验证数据展示
产品信息
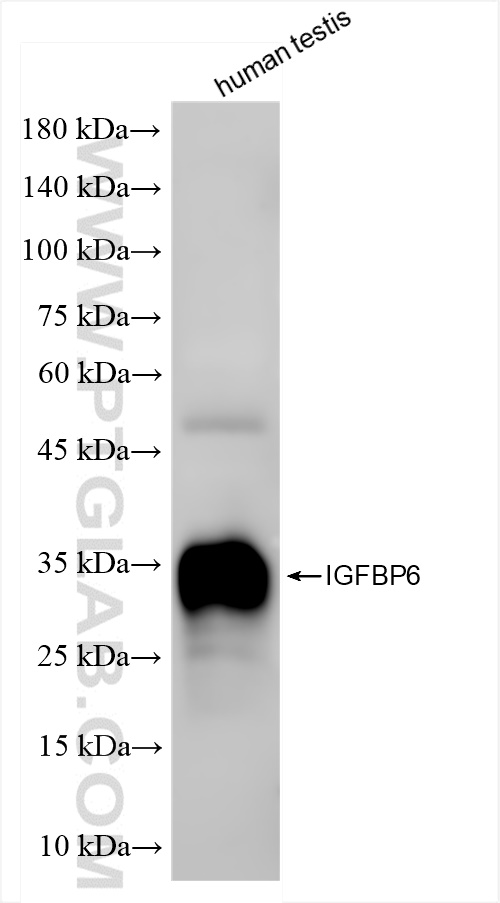
84364-5-PBS targets IGFBP6 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Applications | WB, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein 种属同源性预测 |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Full Name | insulin-like growth factor binding protein 6 |
| Synonyms | IGF-binding protein 6, IGF binding protein 6, IBP-6, IBP6, IBP 6 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 25 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 34 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC011708 |
| Gene Symbol | IGFBP6 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3489 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | P24592 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS Only |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein (IGFBP6), a 240 amino acid protein, contains an IGFBP N-terminal domain and a thyroglobulin type-1 domain. It modulates the activity of IGF and shows independent effects of IGF, such as growth inhibition and apoptosis. It can decrease the proliferation and survival of cancer cells such as lung cancer cells and naso-pharyngeal cancer cells. IGFBP-6 is distinctive for its 50-fold higher binding affinity for IGF-II over IGF-I and this specificity makes it an attractive potential therapeutic candidate for IGF-II-dependent pediatric malignancies such as rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS). In addition, it was found that IGFBP6 can promote the migration of RMS cells in an IGF-independent manner, and MAPK pathways were involved in this process. Further study reported that IGFBP6 is one of most highly expressed proteins in varicose vein tissues and is involved in the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), which may provide insights into the underlying pathogenesis of varicose vein.