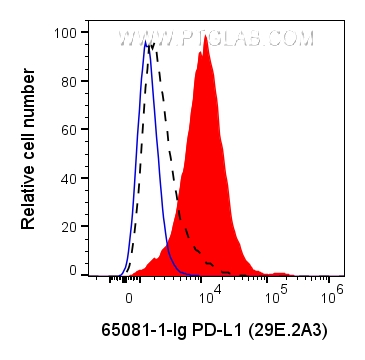
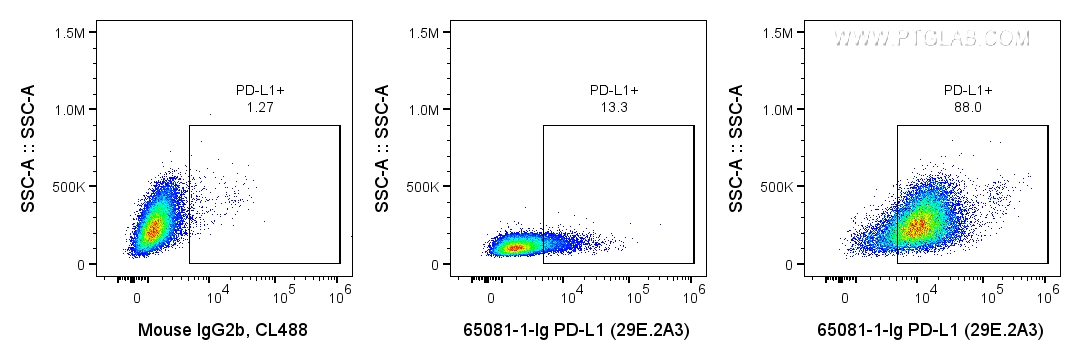
验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
| Positive FC detected in | PHA treated human PBMCs |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry (FC) | FC : 0.2 ug per 10^6 cells in 100 μl suspension |
| This reagent has been tested for flow cytometric analysis. It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
发表文章中的应用
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
产品信息
65081-1-Ig targets PD-L1/CD274 in FC applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | FC Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 文献引用反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 |
Full length human PD-L1 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG2b, kappa |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | CD274 molecule |
| 别名 | CD274, PD-L1, PD L1, hPD-L1, B7-H1 |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC069381 |
| 基因名称 | PD-L1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 29126 |
| RRID | AB_2918384 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9NZQ7 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at 2-8°C. Stable for one year after shipment. |
背景介绍
Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1, CD274, or B7-H1), is the first member of B7 family to be discovered. B7 family molecules are type I transmembrane proteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. In concert with their CD28 family receptors, the B7s are key regulators of the adaptive immune response. PD-L1 is suggested as a negative regulator of T and B cell, and plays important role in mediating tolerance of lymphocytes to self-antigens. It is also involved in the costimulatory signal, essential for T-cell proliferation and production of IL10 and IFNG, in an IL2-dependent and a PD-1-independent manner.
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for PD-L1/CD274 antibody 65081-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Acta Biomater Simultaneous targeting of TGF-β1/PD-L1 via a hydrogel-nanoparticle system to remodel the ECM and immune microenvironment for limiting adhesion formation | ||
Transl Res Immune checkpoint activity exacerbate renal interstitial fibrosis progression by enhancing PD-L1 expression in renal tubular epithelial cells
| ||
Inflammation Protective Effects of a Dihydrodiazepine Against Endotoxin Shock Through Suppression of TLR4/NF-κB/IRF3 Signaling Pathways |