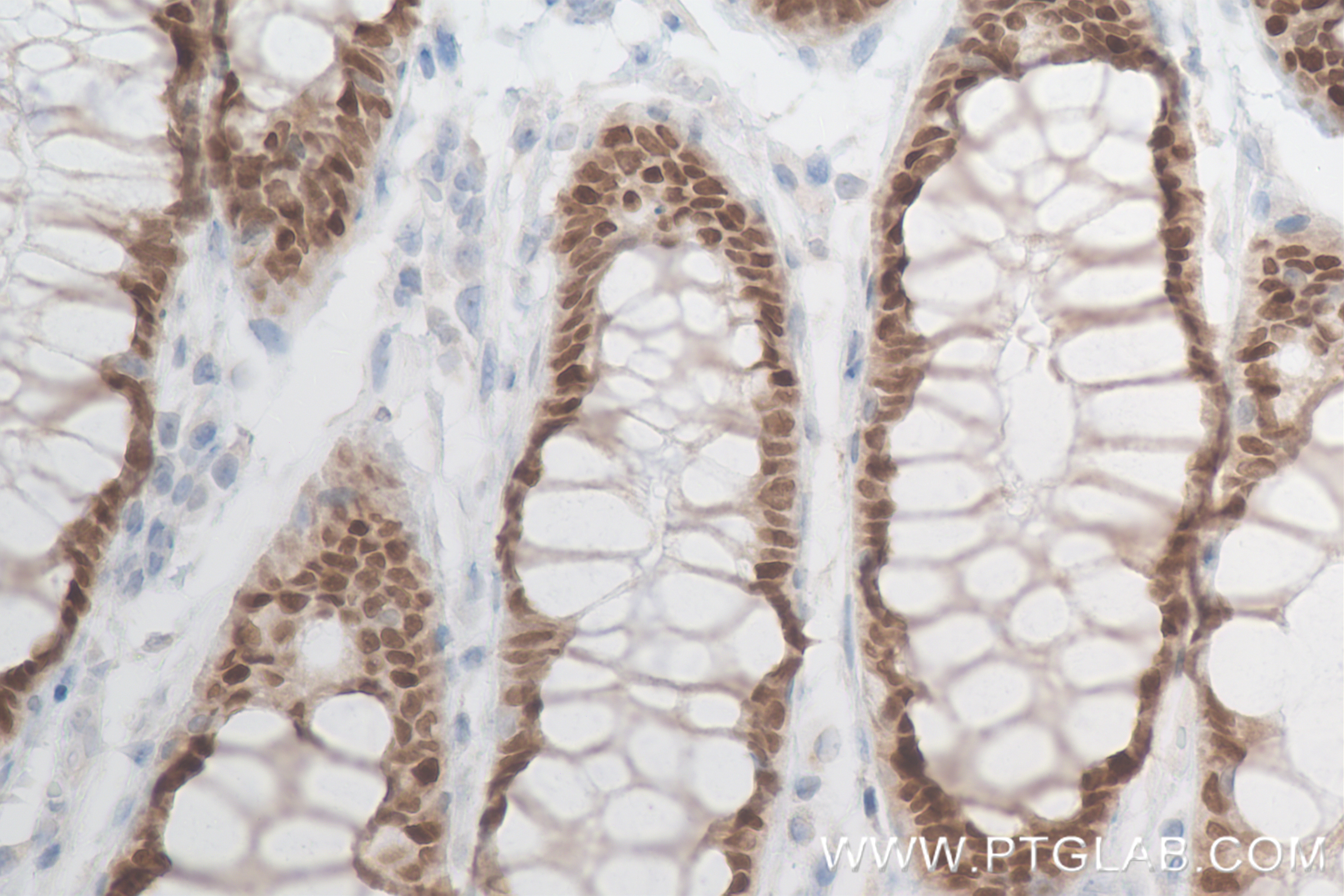
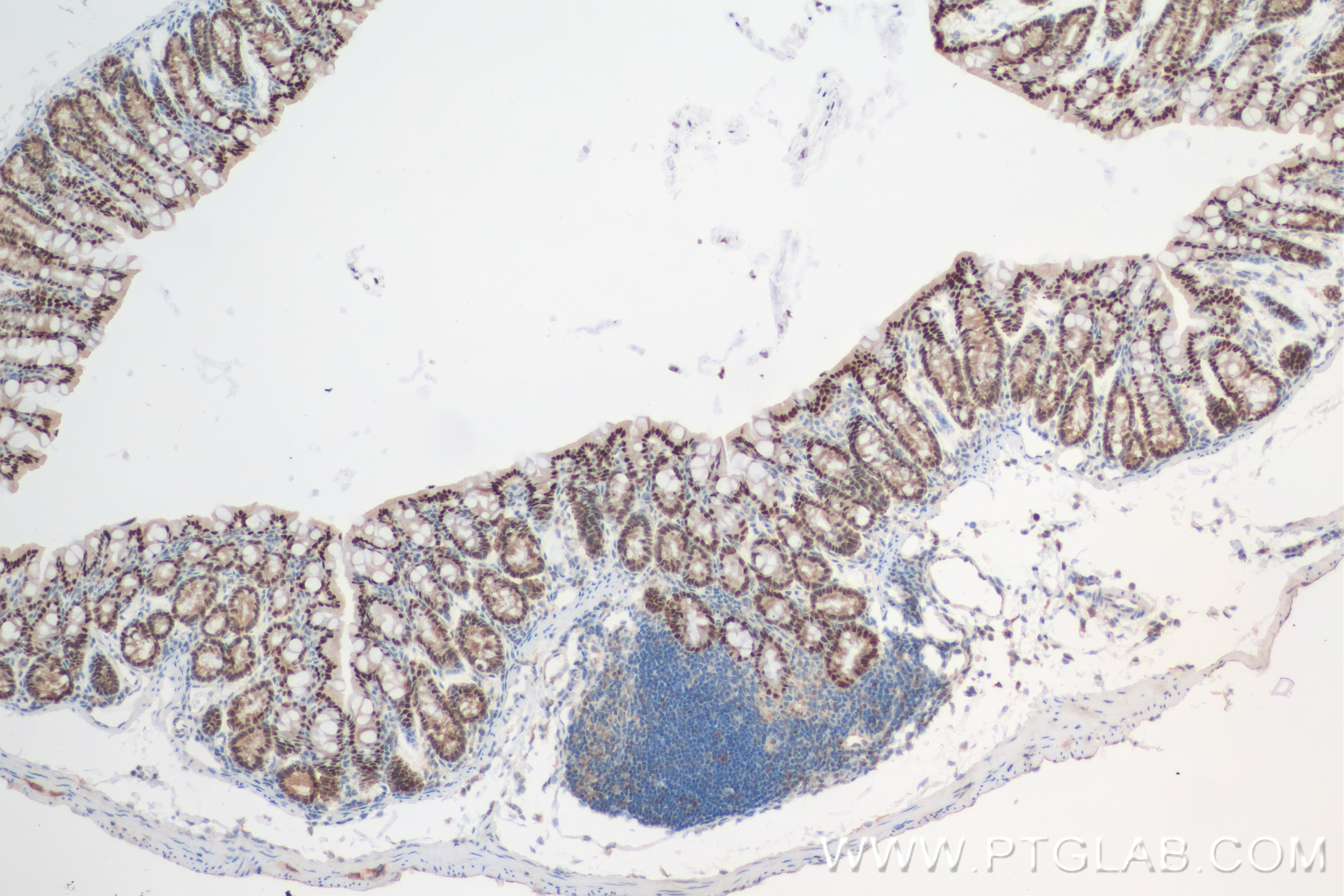
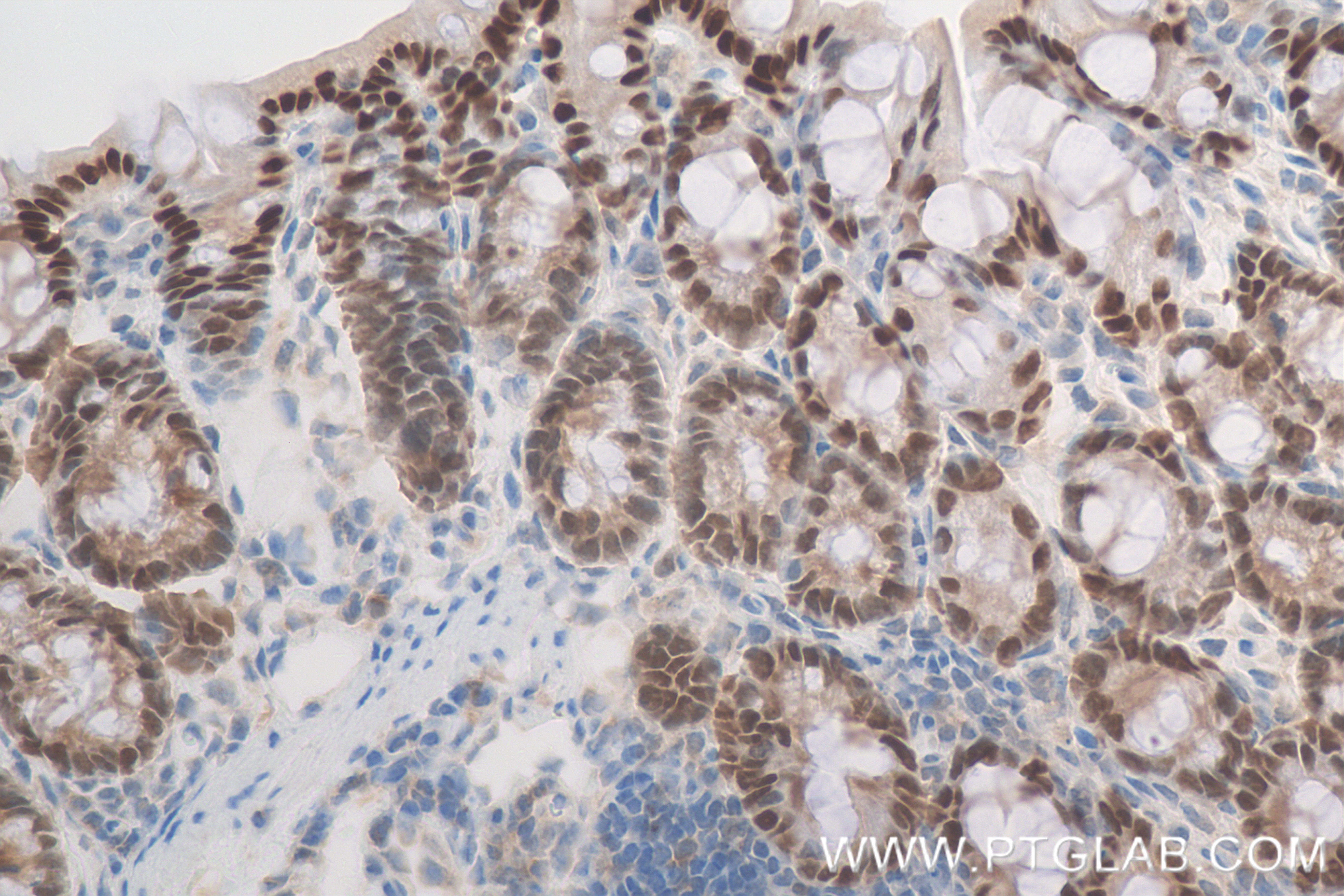
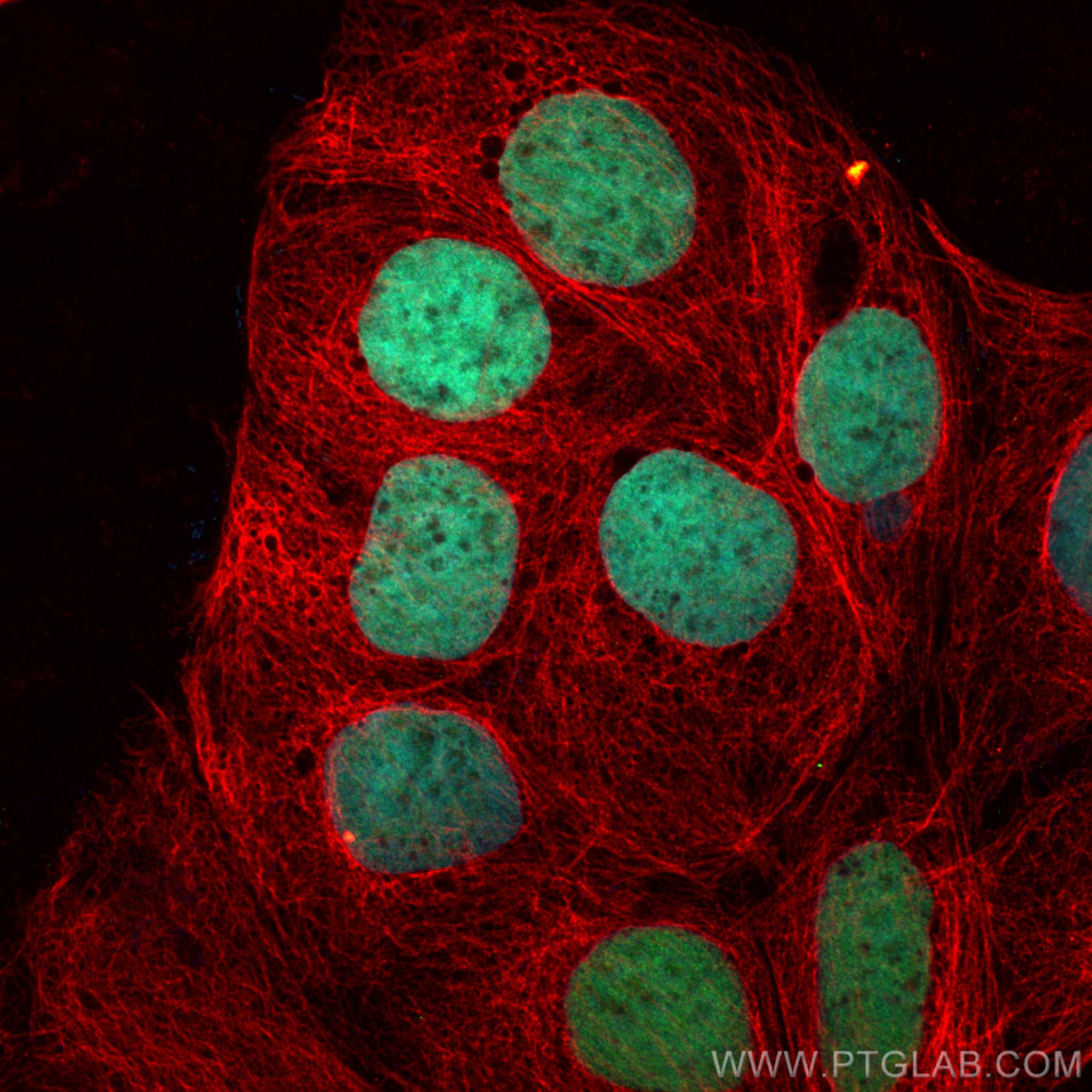
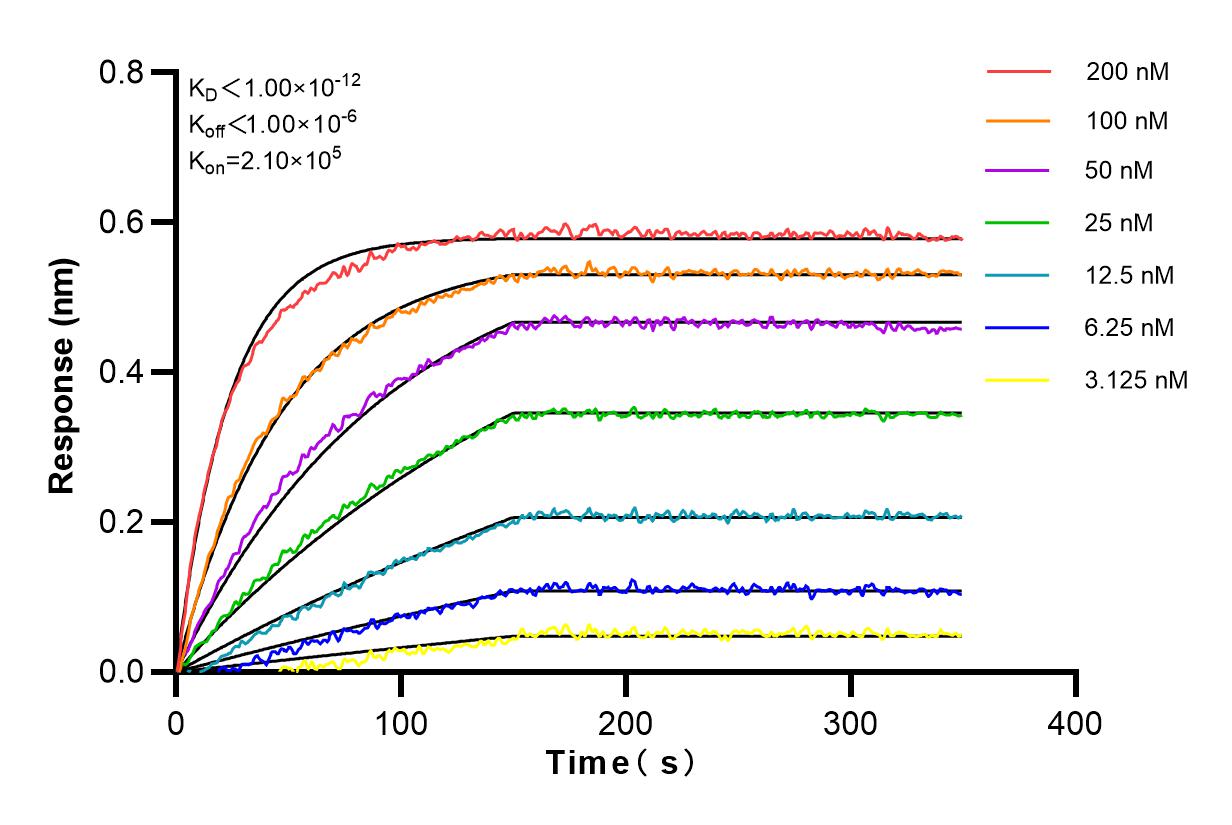
验证数据展示
产品信息
82659-1-PBS targets CDX2 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat |
| 免疫原 | CDX2 fusion protein Ag17310 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Recombinant |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | caudal type homeobox 2 |
| 别名 | CDX-2, CDX 3, Caudal-type homeobox protein 2, Caudal type homeobox protein 2, Caudal type homeobox 2 |
| 计算分子量 | 313 aa, 34 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 33-40 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC014461 |
| 基因名称 | CDX2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1045 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q99626 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS Only |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
CDX2, also named as Homeobox protein CDX-2, is a 313 amino acid protein, which contains one homeobox DNA-binding domain and belongs to the Caudal homeobox family. CDX2 localizes in the nucleus and is involved in the transcriptional regulation of multiple genes expression in the intestinal epithelium. The relative expression of CDX1 to CDX2 protein may be important in the anterior to posterior patterning of the intestinal epithelium and in defining patterns of proliferation and differentiation along the crypt-villus axis. Both Cdx1 and Cdx2 genes must be expressed to reduce tumorigenic potential, to increase sensitivity to apoptosis, and to reduce cell migration, suggesting that the two genes control the normal phenotype by independent pathways.